Abstract
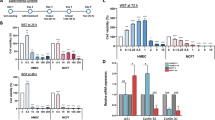
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is a potent mycotoxin that is commonly produced by molds such as Aspergillus (A.) flavus and A. parasiticus. AFB1 is associated with several health adverse effects in humans including mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. Aflatoxin is commonly secreted in the milk leading to deleterious effects on breast tissue and potential nursing infants. However, the effects of aflatoxins, particularly AFB1, on the breast cells are less investigated. In this study, AFB1-associated effects on human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7) were investigated. AFB1 caused significant cytotoxicity on MCF-7 cells. Such cytotoxicity had a positive correlation with the induction of oxidative stress. In addition, AFB1 caused significant transcriptomic alterations in xenobiotics and drug-metabolizing enzymes, transporters, and antioxidant enzymes. Besides, AFB1 upregulated pro-inflammatory markers such as tumor necrosis factor-α and cyclooxygenase-2 with a significant reduction of mRNA expressions of the immunity-related genes including interleukins 8 and 10.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials will be available upon reasonable request.
References
Abd-Elghany SM, Sallam KI (2015) Rapid determination of total aflatoxins and ochratoxins A in meat products by immuno-affinity fluorimetry. Food Chem 179:253–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.140
Ahmad M, Awais M, Ali SW, Ali Khan HA, Riaz M, Sultan A, Shakeel Bashir M, Ishtiaq Chaudhry A (2019) Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in raw and processed milk and assessment of daily Intake in Lahore, Multan cities of Pakistan. Food Addit Contam Part B 12:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2018.1509899
Aljazzar A, El-Ghareeb WR, Darwish WS, Abdel-Raheem SM, Ibrahim AM (2021) Content of total aflatoxin, lead, and cadmium in the bovine meat and edible offal: study of their human dietary intake, health risk assessment, and molecular biomarkers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(43):61225–61234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12641-2
Aljazzar A, El-Ghareeb WR, Darwish WS, Abdel-Raheem SM, Ibrahim AM (2021) Mold contamination of buffalo and cattle meat and offal: a comparative study. Buffalo Bull 40(4):59–69
Chen KL, Li HX, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2014) The protective effect of rosmarinic acid on hyperthermia-induced C2C12 muscle cells damage. Mol Biol Rep 41(8):5525–5531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3429-6
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama SM, Ishizuka M (2014) An overview on mycotoxin contamination of foods in Africa. J Vet Med Sci 76(6):789–797. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.13-0563
Darwish WS, Bayomi RME, El-Moaty AMA, Gad TM (2016) Mould contamination and aflatoxin residues in frozen chicken meat-cuts and giblets. Jpn J Vet Res 64:S167–S171
Darwish WS, Chiba H, El-Ghareeb WR, Elhelaly AE, Hui SP (2019) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content in heat-treated meat retailed in Egypt: health risk assessment, benzo[a]pyrene induced mutagenicity and oxidative stress in human colon (CaCo-2) cells and protection using rosmarinic and ascorbic acids. Food Chem 290:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.127
Darwish WS, Chen Z, Li Y, Wu Y, Chiba H, Hui SP (2020) Identification of cadmium-produced lipid hydroperoxides, transcriptomic changes in antioxidant enzymes, xenobiotic transporters, and pro-inflammatory markers in human breast cancer cells (MCF7) and protection with fat-soluble vitamins. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(2):1978–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06834-z
Eshete M, Gebremedhin S, Alemayehu FR, Taye M, Boshe B, Stoecker BJ (2021) Aflatoxin contamination of human breast milk and complementary foods in southern Ethiopia. Matern Child Nutr 17(1):e13081. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13081
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (2001) Safety evaluation of certain mycotoxins in food / prepared by the fifty-sixth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). FAO. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42467
Forouharmehr A, Harkinezhad T, Qasemi-Panahi B (2013) Effect of aflatoxin B1 on growth of bovine mammary epithelial cells in 3D and monolayer culture system. Adv Pharm Bull 3(1):143–146. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2013.024
Huuskonen P, Myllynen P, Storvik M, Pasanen M (2013) The effects of aflatoxin B1 on transporters and steroid metabolizing enzymes in JEG-3 cells. Toxicol Lett 218(3):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.01.015
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (2002) Aflatoxins IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans Some traditional herbal medicines, some mycotoxins, naphthalene and styrene, vol 82. IARC Press, Lyon, France, pp 171–300
Islam F, Das Trisha A, Hafsa JM, Hasan A, Degen GH, Ali N (2021) Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk in Bangladesh. Mycotoxin Res 37(3):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-021-00436-w
Kensler TW, Roebuck BD, Wogan GN, Groopman JD (2011) Aflatoxin: a 50-year odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol Sci 120:S28-48. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq283
Ma J, Liu Y, Guo Y, Ma Q, Ji C, Zhao L (2021) Transcriptional profiling of aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in macrophages. Toxins (basel) 13(6):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060401
Maleki F, Abdi S, Davodian E, Haghani K, Bakhtiyari S (2015) Exposure of infants to aflatoxin M1 from mother’s breast milk in Ilam, Western Iran. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 6(5):283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.10.001
Manzini L, Halwachs S, Girolami F, Badino P, Honscha W, Nebbia C (2017) Interaction of mammary bovine ABCG2 with AFB1 and its metabolites and regulation by PCB 126 in a MDCKII in vitro model. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 40(6):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.12397
Marchese S, Polo A, Ariano A, Velotto S, Costantini S, Severino L (2018) Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins (basel) 10(6):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060214
Mary VS, Valdehita A, Navas JM, Rubinstein HR, Fernández-Cruz ML (2015) Effects of aflatoxin B1, fumonisin B1 and their mixture on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and cytochrome P450 1A induction. Food Chem Toxicol 75:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.10.030
Mary VS, Arias SL, Otaiza SN, Velez PA, Rubinstein HR, Theumer MG (2017) The aflatoxin B1 -fumonisin B1 toxicity in BRL-3A hepatocytes is associated to induction of cytochrome P450 activity and arachidonic acid metabolism. Environ Toxicol 32(6):1711–1724. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22395
Muhammad I, Wang H, Sun X, Wang X, Han M, Lu Z, Cheng P, Hussain MA, Zhang X (2018) Dual role of dietary curcumin through attenuating AFB1-induced oxidative stress and liver injury via modulating liver phase-I and phase-II enzymes involved in AFB1 bioactivation and detoxification. Front Pharmacol 9:554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00554
Nile SH, Park SW, Khobragade CN (2016) Occurrence and analysis of aflatoxin M1 in milk produced by Indian dairy species. Food Agric Immunol 27:358–366
Omar SS (2012) (2012) Incidence of aflatoxin M1 in human and animal milk in Jordan. J Toxicol Environ Health A 75(22–23):1404–1409. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2012.721174
Sineque AR, Macuamule CL, Dos Anjos FR (2017) Aflatoxin B1 contamination in chicken livers and gizzards from industrial and small abattoirs, measured by ELISA technique in Maputo, Mozambique. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(9):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14090951
Storvik M, Huuskonen P, Kyllönen T, Lehtonen S, El-Nezami H, Auriola S, Pasanen M (2011) Aflatoxin B1 – a potential endocrine disruptor – up-regulates CYP19A1 in JEG-3 cells. Toxicol Lett 202:161–167
Sumon AH, Islam F, Mohanto NC, Kathak RR, Molla NH, Rana S, Degen GH, Ali N (2021) The presence of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products in Bangladesh. Toxins (basel) 13(7):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070440
Suriyaprom K, Kaewprasert S, Putpadungwipon P, Namjuntra P, Klongthalay S (2019) Association of antioxidant status and inflammatory markers with metabolic syndrome in Thais. J Health Popul Nutr 38(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-018-0158-9
Takiguchi M, Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Ohno M, Ishizuka M (2010) Metabolic activation of heterocyclic amines and expression of CYP1A1 in the tongue. Toxicol Sci 116(1):79–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq087
Theumer MG, Henneb Y, Khoury L, Snini SP, Tadrist S, Canlet C, Puel O, Oswald IP, Audebert M (2018) Genotoxicity of aflatoxins and their precursors in human cells. Toxicol Lett 287:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.02.007
Thompson LA, Darwish WS (2019) Environmental chemical contaminants in food: Review of a global problem. J Toxicol 2019:2345283. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2345283
Thompson LA, Ikenaka Y, Sobhy Darwish W, Nakayama SMM, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2019) Effects of the organochlorine p, p’-DDT on MCF-7 cells: investigating metabolic and immune modulatory transcriptomic changes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 72:103249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103249
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01321
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Wang Y, Liu F, Liu M, Zhou X, Wang M, Cao K, Jin S, Shan A, Feng X (2022) Curcumin mitigates aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury via regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 161:112823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112823
Yip KY, Wan MLY, Wong AST, Korach KS, El-Nezami H (2017) Combined low-dose zearalenone and aflatoxin B1 on cell growth and cell-cycle progression in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Toxicol Lett 281:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.09.022
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Faisal University for the financial support under the research group support track (Grant No. 1811022).
Funding
This study was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Faisal University for the financial support under the research group support track (Grant No. 1811022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Study design and experimental work were done by Waleed Rizk El-Ghareeb, Wageh Sobhy Darwish, Eman E. Hegazy, and Esraa A. Mohamed. Material preparation was performed by Waleed Rizk El-Ghareeb and Sherief M. Abdel-Raheem. Chemical analysis and data management were conducted by Ahmed Aljazzar and Abdelazim M. Ibrahim. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Wageh Sobhy Darwish, Ahmed Aljazzar, and Waleed Rizk El-Ghareeb. All authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript and approved the final version before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia.
Consent to participate
All authors approved to participate in this research work and in the manuscript.
Consent to publish
All authors approved this manuscript to be published.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aljazzar, A., El-Ghareeb, W.R., Darwish, W.S. et al. Effects of aflatoxin B1 on human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells: cytotoxicity, oxidative damage, metabolic, and immune-modulatory transcriptomic changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 13132–13140 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23032-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23032-6