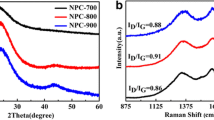
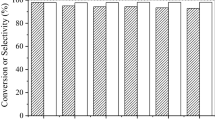
Abstract
We report on the preparation of Co/N-NPCx/y with porous structure and excellent activation properties. The synthesis involves the preparation of Zn/Co-ZIFx and the carbonization of Zn/Co-ZIFx at a high temperature in an inert atmosphere. The volatilization of zinc during carbonization results in a porous structure, which is beneficial to the migration of pollutants. The sizes, specific surface areas, and pore size distribution of Co/N-NPCx/y can be achieved by tuning Zn/Co ratio. The calcination temperatures mainly affect the crystalline phase, crystallinity, and magnetic properties of the as-prepared materials. The effects of the as-prepared materials properties and activation conditions on the Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation by PMS activation were investigated. Overall, it exhibited superior catalytic activity in PMS activation, as evidenced by almost complete removal of RhB (0.020 mM, 100 mL) by using 5 mg/L Co/N-NPC0.5/900 and 1.250 mM PMS within 30 min. Furthermore, it confirmed the participation of SO4•−, •OH, and 1O2 in the catalytic reaction, and both SO4•− and 1O2 were the main reactive oxygen species that play a major role.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable.
References
Cai HY, Zou J, Lin JN, Li JW, Huang YX, Zhang SY, Yuan BL, Ma J (2022) Sodium hydroxide-enhanced acetaminophen elimination in heat/peroxymonosulfate system: production of singlet oxygen and hydroxyl radical. Chem Eng J 429:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132438
Chen H, Xu Y, Zhu K, Zhang H (2021) Understanding oxygen-deficient La2CuO4-δperovskite activated peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol A degradation: the role of localized electron within oxygen vacancy. Appl Catal B: Environ 284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119732
Cheng S, Zhao SD, Xing BL, Shi CL, Meng WB, Zhang CX, Bo Z (2022) Facile one-pot green synthesis of magnetic separation photocatalyst-adsorbent and its application. J Water Process Eng 47:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102802
Collivignarelli MC, Abba A, Miino MC, Damiani S (2019) Treatments for color removal from wastewater: state of the art. J Environ Manage 236:727–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.094
Dai QZ, Jiang L, Luo XB (2017) Electrochemical oxidation of rhodamine B: optimization and degradation mechanism. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:4265–4276. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.05.60
Deng C, Wu KH, Scott J, Zhu SM, Zheng XF, Amal R, Wang DW (2019) Spherical murray-type assembly of Co-N-C nanoparticles as a high-performance trifunctional electrocatalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:9925–9933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b20565
Du W, Zhang Q, Shang Y, Wang W, Li Q, Yue Q, Gao B, Xu X (2020) Sulfate saturated biosorbent-derived Co-S@NC nanoarchitecture as an efficient catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation. Appl Catal B: Environ 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118302
Duan XG, Indrawirawan S, Sun HQ, Wang SB (2015) Effects of nitrogen-, boron-, and phosphorus-doping or codoping on metal-free graphene catalysis. Catal Today 249:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.10.005
Fanaei F, Moussavi G, Srivastava V, Sillanpaa M (2019) The enhanced catalytic potential of sulfur-doped MgO (S-MgO) nanoparticles in activation of peroxysulfates for advanced oxidation of acetaminophen. Chem Eng J 371:404–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.007
Feng XG, Xiao XX, Zhang JD, Guo LP, Xiong Y (2021) Cobalt/nitrogen doped porous carbon as catalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction: towards hybrid enzymatic biofuel cells. Electrochim Acta 389:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138791
Gao YW, Chen ZH, Zhu Y, Li T, Hu C (2020a) New insights into the generation of singlet oxygen in the metal-free peroxymonosulfate activation process: important role of electron-deficient carbon atoms. Environ Sci Technol 54:1232–1241. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05856
Gao YW, Li T, Zhu Y, Chen ZH, Liang JY, Zeng QY, Lyu L, Hu C (2020b) Highly nitrogen-doped porous carbon transformed from graphitic carbon nitride for efficient metal-free catalysis. J Hazard Mater 393:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121280
Guo SP, Wang Q, Luo CJ, Yao JG, Qiu ZP, Li QB (2020) Hydroxyl radical-based and sulfate radical-based photocatalytic advanced oxidation processes for treatment of refractory organic matter in semi-aerobic aged refuse biofilter effluent arising from treating landfill leachate. Chemosphere 243:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125390
Horike S, Umeyama D, Kitagawa S (2013) Ion conductivity and transport by porous coordination polymers and metal-organic frameworks. Accounts Chem Res 46:2376–2384. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar300291s
Kokilavani S, Syed A, Elgorban AM, Bahkali AH, Al-Shwaiman HA, Varma RS, Das A, Khan SS (2022) Designing Z-scheme AgIO4 nanorod embedded with Bi2S3 nanoflakes for expeditious visible light photodegradation of congo red and rhodamine B. Chemosphere 294:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133755
Lee Y, Lee S, Cui MC, Ren YM, Park B, Ma JJ, Han ZC, Khim J (2021) Activation of peroxodisulfate and peroxymonosulfate by ultrasound with different frequencies: impact on ibuprofen removal efficient, cost estimation and energy analysis. Chem Eng J 413:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127487
Li Y, Qi J, Shen J, Yan P, Kang J, Wang B, Wang S, Zuo J, Chen Z (2022) Interface mechanism of peroxymonosulfate activation by cobalt-copper-ferrite nanoparticles mediated by palygorskite for bisphenol S degradation: a dual-path activation mechanism. Chem Eng J 448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137609
Ling L, Zhang DP, Fan CH, Shang C (2017) A Fe(II)/citrate/UV/PMS process for carbamazepine degradation at a very low Fe(II)/PMS ratio and neutral pH: the mechanisms. Water Res 124:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.066
Liu C, Chen LW, Ding DH, Cai TM (2019) From rice straw to magnetically recoverable nitrogen doped biochar: efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of metolachlor. Appl Catal B-Environ 254:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.05.014
Liu T, Mou JR, Wu ZP, Lv C, Huang JL, Liu ML (2020) A facile and scalable strategy for fabrication of superior bifunctional freestanding air electrodes for flexible zinc-air batteries. Adv Funct Mater 30:9. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202003407
Maruthupandy M, Muneeswaran T, Chackaravarthi G, Vennila T, Anand M, Cho WS, Quero F (2022) Synthesis of chitosan/SnO2 nanocomposites by chemical precipitation for enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation efficiency of congo red and rhodamine-B dye molecules. J Photochem Photobiol A-Chem 430:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.113972
Niu BH, Wang LH, Li MZ, Yao WL, Zang K, Zhou L, Hu XW, Zheng Y (2022) Lattice B-doping evolved ferromagnetic perovskite-like catalyst for enhancing persulfate-based degradation of norfloxacin. J Hazard Mater 425:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127949
Peng W, Liao J, Yan Y, Chen L, Ge C, Lin S (2022a) Enriched nitrogen-doped carbon derived from expired drug with dual active sites as effective peroxymonosulfate activator: Ultra-fast sulfamethoxazole degradation and mechanism insight. Chem Eng J 446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022a.137407
Peng Y, Xie G, Shao P, Ren W, Li M, Hu Y, Yang L, Shi H, Luo X (2022b) A comparison of SMX degradation by persulfate activated with different nanocarbons: kinetics, transformation pathways, and toxicity. Appl Catal B: Environ 310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022b.121345
Shang L, Yu HJ, Huang X, Bian T, Shi R, Zhao YF, Waterhouse GIN, Wu LZ, Tung CH, Zhang TR (2016) Well-dispersed ZIF-derived Co, N-Co-doped carbon nanoframes through mesoporous-silica-protected calcination as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Adv Mater 28:1668–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201505045
Solis RR, Mena IF, Nadagouda MN, Dionysiou DD (2020) Adsorptive interaction of peroxymonosulfate with graphene and catalytic assessment via non-radical pathway for the removal of aqueous pharmaceuticals. J Hazard Mater 384:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121340
Terzopoulou A, Hoop M, Chen XZ, Hirt AM, Charilaou M, Shen Y, Mushtaq F, del Pino AP, Logofatu C, Simonelli L, de Mello AJ, Doonan CJ, Sort J, Nelson BJ, Pane S, Puigmarti-Luis J (2019) Mineralization-inspired synthesis of magnetic zeolitic imidazole framework composites. Angew Chem-Int Edit 58:13550–13555. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201907389
Thakur S, Chaudhary J, Thakur A, Gunduz O, Alsanie WF, Makatsoris C, Thakur VK (2022) Highly efficient poly(acrylic acid-co-aniline) grafted itaconic acid hydrogel: Application in water retention and adsorption of rhodamine B dye for a sustainable environment. Chemosphere 303:134917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134917
Wang GL, Chen S, Quan X, Yu HT, Zhang YB (2017) Enhanced activation of peroxymonosulfate by nitrogen doped porous carbon for effective removal of organic pollutants. Carbon 115:730–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.060
Wang GL, Nie XW, Ji XJ, Quan X, Chen S, Wang HZ, Yu HT, Guo XW (2019) Enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co and N codoped porous carbon for degradation of organic pollutants: the synergism between Co and N. Environ Sci-Nano 6:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01231h
Wang LN, Yang HP, Kang L, Wu M, Yang YK (2022a) Highly dispersed of Ag/AgCl nanoparticles on exfoliated FeOCl nanosheets as photo-Fenton catalysts for pollutants degradation via accelerating Fe(II)/ Fe(III) cycle. Chemosphere 296:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134039
Wang S, Wang J (2019) Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived biochar for the degradation of triclosan in water and wastewater. Chem Eng J 356:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.062
Wang Y, Wang Y, Liu YX (2022b) Fe2+/heat-coactivated PMS oxidation-absorption system for H2S removal from gas phase. Sep Purif Technol 286:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120458
Xu H, Jiang N, Wang D, Wang L, Song Y, Chen Z, Ma J, Zhang T (2020a) Improving PMS oxidation of organic pollutants by single cobalt atom catalyst through hybrid radical and non-radical pathways. Appl Catal B: Environ 263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118350
Xu LJ, Wang XT, Sun Y, Gong H, Guo MZ, Zhang XM, Meng L, Gan L (2020b) Mechanistic study on the combination of ultrasound and peroxymonosulfate for the decomposition of endocrine disrupting compounds. Ultrason Sonochem 60:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104749
Xu Z, Wu Y, Ji Q, Li T, Xu C, Qi C, He H, Yang S, Li S, Yan S, Sun C, Zhang L, Zou Z (2021) Understanding spatial effects of tetrahedral and octahedral cobalt cations on peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient pollution degradation. Appl Catal B: Environ 291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120072
Yoo HY, Kim MS, Shin H, Lim J (2022) Peroxymonosulfate activation by black TiO2 nanotube arrays under solar light: switching the activation mechanism and enhancing catalytic activity and stability. J Hazard Mater 433:128796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128796
Yu HX, Zhang Q, Joo JB, Li N, Moon GD, Tao SY, Wang LJ, Yin YD (2013) Porous tubular carbon nanorods with excellent electrochemical properties. J Mater Chem A 1:12198–12205. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta12722b
Yu HX, Zhang Q, Dahl M, Joo JB, Wang X, Wang LJ, Yin YD (2017) Dual-pore carbon shells for efficient removal of humic acid from water. Chem-Eur J 23:16249–16256. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201702318
Zhang YQ, Sun YM, Man Y, Yuan H, Zhao RY, Xiang GQ, Jiang XM, He LJ, Zhang SS (2022) Highly efficient adsorption and catalytic degradation of aflatoxin B(1)by a novel porous carbon material derived from Fe-doped ZIF-8. Chem Eng J 440:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135723
Zheng S, Li XJ, Zhang JY, Wang JF, Zhao CR, Hu X, Wu Y, He YM (2023) One-step preparation of MoOX/ZnS/ZnO composite and its excellent performance in piezocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B under ultrasonic vibration. J Environ Sci 125:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.10.028
Zhu M, Guan D, Hu Z, Lin H-J, Chen C-T, Sheu H-S, Wang S, Zhou J, Zhou W, Shao Z (2021) Synergistic effects in ordered Co oxides for boosting catalytic activity in advanced oxidation processes. Appl Catal B: Environ 297.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120463
Zhu S, Huang X, Ma F, Wang L, Duan X, Wang S (2018) Catalytic removal of aqueous contaminants on N-doped graphitic biochars: inherent roles of adsorption and nonradical mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 52:8649–8658. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01817
Funding
The present work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2019YFC1804002) and National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 51608269).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hongxia Yu: methodology, conceptualization, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing, project administration, funding acquisition; Dan Ding: writing—original draft, conceptualization, methodology, investigation; Shuailing Zhao: investigation, methodology; Muhammad Faheem: writing—reviewing and editing, conceptualization; Weijie Mao: investigation; Li Yang: investigation; Liwei Chen: project administration, funding acquisition; Tianming Cai: writing—reviewing and editing, conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Ding, D., Zhao, S. et al. Co/N co-doped porous carbon as a catalyst for the degradation of RhB by efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 10969–10981 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22548-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22548-1