Abstract
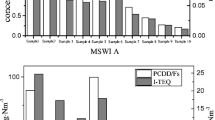
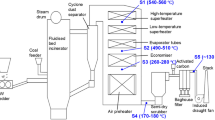
Few studies focused on the emission of polychlorinated-ρ-dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/F) from different kinds of waste incinerators. This study was conducted in a full-scale MSW incineration plant to investigate the influence of different incinerator types on PCDD/F. Experimental results indicated that the 2,3,7,8-PCDD/F concentration in the inlet gas of the air pollution control system (APCS) in the studied fluidized bed was higher (2.03 ng I-TEQ/Nm3) than that of the grate (0.77 ng I-TEQ/Nm3). But gas in the outlet of APCS from both incinerators had an approximate concentration, lower than the Chinese emission limit of 0.1 ng I-TEQ/Nm3. Similar distribution patterns were observed for 2,3,7,8-PCDD/Fs, as well as 136 PCDD/F congeners. Specifically, OCDD and 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD were major isomer constituents for 2,3,7,8-PCDD/F isomers. In terms of formation pathways, a similar formation mechanism was observed based on fingerprint characteristics of 136 PCDD/F congeners. De novo synthesis was the dominating formation pathway for both incinerators. Meanwhile, DD/DF chlorination was another contributor to PCDD/F formation, which in the fluidized bed was higher. In addition, little correlation (0.009 < R2 < 0.533) between conventional pollutants (HCl, CO, PM) and PCDD/Fs was found, suggesting little high-temperature synthesis observed and verifying the dominance of de novo synthesis.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study were included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- APCS:
-
Air pollution control system
- CBz:
-
Chlorobenzene
- CP:
-
Chlorophenol
- DD:
-
Dibenzodioxin
- DF:
-
Dibenzofuran
- EA:
-
Emission amount
- EF:
-
Emission factor
- FA:
-
Fly ash
- FB:
-
Fluidized-bed type incinerator
- GBI:
-
Exhaust gas sampled from the inlet of bag filters
- GCH:
-
Exhaust gas sampled from the chimney, which is also after the outlet of bag filters
- GI:
-
Grate type incinerator
- PCDD/Fs:
-
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans
- PM:
-
Particulate matter
- I-TEF:
-
International toxic equivalency factor
- I-TEQ:
-
International toxic equivalency quantity
References
Altwicker ER (1996) Formation of PCDDF in municipal solid waste incinerators: laboratory and modeling studies. J Hazard Mater 47:137–161
Atkinson J, Hung P, Zhang Z, Chang M, Yan Z, Rood M (2015) Adsorption and destruction of PCDD/Fs using surface-functionalized activated carbons. Chemosphere 118:136–142
Behnisch PA, Hosoe K, Shiozaki K, Kiryu T, Komatsu K, Schramm K-W, Sakai S-I (2002) Melting and incineration plants of municipal waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 9:337–344
Bourtsalas A, Huang Q, Zhang H, Themelis N (2020) Energy recovery in China from solid wastes by the moving grate and circulating fluidized bed technologies. Waste Disposal Sustain Energy 2:27–36
Buekens A, Huang H (1998) Comparative evaluation of techniques for controlling the formation and emission of chlorinated dioxins/furans in municipal waste incineration. J Hazard Mater 62:1–33
Chang Y-M, Fan W-P, Dai W-C, Hsi H-C, Wu C-H, Chen C-H (2011) Characteristics of PCDD/F content in fly ash discharged from municipal solid waste incinerators. J Hazard Mater 192:521–529
Chen T, Gu Y-l, Yan J-h, Li X-d, Lu S-Y, Dai H-F, Cen K-f (2008) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in flue gas emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A 9:1296–1303
Chen Z, Lin X, Lu S, Li X, Qiu Q, Wu A, Ding J, Yan J (2018) Formation pathways of PCDD/Fs during the Co-combustion of municipal solid waste and coal. Chemosphere 208:862–870
Chen T, Sun C, Wang T, Lomnicki S, Zhan M, Li X, Lu S, Yan J (2020) Formation of DF, PCDD/Fs and EPFRs from 1, 2, 3-trichlorobenzene over metal oxide/silica surface. Waste Manag 118:27–35
Cheng J, Shi F, Yi J, Fu H (2020) Analysis of the factors that affect the production of municipal solid waste in China. J Clean Prod 259:120808
Chi KH, Chang MB, Chang-Chien GP, Lin C (2005) Characteristics of PCDD/F congener distributions in gas/particulate phases and emissions from two municipal solid waste incinerators in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 347:148–162
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) (1994) Method 1613 tetra-through octa-chlorinated dioxins and furans by isotope dilution HRGC/HRMS. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Everaert K, Baeyens J (2001) Correlation of PCDD/F emissions with operating parameters of municipal solid waste incinerators. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 51:718–724
Freire M, Lopes H, Tarelho LA (2015) Critical aspects of biomass ashes utilization in soils: Composition, leachability, PAH and PCDD/F. Waste Manag 46:304–315
Giugliano M, Cernuschi S, Grosso M, Miglio R, Aloigi E (2002) PCDD/F mass balance in the flue gas cleaning units of a MSW incineration plant. Chemosphere 46:1321–1328
Hajizadeh Y, Onwudili JA, Williams PT (2011) Removal potential of toxic 2378-substituted PCDD/F from incinerator flue gases by waste-derived activated carbons. Waste Manag 31:1194–1201
Huang H, Buekens A (1995) On the mechanisms of dioxin formation in combustion processes. Chemosphere 31:4099–4117
Huang H, Buekens A (1996) De novo synthesis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans Proposal of a mechanistic scheme. Sci Total Environ 193:121–141
Jančauskas A, Buinevičius K (2020) The grate-firing boilers grate movement impact onto NOx, SO2 emissions. Mechanika 26:503–510
Leckner B, Lind F (2020) Combustion of municipal solid waste in fluidized bed or on grate–a comparison. Waste Manag 109:94–108
Lenoir D, Kaune A, Hutzinger O, Mützenich G, Horch K (1991) Influence of operating parameters and fuel type on PCDD/F emissions from a fluidized bed incinerator. Chemosphere 23:1491–1500
Li Y, Wang H, Jiang L, Zhang W, Li R, Chi Y (2015) HCl and PCDD/Fs emission characteristics from incineration of source-classified combustible solid waste in fluidized bed. RSC Adv 5:67866–67873
Li X, Ma Y, Zhang M, Zhan M, Wang P, Lin X, Chen T, Lu S, Yan JJWD, Energy S (2019) Study on the relationship between waste classification, combustion condition and dioxin emission from waste incineration. Waste Disposal Sustain Energy 1:91–98
Lin Y-S, Chen K-S, Lin Y-C, Hung C-H, Chang-Chien G-P (2008) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans distributions in ash from different units in a municipal solid waste incinerator. J Hazard Mater 154:954–962
Lin X, Ma Y, Chen Z, Li X, Lu S, Yan J (2020) Effect of different air pollution control devices on the gas/solid-phase distribution of PCDD/F in a full-scale municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ Pollut 265:114888
Lomnicki S, Dellinger B (2003) A detailed mechanism of the surface-mediated formation of PCDD/F from the oxidation of 2-chlorophenol on a CuO/silica surface. J Phys Chem A 107:4387–4395
Lu S-Y, Du Y, Yan J-H, Li X-D, Ni M-J, Cen K-F (2012) Dioxins and their fingerprint in size-classified fly ash fractions from municipal solid waste incinerators in China—mechanical grate and fluidized bed units. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 62:717–724
Luijk R, Akkerman DM, Slot P, Olie K, Kapteijn F (1994) Mechanism of formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the catalyzed combustion of carbon. Environ Sci Technol 28:312–321
Ma C, Li B, Chen D, Wenga T, Ma W, Lin F, Chen G (2019) An investigation of an oxygen-enriched combustion of municipal solid waste on flue gas emission and combustion performance at a 8 MWth waste-to-energy plant. Waste Manag 96:47–56
Ma Y, Lin X, Chen Z, Li X, Lu S, Yan J (2020) Influence factors and mass balance of memory effect on PCDD/F emissions from the full-scale municipal solid waste incineration in China. Chemosphere 239:124614
Matsuda H, Ozawa S, Naruse K, Ito K, Kojima Y, Yanase T (2005) Kinetics of HCl emission from inorganic chlorides in simulated municipal wastes incineration conditions. Chem Eng Sci 60:545–552
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China) (2008) HJ 77.2-2008 Ambient air and flue gas – determination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) isotope dilution HRGC-HRMS. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics) (2021) China Statistics Yearbook-2021, China statistics Press (Beijing)
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics), MEEPRC (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China) (2021) China Environmental Statistics Yearbook-2020, China Environmental Statistics Press (Beijing)
Nganai S, Dellinger B, Lomnicki S (2014) PCDD/PCDF ratio in the precursor formation model over CuO surface. Environ Sci Technol 48:13864–13870
Ni Y, Zhang H, Fan S, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Chen J (2009) Emissions of PCDD/Fs from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 75:1153–1158
Olie K, Addink R, Schoonenboom M (1998) Metals as catalysts during the formation and decomposition of chlorinated dioxins and furans in incineration processes. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 48:101–105
Pan Y, Yang L, Zhou J, Liu J, Qian G, Ohtsuka N, Motegi M, Oh K, Hosono S (2013) Characteristics of dioxins content in fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 92:765–771
Qiu J, Tang M, Peng Y, Lu S, Li X, Yan J (2020) Characteristics of PCDD/Fs in flue gas from MSWIs and HWIs: emission levels, profiles and environmental influence. Aerosol Air Qual Res 20:2085–2097
Ruokojärvi PH, Halonen IA, Tuppurainen KA, Tarhanen J, Ruuskanen J (1998) Effect of gaseous inhibitors on PCDD/F formation. Environ Sci Technol 32:3099–3103
Ruokojärvi PH, Asikainen AH, Tuppurainen KA, Ruuskanen J (2004) Chemical inhibition of PCDD/F formation in incineration processes. Sci Total Environ 325:83–94
Ryu J-Y, Mulholland JA, Dunn JE, Iino F, Gullett BK (2004) Potential role of chlorination pathways in PCDD/F formation in a municipal waste incinerator. Environ Sci Technol 38:5112–5119
Ryu J-Y, Choi K-C, Mulholland JA (2006) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDD) and dibenzofurna (PCDF) isomer patterns from municipal waste combustion: Formation mechanism fingerprints. Chemosphere 65:1526–1536
Shaub WM, Tsang W (1983) Dioxin formation in incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 17:721–730
Stieglitz L, Zwick G, Beck J, Roth W, Vogg H (1989) On the de-novo synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on fly ash of municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere 18:1219–1226
Tuppurainen K, Halonen I, Ruokojärvi P, Tarhanen J, Ruuskanen J (1998) Formation of PCDDs and PCDFs in municipal waste incineration and its inhibition mechanisms: a review. Chemosphere 36:1493–1511
Wang L-C, Hsi H-C, Chang J-E, Yang X-Y, Chang-Chien G-P, Lee W-S (2007) Influence of start-up on PCDD/F emission of incinerators. Chemosphere 67:1346–1353
Wang T, Chen T, Lin X, Zhan M, Li X (2017) Emission and distribution of PCDD/Fs, chlorobenzenes, chlorophenols, and PAHs from stack gas of a fluidized bed and a stoker waste incinerator in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5607–5618
Wielgosiński G (2011) The reduction of dioxin emissions from the processes of heat and power generation. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 61:511–526
Xia H, Tang J, Aljerf L (2022) Dioxin emission prediction based on improved deep forest regression for municipal solid waste incineration process. Chemosphere 294:133716
Ying Y, Ma Y, Li X, Lin X (2021) Emission and migration of PCDD/Fs and major air pollutants from co-processing of sewage sludge in brick kiln. Chemosphere 265:129120
You X (2008) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) emission from co-firing municipal solid waste (MSW) and coal in a fluidized bed incinerator. Waste Manag 28:1543–1551
Zhang H-J, Ni Y-W, Chen J-P, Zhang Q (2008) Influence of variation in the operating conditions on PCDD/F distribution in a full-scale MSW incinerator. Chemosphere 70:721–730
Zhang G, Hai J, Cheng J (2012) Characterization and mass balance of dioxin from a large-scale municipal solid waste incinerator in China. Waste Manag 32:1156–1162
Zhang M, Yang J, Buekens A, Olie K, Li X (2016) PCDD/F catalysis by metal chlorides and oxides. Chemosphere 159:536–544
Zhang M, Buekens A, Olie K, Li X (2017) PCDD/F-isomers signature-effect of metal chlorides and oxides. Chemosphere 184:559–568
Zhang M, Buekens A, Li X (2018a) Statistical analysis as a tool for discriminating dioxin formation pathways. J Mater Cycl Waste Manag 20:1516–1529
Zhang M, Buekens A, Li X (2018b) Characterising boiler ash from a circulating fluidised bed municipal solid waste incinerator and distribution of PCDD/F and PCB. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:22775–22789
Zhang R-z, Luo Y-h, Yin R-h (2018c) Experimental study on dioxin formation in an MSW gasification-combustion process: an attempt for the simultaneous control of dioxins and nitrogen oxides. Waste Manag 82:292–301
Zhou H, Meng A, Long Y, Li Q, Zhang Y (2014) An overview of characteristics of municipal solid waste fuel in China: physical, chemical composition and heating value. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 36:107–122
Zhu F, Li X, Lu J-W, Hai J, Zhang J, Xie B, Hong C (2018) Emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs in stack gas from municipal solid waste incineration plants in Northern China. Chemosphere 200:23–29
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFC1910100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuxuan Ying: writing, methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, visualization; Liang Xu: review and editing, formal analysis; Hao Zhang: methodology, data investigation; Xiaodong Li: project administration, funding acquisition; Shengyong Lu: funding acquisition; Yang Cao: data investigation; Xiaoqing Lin, Jisheng Long: methodology, validation, resources, writing — review and editing, project administration, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Constantini Samara
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 95 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, Y., Xu, L., Lin, X. et al. Influence of different kinds of incinerators on PCDD/Fs: a case study of emission and formation pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 5903–5916 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22437-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22437-7