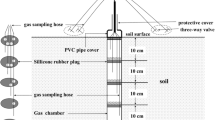
Abstract
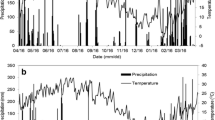
Nitrogen fertilizer has considerable effects on soil carbon fluxes. However, the responses of soil CO2 emission to N fertilizer remain controversial. A field experiment was conducted to examine the effect of application of N fertilizer on soil CO2 emission in a maize (Zea mays L.) field in Northeast China. Soil CO2 emission was measured from May 2010 to April 2016. Soil CO2 emission during the growing season and non-growing season contributed 79.7–83.6% and 16.4–20.3%, respectively, to the total annual CO2 emission. Cumulative annual soil CO2 emissions were significantly higher in no-N addition treatment (CK) than that in N addition treatment (SU) from 2012/2013 to 2015/2016 (p < 0.05). Mean annual soil CO2 emission decreased on averaged by 21.2% after N fertilization (p < 0.05). 49.6–82.2% of CO2 flux variation was explained by soil temperature at 5 cm depth. Q10 of soil CO2 emission in the annual scale was not significantly affected by N fertilizer. The results highlight the importance of N fertilizer on soil CO2 emission in agricultural ecosystem.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
References
Al-Kaisi MM, Kruse ML, Sawyer JE (2008) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on growing season soil carbon dioxide emission in a corn–soybean rotation. J Environ Qual 37:325–332
Bowden RD, Davidson E, Savage K, Arabia C, Steudler P (2004) Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. Forest Ecol Manag 196:43–56
Chen D, Li J, Lan Z, Hu S, Bai Y (2016) Soil acidification exerts a greater control on soil respiration than soil nitrogen availability in grasslands subjected to long-term nitrogen enrichment. Funct Ecol 30:658–669
Chen Z, Xu Y, He Y, Zhou X, Fan J, Yu H, Ding W (2018) Nitrogen fertilization stimulated soil heterotrophic but not autotrophic respiration in cropland soils: a greater role of organic over inorganic fertilizer. Soil Biol Biochem 116:253–264
Chen Z, Xu Y, Zhou X, Tang J, Kuzyakov Y, Yu H, Fan J, Ding W (2017) Extreme rainfall and snowfall alter responses of soil respiration to nitrogen fertilization: a 3-year field experiment. Global Chang Biol 23:3403
Craine JM, Wedin DA, Reich PB (2001) The response of soil CO2 flux to changes in atmospheric CO2, nitrogen supply and plant diversity. Global Chang Biol 7:947–953
Demoling F, Nilsson LO, Bååth E (2008) Bacterial and fungal response to nitrogen fertilization in three coniferous forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:370–379
Ding WX, Yu HY, Cai ZC, Han FX, Xu ZH (2010) Responses of soil respiration to N fertilization in a loamy soil under maize cultivation. Geoderma 155:381–389
Dong D, Kou Y, Yang W, Chen G, Xu H (2018) Effects of urease and nitrification inhibitors on nitrous oxide emissions and nitrifying/denitrifying microbial communities in a rainfed maize soil: a 6-year field observation. Soil till Res 180:82–90
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward and ecological clssification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Gagnon B, Ziadi N, Rochette P, Chantigny MH, Angers DA, Bertrand N, Smith WN (2016) Soil-surface carbon dioxide emission following nitrogen fertilization in corn. Can J Soil Sci 96:219–232
Hasselquist NJ, Metcalfe DB, Högberg P (2012) Contrasting effects of low and high nitrogen additions on soil CO2 flux components and ectomycorrhizal fungal sporocarp production in a boreal forest. Global Chang Biol 18:3596–3605
Iqbal J, Hu R, Feng M, Lin S, Malghani S, Ali IM (2010) Microbial biomass, and dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen strongly affect soil respiration in different land uses: a case study at Three Gorges Reservoir Area, South China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 137:294–307
Janssens I, Dieleman W, Luyssaert S, Subke J-A, Reichstein M, Ceulemans R, Ciais P, Dolman AJ, Grace J, Matteucci G (2010) Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat Geosci 3:315
Jian S, Li J, Chen J, Wang G, Mayes MA, Dzantor KE, Hui D, Luo Y (2016) Soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil carbon and nitrogen storage under nitrogen fertilization: a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 101:32–43
Knorr M, Frey SD, Curtis PS (2005) Nitrogen additions and litter decomposition: a meta-analysis. Ecology 86:3252–3257
Lai L, Zhao X, Jiang L, Wang Y, Luo L, Zheng Y, Chen X, Rimmington GM (2012) Soil respiration in different agricultural and natural ecosystems in an arid region. PLos One 7:e48011
Lee KH, Jose S (2003) Soil respiration, fine root production, and microbial biomass in cottonwood and loblolly pine plantations along a nitrogen fertilization gradient. Forest Ecol Manag 185:263–273
Lee M, Nakan K, Nakatsubo T, Koizumi H (2003) Seasonal changes in the contribution of root respiration to total soil respiration in a cool temperate deciduous forest. Plant Soil 255:311–318
Li L-J, You M-Y, Shi H-A, Ding X-L, Qiao Y-F, Han X-Z (2013) Soil CO2 emissions from a cultivated Mollisol: effects of organic amendments, soil temperature, and moisture. Eur J Soil Biol 55:83–90
Li R, Zhou G, Wang Y (2010) Responses of soil respiration in non-growing seasons to environmental factors in a maize agroecosystem, Northeast China. Chinese Sci Bull 55:2723–2730
Liu Q, Chen Y, Li W, Liu Y, Han J, Wen X, Liao Y (2016a) Plastic-film mulching and urea types affect soil CO2 emissions and grain yield in spring maize on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci Rep 6:28150
Liu Q, Wang R, Li R, Hu Y, Guo S (2016b) Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration to nitrogen fertilization: varying effects between growing and non-growing seasons. PLos One 11:e0168599
Lloyd J, Taylor J (1994) On the temperature dependence of soil respiration. Funct Ecol 8: 315–323
Mo J, Zhang W, Zhu W, Gundersen P, Fang Y, Dejun LI, Wang H (2008) Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Global Chang Biol 14:403–412
Ni K, Ding W, Cai Z, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhou B (2012) Soil carbon dioxide emission from intensively cultivated black soil in Northeast China: nitrogen fertilization effect. J Soil Sediment 12:1007–1018
Olsson P, Linder S, Giesler R, Högberg P (2005) Fertilization of boreal forest reduces both autotrophic and heterotrophic soil respiration. Global Chang Biol 11:1745–1753
Peng Q, Dong Y, Qi Y, Xiao S, He Y, Ma T (2011) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil respiration in temperate grassland in Inner Mongolia China. Environ Earth Sci 62:1163–1171
Peng S, Shilong P, Tao W, Sun J, Shen Z (2009) Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in different ecosystems in China. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1008–1014
Post WM, Peng TH, Emanuel WR, King AW, Dale VH, Deangelis DL (1990) The global carbon-cycle. Am Sci 78:310–326
Ramirez KS, Craine JM, Fierer N (2012) Consistent effects of nitrogen amendments on soil microbial communities and processes across biomes. Glob Chang Biol 18:1918–1927
Rousk J, Brookes PC, Bååth E (2009) Contrasting soil pH effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1589–1596
Schlesinger WH, Andrews JA (2000) Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 48:7–20
Shao R, Deng L, Yang QH, Shangguan ZP (2014) Nitrogen fertilization increase soil carbon dioxide efflux of winter wheat field: a case study in Northwest China. Soil Till Res 143:164–171
Song C, Zhang J (2009) Effects of soil moisture, temperature, and nitrogen fertilization on soil respiration and nitrous oxide emission during maize growth period in Northeast China. Acta Agr Scand B-S P 59:97–106
Song M, Jiang J, Cao G, Xu X (2010) Effects of temperature, glucose and inorganic nitrogen inputs on carbon mineralization in a Tibetan alpine meadow soil. Eur J Soil Biol 46:375–380
Tu LH, Hu TX, Zhang J, Li XW, Hu HL, Liu L, Xiao YL (2013) Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 58:255–264
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Verma SB, Dobermann A, Cassman KG, Walters DT, Knops JM, Arkebauer TJ, Suyker AE, Burba GG, Amos B, Yang H, Ginting D, Hubbard KG, Gitelson AA, Walter-Shea EA (2005) Annual carbon dioxide exchange in irrigated and rainfed maize-based agroecosystems. Agr forest Meteorol 131:77–96
Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun T, Chen L, Pang X, Wang Y, Xiao F (2017) N and P fertilization reduced soil autotrophic and heterotrophic respiration in a young Cunninghamia lanceolata forest. Agr forest Meteorol 232:66–73
Wang R, Hu Y, Wang Y, Ali S, Liu Q, Guo S (2019) Nitrogen application increases soil respiration but decreases temperature sensitivity: combined effects of crop and soil properties in a semiarid agroecosystem. Geoderma 353:320–330
Wang R, Sun Q, Wang Y, Zheng W, Yao L, Hu Y, Guo S (2018) Contrasting responses of soil respiration and temperature sensitivity to land use types: cropland vs. apple orchard on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 621:425–433
Wang R, Wang Z, Sun Q, Zhao M, Du L, Wu D, Li R, Gao X, Guo S (2016) Effects of crop types and nitrogen fertilization on temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Soil Till Res 163:1–9
Xu W, Wan S (2008) Water- and plant-mediated responses of soil respiration to topography, fire, and nitrogen fertilization in a semiarid grassland in northern China. Soil Biol Biochem 40:679–687
Xu Y, Yu W, Ma Q, Zhou H (2010) Effects of long-term fertilizations on microbial biomass C and N and bacterial community structure in an aquic brown soil (in Chinese). Chinese J Appl Ecol 21:2078–2085
Yan W, Zhong Y, Liu J, Shangguan Z (2021) Response of soil respiration to nitrogen fertilization: evidence from a 6-year field study of croplands. Geoderma 384:114829
Zeng Y, Feng F, Medová H, Dean J, Koblížek M (2014) Functional type 2 photosynthetic reaction centers found in the rare bacterial phylum Gemmatimonadetes. P Natl Acad Sci USA 111:7795–7800
Zhang X, Xu M, Sun N, Wang X, Wu L, Wang B, Li D (2013) How do environmental factors and different fertilizer strategies affect soil CO2 emission and carbon sequestration in the upland soils of southern China? Appl Soil Ecol 72:109–118
Zhong Y, Yan W, Shangguan Z (2016) The effects of nitrogen enrichment on soil CO2 fluxes depending on temperature and soil properties. Global Ecol Biogeogr 25:475–488
Zhou L, Zhou X, Zhang B, Lu M, Luo Y, Liu L, Li B (2014) Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: a meta-analysis. Global Chang Biol 20:2332–2343
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Non-Profit Research Foundation for Agriculture (201103039), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0907800), Open Research Project of Shouguang Facilities Agriculture Center in Institute of Applied Ecology (2018SG-S-02), the Natural Science Research Programme of Huai’an (HAB202055), and Huai’an Excellent Youth Science Foundation and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42107348).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dan Dong: writing of draft, visualization, and funding acquisition; Weichao Yang: supervision, reviewing and editing; Hao Sun: methodology; Shuang Kong: visualization editing; Hui Xu: investigation and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor:y Zhihong Xu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, D., Yang, W., Sun, H. et al. Nitrogen fertilization decrease soil CO2 emission in a rainfed maize field in Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 81256–81264 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21502-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21502-5