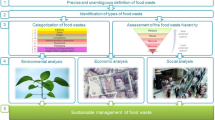
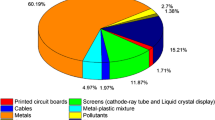
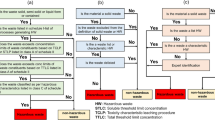
Abstract
An increasing amount of electronic waste (e-waste) is not a new concern. It has been causing trouble globally. This waste comprises valuable metals and harmful compounds that lead to detrimental environmental conditions. Managing this kind of waste in developing economies is difficult due to different barriers hindering the process. Therefore, the goal of this research work is to determine the barriers while taking expert opinions and through available literature, and subsequently prioritize them to address the challenges in e-waste management. Moreover, this study utilizes an integrated Fuzzy Decision-Making Trail and Evaluation Laboratory (F-DEMATEL) and Fuzzy Interpretive Structural Modeling (F-ISM) approaches to determine the interrelationship between these identified barriers. Performance data obtained from this combined approach is applied to determine an overall rank for 15 identified barriers. The F-DEMATEL technique facilitates in obtaining the influence of barriers on each other and categorizes them into causal or effect groups. In addition, a Fuzzy Matrice d’impacts Croisés Multiplication Appliquée an un Classeement (F-MICMAC) analysis is exercised to sort them into dependent or driving factor. The findings suggest that the underlying cause barriers include “lack of customer awareness about return,” “less policies addressing e-waste problem,” “lack of long-term planning,” and “insensitiveness of public towards environmental issues.” The methodology is integrated with fuzzy logic to take uncertainty in the data gathered into consideration. This approach aids policymakers and decision-makers in determining the barriers’ mutual relationships and interconnections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrahman MD, Gunasekaran A, Subramanian N (2014) Critical barriers in implementing reverse logistics in the Chinese manufacturing sectors. Int J Prod Econ 147:460–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.08.003
Akyuz E, Celik E (2015) A fuzzy DEMATEL method to evaluate critical operational hazards during gas freeing process in crude oil tankers. J Loss Prev Process Ind 38:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2015.10.006
Arbués F, Villanúa I (2021) Why do Spanish households separate their e-waste for proper disposal? An econometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15933-9
Attri R, Dev N, Sharma V (2013) Interpretive structural modelling (ISM) approach: an overview. Res J Manag Sci 2319:1171
Balon V, Sharma AK, Barua MK (2016) Assessment of barriers in green supply chain management using ISM: a case study of the automobile industry in India. Glob Bus Rev 17:116–135. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150915610701
Batoo KM, Pandiaraj S, Muthuramamoorthy M et al (2021) Fuzzy-based adaptive learning network using search and rescue optimization for e-waste management model: case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15320-4
Bhatia MS, Srivastava RK (2018) Analysis of external barriers to remanufacturing using grey-DEMATEL approach: an Indian perspective. Resour Conserv Recycl 136:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.03.021
Boyden A, Soo VK, Doolan M (2016) The environmental impacts of recycling portable lithium-ion batteries. Procedia CIRP 48:188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.03.100
Chauhan A, Singh A, Jharkharia S (2018) An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) and decision-making trail and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) method approach for the analysis of barriers of waste recycling in India. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 68:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2016.1249441
Chung KH, Zhang H (2011) Corporate governance and institutional ownership. J Financ Quant Anal 46:247–273. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022109010000682
de Albuquerque CA, Mello CHP, de Freitas Gomes JH, dos Santos VC (2021) Bibliometric analysis of studies involving e-waste: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:47773–47784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15420-1
Dwivedy M, Mittal RK (2010) Estimation of future outflows of e-waste in India. Waste Manag 30:483–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.09.024
Fontela E, Gabus A (1972) World problems an invitation to further thought within the framework of DEMATEL. Battelle Geneva Res Centre, Geneva
Garlapati VK (2016) E-waste in India and developed countries: management, recycling, business and biotechnological initiatives. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:874–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.106
Gorane SJ, Kant R (2013) Modelling the SCM enablers: an integrated ISM-fuzzy MICMAC approach. Asia Pac J Mark Logist 25:263–286. https://doi.org/10.1108/13555851311314059
Gunasekaran A, Ngai EWT (2004) Information systems in supply chain integration and management. Eur J Oper Res 159:269–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2003.08.016
Islam MT, Abdullah AB, Shahir SA et al (2016) A public survey on knowledge, awareness, attitude and willingness to pay for WEEE management: case study in Bangladesh. J Clean Prod 137:728–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.111
Jindal A, Sangwan KS (2011) Glocalized solutions for sustainability in manufacturing. Glocal Solut Sustain Manuf 448–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19692-8
Kumar A, Dixit G (2018a) Evaluating critical barriers to implementation of WEEE management using DEMATEL approach. Resour Conserv Recycl 131:101–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.12.024
Kumar A, Dixit G (2018b) An analysis of barriers affecting the implementation of e-waste management practices in India: a novel ISM-DEMATEL approach. Sustain Prod Consum 14:36–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2018.01.002
Luthra S, Kumar V, Kumar S, Haleem A (2011) Barriers to implement green supply chain management in automobile industry using interpretive structural modeling technique-an Indian perspective. J Ind Eng Manag 4:231–257. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.2011.v4n2.p231-257
Maqbool A, Khan S, Haleem A, Khan MI (2020) Investigation of drivers towards adoption of circular economy: a DEMATEL approach. Lect Notes Mech Eng 147–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1071-7_14
Mathiyazhagan K, Haq AN (2013) Analysis of the influential pressures for green supply chain management adoption-an Indian perspective using interpretive structural modeling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:817–833
Menikpura SNM, Santo A, Hotta Y (2014) Assessing the climate co-benefits from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) recycling in Japan. J Clean Prod 74:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.040
Mousavizade F, Shakibazad M (2019) Identifying and ranking CSFs for KM implementation in urban water and sewage companies using ISM-DEMATEL technique. J Knowl Manag 23:200–218. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-05-2018-0321
Mudgal RK, Shankar R, Parvaiz T, Tilak R (2010) Modelling the barriers of green supply chain practices. Int J Logist Syst Manag 7:81–107. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLSM.2010.033891
Mulliner E, Smallbone K, Maliene V (2013) An assessment of sustainable housing affordability using a multiple criteria decision making method. Omega (United Kingdom) 41:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2012.05.002
Park K, Kremer GEO (2017) Text mining-based categorization and user perspective analysis of environmental sustainability indicators for manufacturing and service systems. Ecol Indic 72:803–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.027
Patil SK, Kant R (2014) A fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS framework for ranking the solutions of Knowledge Management adoption in Supply Chain to overcome its barriers. Expert Syst Appl 41:679–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.07.093
Prakash C, Barua MK (2016) A multi-criteria decision-making approach for prioritizing reverse logistics adoption barriers under fuzzy environment: case of Indian electronics industry. Glob Bus Rev 17:1107–1124. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150916656667
Presley A, Meade L, Sarkis J (2007) A strategic sustainability justification methodology for organizational decisions: a reverse logistics illustration. Int J Prod Res 45:4595–4620. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207540701440220
Rahman S, Subramanian N (2012) Factors for implementing end-of-life computer recycling operations in reverse supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 140:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.07.019
Ravi V (2015) Analysis of interactions among barriers of eco-efficiency in electronics packaging industry. J Clean Prod 101:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.002
Satapathy S (2017) An analysis of barriers for plastic recycling in the Indian plastic industry. Benchmark Int J. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-11-2014-0103
Scheinberg A, Spies S, Simpson MH, Mol APJ (2011) Assessing urban recycling in low- and middle-income countries: building on modernised mixtures. Habitat Int 35:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2010.08.004
Shih K-H, Lin W, Wang Y, Hung T-E (2013) Applying Dematel-Anp for assessing organizational. 349–365
Srivastava R, Sharma D (2015) Factors affecting e-waste management: an interpretive structural modeling approach. Proc - 2015 5th Int Conf Commun Syst Netw Technol CSNT 2015 1307–1312. https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNT.2015.158
Turaga RMR, Bhaskar K, Sinha S et al (2019) E-waste management in India: issues and strategies. Vikalpa 44:127–162. https://doi.org/10.1177/0256090919880655
Verma DS, Agrawal S (2014) E-waste management practices : specific focus on Indore & Jabalpur. IjmemrOrg 2:523–530 International Journal of Engineering Research and General Science Volume 2, Issue 4, ISSN 2091–2730
Vieira BO, Guarnieri P, Nofal R, Nofal B (2020) Multi-criteria methods applied in the studies of logistics of E-waste : a research agenda. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics4020011
Wakolbinger T, Toyasaki F, Nowak T, Nagurney A (2014) When and for whom would e-waste be a treasure trove? Insights from a network equilibrium model of e-waste flows. Int J Prod Econ 154:263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.04.025
Warfield J (1973) Binary matrices in system modeling. IEEE Trans Syst MAN, Cybern SMC-3(5):pp 441–449
Welfens MJ, Nordmann J, Seibt A (2016) Drivers and barriers to return and recycling of mobile phones. Case studies of communication and collection campaigns. J Clean Prod 132:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.082
Wong CY, Boon-Itt S, Wong CWY (2011) The contingency effects of environmental uncertainty on the relationship between supply chain integration and operational performance. J Oper Manag 29:604–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2011.01.003
Xu Y, Yeh CH, Liu CG et al (2021) Evaluating and managing interactive barriers for sustainable e-waste management in China. J Oper Res Soc 72:2018–2031. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2020.1759381
Yukalang N, Clarke B, Ross K (2017) Barriers to effective municipal solid waste management in a rapidly urbanizing area in Thailand. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:9–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14091013
Zarte M, Pechmann A, Nunes IL (2018) Sustainable evaluation of production programs using a fuzzy inference model - a concept. Procedia CIRP 73:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.04.012
Acknowledgements
This work has been conducted at the National Institute of Technology Jamshedpur. The authors are grateful to the institute for providing essential facilities to conduct the work smoothly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KP designed the study. KP and DP supervised the study. JJ recruited the participants and collected data. KP, JJ, and DP analyzed and interpreted of results. KP and JJ wrote an early draft of the manuscript. KP, JJ, and DP revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jangre, J., Prasad, K. & Patel, D. Analysis of barriers in e-waste management in developing economy: an integrated multiple-criteria decision-making approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 72294–72308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21363-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21363-y