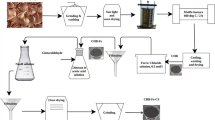
Abstract
In the present study, recyclable porous nano-carbons (PNCs) were used to remove textile dyes (mainly methylene blue, methyl orange, and rhodamine B) from an aqueous environment. Due to their high surface area and mesoporous nature, PNCs exhibited extremely fast and efficient adsorption behavior. PNCs synthesized at an elevated temperature of 1000 °C are used in batch experiments, as they showed maximum dye removal with high surface area. Batch mode was used to optimize operational parameters such as initial dye concentration, contact time, adsorbent dose and pH as a function of time. Within ~7 minutes of treatment, PNCs achieved a maximum removal efficacy of ~99 percent for methylene blue. The recyclability of PNCs was investigated, and it retained its efficiency even after seven cycles. The efficacy of PNCs in treating industrial water contaminated with methylene blue dye was assessed. Different adsorption isotherms were carried out to determine maximum amount of dye that can be adsorbed on to surface of PNCs. The maximum adsorption capacity attained using Langmuir isotherm for methylene blue was around 1216.54 mg g-1. Adsorption kinetics were applied on experimental data to identify the rate of adsorption. It was confirmed that novel onion peel-based porous PNCs were successful in removing methylene blue dye effectively with short duration in comparison with other dyes mainly rhodamine B and methyl orange.
Graphical abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during the current study are presented in the manuscript and supplementary.
References
Akshaya KB, Bhat VS, Varghese A et al (2019) Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Determination of Progesterone Using Carbon Nanospheres from Onion Peels Coated on Carbon Fiber Paper. J Electrochem Soc 166:B1097–B1106. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0251913jes
Ali GAM, Supriya S, Chong KF et al (2019) Superior supercapacitance behavior of oxygen self-doped carbon nanospheres: a conversion of Allium cepa peel to energy storage system. Biomass Conv Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00520-3
AlOthman ZA, Habila MA, Ali R et al (2014) Valorization of two waste streams into activated carbon and studying its adsorption kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and thermodynamics for methylene blue removal. Arab J Chem 7:1148–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.007
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J Chem 2017:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Aysan H, Edebali S, Ozdemir C et al (2016) Use of chabazite, a naturally abundant zeolite, for the investigation of the adsorption kinetics and mechanism of methylene blue dye. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 235:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.08.007
Azami M, Bahram M, Nouri S, Naseri A (2012) A central composite design for the optimization of the removal of the azo dye, Methyl Orange, from waste water using the Fenton reaction. J Serbian Chem Soc 77:235–246. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC110315165A
Azouaou N, Sadaoui Z, Djaafri A, Mokaddem H (2010) Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution onto untreated coffee grounds: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 184:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.014
Bankoti K, Rameshbabu AP, Datta S et al (2017) Onion derived carbon nanodots for live cell imaging and accelerated skin wound healing. J Mater Chem B 5:6579–6592. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb00869d
Bentahar S, Dbik A, el Khomri M et al (2018) Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution by natural clay. Groundw Sustain Dev 6:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.02.002
Bhat VS, Kanagavalli P, Sriram G et al (2020) Low cost, catalyst free, high performance supercapacitors based on porous nano carbon derived from agriculture waste. J Energy Storage 32:101829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101829
Chang B, Guan D, Tian Y et al (2013) Convenient synthesis of porous carbon nanospheres with tunable pore structure and excellent adsorption capacity. J Hazard Mater 262:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.054
Chaukura N, Murimba EC, Gwenzi W (2017a) Synthesis, characterisation and methyl orange adsorption capacity of ferric oxide–biochar nano-composites derived from pulp and paper sludge. Appl Water Sci 7:2175–2186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0392-5
Chaukura N, Murimba EC, Gwenzi W (2017b) Sorptive removal of methylene blue from simulated wastewater using biochars derived from pulp and paper sludge. Environ Technol Innov 8:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2017.06.004
Chen X (2015) Modeling of experimental adsorption isotherm data. Information (Switzerland) 6:14–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010014
Chen Q, Wu Q (2015) Preparation of carbon microspheres decorated with silver nanoparticles and their ability to remove dyes from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 283:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.024
Chen A, Li Y, Yu Y et al (2016) Synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanospheres for highly efficient adsorption of bulky dye molecules. J Mater Sci 51:7016–7028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9991-7
Chen X, Li H, Liu W et al (2019) Effective removal of methyl orange and rhodamine B from aqueous solution using furfural industrial processing waste: Furfural residue as an eco-friendly biosorbent. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 583:123976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123976
Cheung C, Porter J, Mckay G (2000) Elovich Equation and Modified Second-Order Equation for Sorption of Cadmium Ions onto Bone Char. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 75:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4660(200011)75:11<963::AID-JCTB302>3.0.CO;2-Z
Chia PW, Lim BS, Yong FSJ et al (2018) An efficient synthesis of bisenols in water extract of waste onion peel ash. Environ Chem Lett 16:1493–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0764-1
Cruz JC, Nascimento MA, Amaral HAV et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt nanoparticles for application in the removal of textile dye. J Environ Manag 242:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.059
Danish M, Ahmad T, Hashim R et al (2018) Comparison of surface properties of wood biomass activated carbons and their application against rhodamine B and methylene blue dye. Surf Interfaces 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2018.02.001
Farouq R, Yousef N (2015) Equilibrium and Kinetics Studies of adsorption of Copper (II) Ions on Natural Biosorbent. Int J Chem Eng Appl 6:319–324. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJCEA.2015.V6.503
Georgakilas V, Perman JA, Tucek J, Zboril R (2015) Broad Family of Carbon Nanoallotropes: Classification, Chemistry, and Applications of Fullerenes, Carbon Dots, Nanotubes, Graphene, Nanodiamonds, and Combined Superstructures. Chem Rev 115:4744–4822. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500304f
Goswami M, Phukan P (2017) Enhanced adsorption of cationic dyes using sulfonic acid modified activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 5:3508–3517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.016
Gu H, Xu X, Dong M et al (2019) Carbon nanospheres induced high negative permittivity in nanosilver-polydopamine metacomposites. Carbon 147:550–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.03.028
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, Ali R et al (2014) Removal of Tartrazine Dye onto MixedWaste Activated Carbon: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Clean-soil Air Water 42:1824–1831
Habila MA, Al Othman ZA, Al-Tamrah SA et al (2015) Activated carbon from waste as an efficient adsorbent for malathion for detection and removal purposes. J Ind Eng Chem 32:336–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.09.009
Harja M, Ciobanu G, Favier L et al (2016) ADSORPTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET DYE ONTO MODIFIED ASH. Bulletin of the Polytechnic Institute of Iasi, Section Chemistry and Chemical. Engineering 62:27–37. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2016.19725
Hegde S, Kumar A, Hegde G (2020) Synthesis of sustainable carbon nanospheres from natural bioresources and their diverse applications. In: ACS symposium series in the book adapting 2D nanomaterials for advanced applications, Chapter 16, pp 393–420, vol 1353
Hu Q, Zhang Z (2019) Application of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: A theoretical analysis. J Mol Liq 277:646–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.01.005
Hu T, Li Y, Gao W et al (2019) Engineering of rich nitrogen-doped and magnetic mesoporous carbon nanospheres with predictable size uniformity for acid dye molecules adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 279:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.12.034
Iram M, Guo C, Guan Y et al (2010) Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. J Hazard Mater 181:1039–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.119
Jain SN, Gogate PR (2018) Efficient removal of Acid Green 25 dye from wastewater using activated Prunus Dulcis as biosorbent: Batch and column studies. J Environ Manag 210:226–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.008
Khan EA, Shahjahan, Khan TA (2018) Adsorption of methyl red on activated carbon derived from custard apple (Annona squamosa) fruit shell: Equilibrium isotherm and kinetic studies. J Mol Liq 249:1195–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.125
Konicki W, Cendrowski K, Chen X, Mijowska E (2013) Application of hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres as an high effective adsorbent for the fast removal of acid dyes from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 228:824–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.067
Kumar A, Hegde G, Manaf SABA et al (2014) Catalyst free silica templated porous carbon nanoparticles from bio-waste materials. Chem Commun 50:12702–12705. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc04378b
Kundu S, Chowdhury IH, Naskar MK (2017) Synthesis of hexagonal shaped nanoporous carbon for efficient adsorption of methyl orange dye. J Mol Liq 234:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.03.090
Kundu S, Chowdhury IH, Naskar MK (2018) Hierarchical Porous Carbon Nanospheres for Efficient Removal of Toxic Organic Water Contaminants of Phenol and Methylene Blue. J Chem Eng Data 63:559–573. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00745
Li Y, Liu FT, Zhang HX et al (2019) DMF-treated strategy of carbon nanospheres for high-efficient and selective removal of organic dyes. Appl Surf Sci 484:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.04.080
Luo D, Wang X, Zhang Z et al (2020) Enhancement of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from dye–sensitized amide–functionalized carbon nanospheres by superior adsorption performance. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:30375–30386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.001
Manaf SAA, Roy P, Sharma KV et al (2015) Catalyst-free synthesis of carbon nanospheres for potential biomedical applications: Waste to wealth approach. RSC Adv 5:24528–24533. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra14693j
Meng L, Zhang X, Tang Y et al (2015) Hierarchically porous silicon-carbon-nitrogen hybrid materials towards highly efficient and selective adsorption of organic dyes. Sci Rep 5:7910. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07910
Mihaly Cozmuta L, Mihaly Cozmuta A, Peter A et al (2011) The influence of pH on the Adsorption of Lead by Na-Clinoptilolite: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Water SA 38:269–278. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v38i2.13
Mouni L, Belkhiri L, Bollinger JC et al (2018) Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Kaolin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl Clay Sci 153:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.034
Mukherjee S, Thakur A, Goswami R et al (2021) Efficacy of agricultural waste derived biochar for arsenic removal: Tackling water quality in the Indo-Gangetic plain. J Environ Manag 281:111814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111814
Munagapati VS, Kim D-S (2016) Adsorption of anionic azo dye Congo Red from aqueous solution by Cationic Modified Orange Peel Powder. J Mol Liq 220:540–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.119
Nadra LAR (2019) Developed greener method based on MW implementation in manufacturing CNFs. Int J Nanomanuf 15:269–289
Nieto-Márquez A, Romero R, Romero A, Valverde JL (2011) Carbon nanospheres: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and applications. J Mater Chem 21:1664–1672. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm01350a
Novais RM, Caetano AP, Seabra MP, Labrincha JA, Pullar RC (2018) Extremely fast and efficient methylene blue adsorption using eco-friendly cork and paper waste-based activated carbon adsorbents. J Clean Prod 197:1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.278
Papegowda PK, Syed AA (2017) Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies on the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Saw Palmetto Spent. Int J Environ Res 11:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0010-x
Qu J, Zhang Q, Xia Y et al (2015) Synthesis of carbon nanospheres using fallen willow leaves and adsorption of Rhodamine B and heavy metals by them. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1408–1419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3447-x
Rabbani M, Seghatoleslami ZS, Rahimi R (2017) Selective adsorption of organic dye methylene blue by Cs4H2PMo11FeO40·6H2O in presence of methyl orange and Rhodamine-B. J Mol Struct 1146:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.05.134
Sen TK (2013) Review on Dye Removal from Its Aqueous Solution into Alternative Cost Effective and Non-Conventional Adsorbents. J Chem Process Eng. https://doi.org/10.17303/jce.2014.105
Shao Y, Zhou L, Bao C, Ma J (2015) A facile approach to the fabrication of rattle-type magnetic carbon nanospheres for removal of methylene blue in water. Carbon 89:378–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.03.047
Simi A, Azeeza V (2010) Removal of methylene blue dye using low cost adsorbent. Asian J Chem 22:4371–4376
Singh NB, Nagpal G, Agrawal S, Rachna (2018) Water purification by using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ Technol Innov 11:187–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006
Song X, Wang Y, Wang K, Xu R (2012) Low-cost carbon nanospheres for efficient removal of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:13438–13444. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300914h
Spagnoli AA, Giannakoudakis DA, Bashkova S (2017) Adsorption of methylene blue on cashew nut shell based carbons activated with zinc chloride: The role of surface and structural parameters. J Mol Liq 229:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.12.106
Sriram G, Supriya S, Kurkuri M, Hegde G (2019) Efficient CO2 adsorption using mesoporous carbons from biowastes. Mater Res Express 7:015605. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5f2c
Subramaniam R, Kumar Ponnusamy S (2015) Novel adsorbent from agricultural waste (cashew NUT shell) for methylene blue dye removal: Optimization by response surface methodology. Water Resources Ind 11:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2015.07.002
Supriya S, Sriram G, Ngaini Z et al (2020) The Role of Temperature on Physical–Chemical Properties of Green Synthesized Porous Carbon Nanoparticles. Waste Biomass Valoriz 11:3821–3831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00675-0
Thakkar SV, Malfatti L (2021) Silica-graphene porous nanocomposites for environmental remediation: A critical review. J Environ Manag 278:111519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111519
Uyar G, Kaygusuz H, Erim FB (2016) Methylene blue removal by alginate–clay quasi-cryogel beads. React Funct Polym 106:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2016.07.001
Waheed A, Baig N, Ullah N, Falath W (2021) Removal of hazardous dyes, toxic metal ions and organic pollutants from wastewater by using porous hyper-cross-linked polymeric materials: A review of recent advances. J Environ Manag 287:112360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112360
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li S et al (2018) Enhanced methylene blue adsorption onto activated reed-derived biochar by tannic acid. J Mol Liq 268:658–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.085
Wen X, Liu H, Zhang L et al (2019) Large-scale converting waste coffee grounds into functional carbon materials as high-efficient adsorbent for organic dyes. Bioresour Technol 272:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.10.011
Xia K, Wang G, Zhang H et al (2017) Synthesis of bimodal mesoporous carbon nanospheres for methyl orange adsorption. J Porous Mater 24:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0400-7
Xue Y, Xiang P, Wang H et al (2019) Mechanistic insights into selective adsorption and separation of multi-component anionic dyes using magnetic zeolite imidazolate framework-67 composites. J Mol Liq 296:111990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111990
Yallappa S, Manaf SAA, Shiddiky MJA et al (2017) Synthesis of carbon nanospheres through carbonization of Areca nut. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:2837–2842. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.13450
Yin J, Pei M, He Y et al (2015) Hydrothermal and activated synthesis of adsorbent montmorillonite supported porous carbon nanospheres for removal of methylene blue from waste water. RSC Adv 5:89839–89847. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra17322a
Zafar M, Dar Q, Nawaz F et al (2018) Effective adsorptive removal of azo dyes over spherical ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Res Technol 8:713–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.06.002
Zhao X, Wang D, Xiang C et al (2018) Facile Synthesis of Boron Organic Polymers for Efficient Removal and Separation of Methylene Blue, Rhodamine B, and Rhodamine 6G. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:16777–16787. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04049
Funding
This work was supported by Centre for Research Projects (CRP), CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bengaluru, with the file number SMSS-2102 (Seed Money).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Bhavya K, Supriya S, Jyothi M S, Maya Naik. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Bhavya K, Jpoyhti M S and Gurumurthy Hegde, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Enhanced surface area was achieved from onion peel-based carbon nanospheres.
• ~99% of removal efficiency was accomplished with respect to various operational parameters.
• A speedy removal of considered textile dyes (within 7 min) is the key feature.
• The efficacy of porous carbon nanospheres was around 95% even after seven recycles.
• Nearly 89 % removal was attained using industrial samples.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 6448 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnappa, B., Saravu, S., Shivanna, J.M. et al. Fast and effective removal of textile dyes from the wastewater using reusable porous nano-carbons: a study on adsorptive parameters and isotherms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 79067–79081 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21251-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21251-5