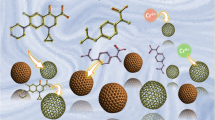
Abstract
To facilitate removing As(III) from water through an “oxidation-adsorption” process, the double-shell CuOx@MnOy hollow spheres (DCMHS) have been fabricated via a two-step co-precipitation route combined with the soft-template method. The surface characterization results showed that Mn oxides were formed without segregation and uniformly distributed on the surface of CuOx hollow spheres. DCMHS could achieve outstanding performance to remove As(III) with an As maximum adsorption capacity of 32.15 mg/g. Meanwhile, the kinetics results illustrated that the oxidative activity of DCMHS was strengthened due to its specific structure, and part of As(III) was converted to As(V) during the adsorption process. Also, air aeration could further enhance As(III) oxidation and thus improving As removal. The As(III) removal performance could be maintained under neutral and weak alkaline conditions. Phosphate, silicate, and carbonate anions could depress the removal performance, while chloride ions and sulfate anions barely influenced As removal. Moreover, DCMHS could be regenerated using NaOH and KMnO4 solutions without breaking the hollow sphere structure. Based on the spectroscopic analysis results, As(III) molecules were converted to As(V) via two pathways, including the oxidation by Mn oxides or superoxide radicals. The Cu–Mn synergistic effect could not only enhance the oxidative activity of Mn oxides but also produce superoxide radicals via the activation of surface-adsorbed oxygen molecules. Afterwards, the newly formed As(V) could be attached to the hydroxyl groups through surface complexation. Therefore, this work has provided insights into the morphology design of Mn-oxide-containing adsorbents and supplemented the interface reaction mechanisms for enhancing As(III) removal.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon request.
References
Abd Aziz R, Jose R (2017) Charge storage capability of tunnel MnO2 and alkaline layered Na-MnO2 as anode material for aqueous asymmetry supercapacitor. J Electronal Chem 799:538–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.06.014
Alka S, Shahir S, Ibrahim N, Ndejiko MJ, Vo DVN, Abd Manan F (2021) Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: a mini review. J Clean Prod 278:123805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123805
Baltrusaitis J, Cwiertny DM, Grassian VH (2007) Adsorption of sulfur dioxide on hematite and goethite particle surfaces. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:5542–5554. https://doi.org/10.1039/b709167b
Charbonnet JA, Duan Y, van Genuchten CM, Sedlak DL (2021) Regenerated manganese-oxide coated sands: the role of mineral phase in organic contaminant reactivity. Environ Sci Technol 55:5282–5290. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c05745
Chen J, Wang J, Zhang G, Wu Q, Wang D (2018) Facile fabrication of nanostructured cerium-manganese binary oxide for enhanced arsenite removal from water. Chem Eng J 334:1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.062
Cheng H, Yang T, Jiang J, Lu X, Wang P, Ma J (2020) Mn2+ effect on manganese oxides (MnOx) nanoparticles aggregation in solution: chemical adsorption and cation bridging. Environ Pollut 267:115561
Cui J, Zhu N, Kang N, Ha C, Shi C, Wu P (2017) Biorecovery mechanism of palladium as nanoparticles by Enterococcus faecalis: from biosorption to bioreduction. Chem Eng J 328:1051–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.124
Ferreira NS, Oliveira LHB, Agrelli V, de Oliveira AF, Nogueira ARA, Oliveira A, Gonzalez MH (2019) Bioaccumulation and acute toxicity of As(III) and As(V) in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Chemosphere 217:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.013
Flora SJS (2015) 1 - Arsenic: chemistry, occurrence, and exposure. Academic Press, In Handbook of arsenic toxicology, pp 1–49
Giles DE, Mohapatra M, Issa TB, Anand S, Singh P (2011) Iron and aluminium based adsorption strategies for removing arsenic from water. J Environ Manage 92:3011–3022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.07.018
Gude JCJ, Rietveld LC, van Halem D (2017) As(III) oxidation by MnO2 during groundwater treatment. Water Res 111:41–51
Goldberg S, Johnston CT (2001) Mechanisms of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. J Colloid Interf Sci 234:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7295
He C, Yu Y, Shen Q, Chen J, Qiao N (2014) Catalytic behavior and synergistic effect of nanostructured mesoporous CuO-MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for chlorobenzene destruction. Appl Surf Sci 297:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.076
Hsieh CT, Chen JM, Lin HH, Shih HC (2003) Field emission from various CuO nanostructures. Appl Phys Lett 83:3383–3385. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1619229
Hu Y-y, Pan C, Zheng X, Hu F, Xu L, Xu G, Jian Y, Peng X (2021) Prediction and optimization of adsorption properties for Cs+ on NiSiO@NiAlFe LDHs hollow spheres from aqueous solution: Kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. J Hazard Mater 401:23374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123374
Huang W, Xu JZ, Lu DK, Deng JJ, Shi GY, Zhou TS (2018a) Rational design of magnetic infinite coordination polymer core-shell nanoparticles as recyclable adsorbents for selective removal of anionic dyes from colored wastewater. Appl Surf Sci 462:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.122
Huang Y, Tian X, Nie Y, Yang C, Wang Y (2018b) Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation for phenol degradation over MnO2 at pH 3.5-9.0 via Cu(II) substitution. J Hazard Mater 360:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.028
Im JS, Park S-J, Lee Y-S (2007) Preparation and characteristics of electrospun activated carbon materials having meso- and macropores. J Colloid Interf Sci 314:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.05.033
Jha PK, Tripathi P (2021) Arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater: a review of global scenarios with special reference to India. Groundw Sustain Dev 13:100576
Kozhukharov V, Machkova M, Ivanov P, Bouwmeester H, Doorn R (1996) Surface analysis of doped lanthanide cobalt perovskites by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Mater Sci Lett 15:1727–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636208
Kubiak A, Bielan Z, Kubacka M, Gabala E, Zgola-Grzeskowiak A, Janczarek M, Zalas M, Zielinska-Jurek A, Siwinska-Ciesielczyk K, Jesionowski T (2020) Microwave-assisted synthesis of a TiO2-CuO heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity against tetracycline. Appl Surf Sci 520:146344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146344
Kumar Y, Chopra S, Gupta A, Kumar Y, Mardikar SP (2020) Low temperature synthesis of MnO2 nanostructures for supercapacitor application. Mater Sci for Energy Techno 3:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2020.06.002
Lassoued A, Dkhil B, Gadri A, Ammar S (2017) Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (alpha-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys 7:3007–3015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.066
Latif A, Sheng D, Sun K, Si YB, Azeem M, Abbas A, Bilal M (2020) Remediation of heavy metals polluted environment using Fe-based nanoparticles: mechanisms, influencing factors, and environmental implications. Environ Pollut 264:114728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114728
Lenoble V, Laclautre C, Serpaud B, Deluchat V, Bollinger JC (2004) As(V) retention and As(III) simultaneous oxidation and removal on a MnO2-loaded polystyrene resin. Sci Total Environ 326(1–3):197–207
Li L, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liang M, Li F, Yuan Y (2020a) Enhanced mineralization of bisphenol A by eco-friendly BiFeO3-MnO2 composite: performance, mechanism and toxicity assessment. J Hazard Mater 399:122883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122883
Li Y, Han Y, Li W, Li Y, Zhang D, Lan Y (2020b) Efficient removal of As(III) via simultaneous oxidation and adsorption by magnetic sulfur-doped Fe-Cu-Y trimetal oxide nanoparticles. Environ Res 180:108896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108896
Liang X, Hart C, Pang Q, Garsuch A, Weiss T, Nazar LF (2015) A highly efficient polysulfide mediator for lithium-sulfur batteries. Nat Commun 6:85682. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6682
Lin LN, Qiu WW, Wang D, Huang Q, Song ZG, Chau HW (2017a) Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: characterization and mechanism. Ecotox Environ Safe 144:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.063
Lin X, Zhao S, Fu L, Luo Y, Zhu R, Liu Z (2017b) Synthesis of Co-N-C grafted on well-dispersed MnOx-CeO2 hollow mesoporous sphere with efficient catalytic performance. Mol Catal 437:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2017.04.026
Lin S, Yang H, Na Z, Lin K (2018) A novel biodegradable arsenic adsorbent by immobilization of iron oxyhydroxide (FeOOH) on the root powder of long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 192:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.163
Liu B, Kim KH, Kumar V, Kim S (2020) A review of functional sorbents for adsorptive removal of arsenic ions in aqueous systems. J Hazard Mater 388:121815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121815
Liu D, Deng S, Maimaiti A, Wang B, Huang J, Wang Y, Yu G (2018) As(III) and As(V) adsorption on nanocomposite of hydrated zirconium oxide coated carbon nanotubes. J Colloid Interf Sci 511:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.10.004
Liu H, Zuo K, Vecitis CD (2014) Titanium dioxide-coated carbon nanotube network filter for rapid and effective arsenic sorption. Environl Sci Technol 48:13871–13879. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502312t
Lin L, Zhang G, Liu X, Khan ZH, Qiu W, Song Z (2019) Synthesis and adsorption of Fe-Mn-La-impregnated biochar composite as an adsorbent for As(III) removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Pollut 247:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.044
Lou Z, Cao Z, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhu J, Liu X, Baig SA, Zhou J, Xu X (2017) Enhanced removal of As(III)/(V) from water by simultaneously supported and stabilized Fe-Mn binary oxide nanohybrids. Chem Eng J 322:710–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.079
Luo J, Fu K, Yu D, Hristovski KD, Westerhoff P, Crittenden JC (2021) Review of advances in engineering nanomaterial adsorbents for metal removal and recovery from water: synthesis and microstructure impacts. ACS ES&T Eng 1(4):623–661
Mandal BK, Suzuki KJT (2002) Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58:201–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00268-0
Martin L, Martinez H, Poinot D, Pecquenard B, Le Cras F (2013) Comprehensive X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the conversion reaction mechanism of CuO in lithiated thin film electrodes. J Phys Chem C 117:4421–4430. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3119633
Martinson CA, Reddy KJ (2009) Adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interf Sci 336:406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.075
Nesbitt HW, Banerjee DJAM (1998) Interpretation of XPS Mn(2p) spectra of Mn oxyhydroxides and constraints on the mechanism of MnO2 precipitation. Am Mineral 83:305–315. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1998-3-414
Pang M, Long G, Shang J, Yuan J, Wei H, Wang B, Liu X, Xi Y (2015) Rapid synthesis of graphene/amorphous α-MnO2 composite with enhanced electrochemical performance for electrochemical capacitor. Mat Sci Eng B-Adv 194:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.12.028
Parikh SJ, Lafferty BJ, Meade TG, Sparks DL (2010) Evaluating environmental influences on AsIII oxidation kinetics by a poorly crystalline Mn-oxide. Environ Sci Technol 44:3772–3778. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903408g
Pathan S, Pandita N, Kishore N (2019) Acid functionalized-nanoporous carbon/MnO2 composite for removal of arsenic from aqueous medium. Arab J Chem 12:5200–5211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.12.011
Petrie RA, Grossl PR, Sims RC (2002) Oxidation of pentachlorophenol in manganese oxide suspensions under controlled Eh and pH environments. Environ Sci Technol 36:3744–3748. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0109491
Podgorski J, Berg M (2020) Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 368:845–850. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba1510
Qi J, Zhang G, Li H (2015) Efficient removal of arsenic from water using a granular adsorbent: Fe-Mn binary oxide impregnated chitosan bead. Bioresource Technol 193:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.102
Qiu H, Liang C, Yu J, Zhang Q, Song M, Chen F (2017) Preferable phosphate sequestration by nano-La(III) (hydr)oxides modified wheat straw with excellent properties in regeneration. Chem Eng J 315:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.043
Qiu Z, Shi S, Qiu F, Xu X, Yang D, Zhang T (2020) Enhanced As(III) removal from aqueous solutions by recyclable Cu@MNM composite membranes via synergistic oxidation and absorption. Water Res 168:115147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115147
Rady O, Liu L, Yang X, Tang X, Tan W, Qiu G (2020) Adsorption and catalytic oxidation of arsenite on Fe-Mn nodules in the presence of oxygen. Chemosphere 259:127503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127503
Sahu K, Satpati B, Singhal R, Mohapatra S (2020) Enhanced catalytic activity of CuO/Cu2O hybrid nanowires for reduction of 4-nitrophenol in water. J Phys Chem Solids 136:109143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.109143
Sha T, Hu W, Dong J, Chi Z, Zhao Y, Huang H (2020) Influence of the structure and composition of Fe-Mn binary oxides on rGO on As(III) removal from aquifers. J Environ Sci 88:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.08.008
Siddiqui SI, Zohra F, Chaudhry SA (2019) Nigella sativa seed based nanohybrid composite-Fe2O3-SnO2/BC: a novel material for enhanced adsorptive removal of methylene blue from water. Environ Res 178:108667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108667
Simon M, Vianello A, Shashoua Y, Vollertsen J (2021) Accelerated weathering affects the chemical and physical properties of marine antifouling paint microplastics and their identification by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Chemosphere 274:129749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129749
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DGJAG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
Song S, Zhang S, Huang SY, Zhang R, Yin L, Hu YZ, Wen T, Zhuang L, Hu BW, Wang XK (2019) A novel multi-shelled Fe3O4@MnOx hollow microspheres for immobilizing U(VI) and Eu(III). Chem Eng J 355:697–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.205
Uthirakumar P, Devendiran M, Kim TH, Kalaiarasan S, Lee I (2020) Fabrication of flexible sheets of Cu/CuO/Cu2O heterojunction nanodisks: a dominant performance of multiple photocatalytic sheets under natural sunlight - ScienceDirect. Mat Sci Eng B-Adv 260:114652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114652
Teixeira MC, Santos AC, Fernandes CS, Ng JC (2020) Arsenic contamination assessment in Brazil - past, present and future concerns: a historical and critical review. Sci Total Environ 730:138217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138217
Thirupathi B, Smirniotis PG (2012) Nickel-doped Mn/TiO2 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: catalytic evaluation and characterizations. J Catal 288:74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2012.01.003
Tiberg C, Sjostedt C, Eriksson AK, Klysubun W, Gustafsson JP (2020) Phosphate competition with arsenate on poorly crystalline iron and aluminum (hydr)oxide mixtures. Chemosphere 255:126937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126937
Toshifumi I, Hideaki Physics IJJJoA (1992) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis of the oxide of GaAs. Jpn J Appl Phys 31: 3981-3981. https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.31.3981
Villalobos M, Escobar-Quiroz IN, Salazar-Camacho C (2014) The influence of particle size and structure on the sorption and oxidation behavior of birnessite: I. Adsorption of As(V) and oxidation of As(III). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 125(15):564–581
Wang A, Zhu Q, Xing Z (2019) Design and synthesis of a calcium modified quaternized chitosan hollow sphere for efficient adsorption of SDBS. J Hazard Mater 369:342–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.047
Wang F, Zhang Y, Fang Q, Li Z, Lai Y, Yang H (2021) Prepared PANI@nano hollow carbon sphere adsorbents with lappaceum shell like structure for high efficiency removal of hexavalent chromium. Chemosphere 263:128109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128109
Wang Q, Yang L, Jia F, Li Y, Song S (2018) Removal of Cd (II) from water by using nano-scale molybdenum disulphide sheets as adsorbents. J Mol Liq 263:526–533
Wang X, Feng J, Bai Y, Zhang Q, Yin Y (2016) Synthesis, properties, and applications of hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem Rev 116(18):10983–11060
Weerasundara L, Ok YS, Bundschuh J (2021) Selective removal of arsenic in water: a critical review. Environ Pollut 268:115668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115668
Wichaita W, Polpanich D, Tangboriboonrat PJI (2019) A review on synthesis of colloidal hollow particles and their applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 58. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02330
Wu K, Zhang J, Chang B, Liu T, Zhang F, Jin P, Wang W, Wang X (2017) Removal of arsenic(III, V) by a granular Mn-oxide-doped Al oxide adsorbent: surface characterization and performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:18505–18519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9465-8
Wu K, Zhang C, Liu T, Lei H, Yang S, Jin P (2020) The removal of tetracycline, oxytetracycline, and chlortetracycline by manganese oxide-doped copper oxide: the behaviors and insights of Cu-Mn combination for enhancing antibiotics removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:12613–12623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07810-8
Xiong Y, Tong Q, Shan W, Xing Z, Wang Y, Wen S, Lou Z (2017) Arsenic transformation and adsorption by iron hydroxide/manganese dioxide doped straw activated carbon. Appl Surf Sci 416:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.145
Yadav MK, Saidulu D, Gupta AK, Ghosal PS, Mukherjee A (2021) Status and management of arsenic pollution in groundwater: a comprehensive appraisal of recent global scenario, human health impacts, sustainable field-scale treatment technologies. J Environ Chem Eng 9(3):105203
Yin Y, Zhou T, Luo H, Geng J, Yu W, Jiang Z (2019) Adsorption of arsenic by activated charcoal coated zirconium-manganese nanocomposite: performance and mechanism. Colloids Surface A 575:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.04.093
Yu J, Wang G, Bei C, Zhou M (2007) Effects of hydrothermal temperature and time on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of bimodal mesoporous TiO2 powders. Appl Catal B Environ 69:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.06.022
Zhang G, Liu H, Qu J, Jefferson W (2012) Arsenate uptake and arsenite simultaneous sorption and oxidation by Fe-Mn binary oxides: influence of Mn/Fe ratio, pH, Ca2+, and humic acid. J Colloid Interf Sci 366:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.058
Zhang G, Liu Y, Wang J, Li H (2020) Efficient arsenic(III) removal from aqueous solution by a novel nanostructured iron-copper-manganese trimetal oxide. J Mol Liq 309:112993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112993
Zhang G, Qu J, Liu H, Liu R, Li G (2007) Removal mechanism of As(III) by a novel Fe−Mn binary oxide adsorbent: oxidation and sorption. Environ Sci Technol 41(13):4613–4619
Zhang W, Liu C, Zheng T, Ma J, Zhang G, Ren G, Wang L, Liu Y (2018) Efficient oxidation and sorption of arsenite using a novel titanium(IV)-manganese(IV) binary oxide sorbent. J Hazard Mater 353:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.034
Zhang W, Liu C, Wang L, Zheng T, Ren G, Li J, Ma J, Zhang G, Song H, Zhang Z, Li Z (2019) A novel nanostructured Fe-Ti-Mn composite oxide for highly efficient arsenic removal: preparation and performance evaluation. Colloid Surface A 561:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.10.077
Zhou J, Zhou X, Yang K, Gao Z, Wang Z, Zhou C, Baig SA, Xu X (2020) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of arsenic on mesoporous silica modified by iron-manganese binary oxide (FeMnOx/SBA-15) from aqueous systems. J Hazard Mater 384:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121229
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, China (Grant No. 2019YFD1100102-04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China (Grant No. 51578440/51808512), the Key Research and Development Project of Shaanxi Province, China (Grant No. 2019ZDLSF05-03/2021ZDLSF05-06), the Science and Technology Program Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Water Resources (202022YBKT17), and the New Style Think Tank of Shaanxi Universities, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kun Wu contributed to the conception and the funding of the study. Birong Miao and Yang Li performed the experiment. Kun Wu performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript. Birong Miao, Yuyang Xiao, and Chuanqiao Zhang contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. Ting Liu, Shengjiong Yang, and Jinfu Liu helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
There are no data collected from human subjects in this research, so the ethics approval is not required for this paper.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Miao, B., Xiao, Y. et al. The enhanced removal of arsenite from water by double-shell CuOx@MnOy hollow spheres (DCMHS): behavior and mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 76417–76431 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20702-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20702-3