Abstract
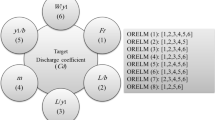
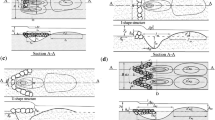
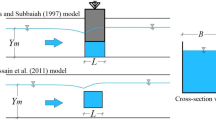
One of the most essential difficulties in the design and management of bridge piers is the estimation and modeling of scouring around the piers. The scour depth downstream of twin and three piers were simulated using a new outlier robust extreme learning machine (ORELM) model in this study. Furthermore, k-fold cross-validation with k = 4 was employed to validate the outcomes of numerical models. Four ORELM models with effective scouring parameters were first created to simulate scour depth. After then, the number of hidden layer neurons increased from two to thirty. The number of ideal hidden neurons was determined by examining the modeling results. The sigmoid activation function was also introduced as the best function. Furthermore, a sensitivity analysis was used to identify the superior model. The best model predicted scour depth as a function of the Froude number (Fr), the pier diameter to flow depth ratio (D/h), and the distance between the piers to flow depth ratio (d/h). The values of the objective function were accurately approximated by this model. As a result, using the ORELM model, the R2, scatter index, and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient were calculated to be 0.953, 0.146, and 0.949, respectively. The most efficient parameters for simulating the scour depth were Fr and D/h, according to the modeling results. It is worth noting that nearly half of the superior model’s simulated outputs had an inaccuracy of less than 10%. The superior model’s performance has been underestimated, according to uncertainty analysis. After that, a simple and practical equation for calculating the scour depth was established for the superior model. Additionally, the influence of each input parameter on the objective function was assessed using a partial derivative sensitivity analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Amini A, Melville BW, Ali TM, Ghazali AH (2012) Clear-water local scour around pile groups in shallow-water flow. J Hydraul Eng 138(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hy.1943-7900.0000488
AminiBaghbadorani D, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Beheshti A, Hadjzaman M, Jamali M (2018) Prediction of current-induced local scour around complex piers: review, revisit, and integration. Coast Eng 133(December 2017):43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.12.006
AminiBaghbadorani D, Beheshti AA, Ataie-Ashtiani B (2017) Scour hole depth prediction around pile groups: review, comparison of existing methods, and proposition of a new approach. Nat Hazards 88(2):977–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2900-9
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Aslani-Kordkandi A (2012) Flow field around side-by-side piers with and without a scour hole. Eur J Mech B Fluids 36:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2012.03.007
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Baratian-Ghorghi Z, Beheshti AA (2010) Experimental investigation of clear-water local scour of compound piers. J Hydraul Eng 136(6):343–351. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2010)136:6(343)
Azimi H, Bonakdari H, Ebtehaj I, Ashraf Talesh SH, Michelson DG, Jamali A (2017) Evolutionary Pareto optimization of an ANFIS network for modeling scour at pile groups in clear water condition. Fuzzy Sets Syst 319:50–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2016.10.010
Bazrafshan O, Ehteram M, Dashti Latif S, Feng Huang Y, YennTeo F, Najah Ahmed A, El-Shafie A (2022) Predicting crop yields using a new robust Bayesian averaging model based on multiple hybrid ANFIS and MLP models: predicting crop yields using a new robust Bayesian averaging model. Ain Shams Eng J 13(5):101724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2022.101724
Bozkuş Z, Özalp MC, Dinçer AE (2018) Effect of pier inclination angle on local scour depth around bridge pier groups. Arab J Sci Eng 43(10):5413–5421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3141-2
Coleman SE (2005) Clearwater local scour at complex piers. J Hydraul Eng 131(4):330–334. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9429(2005)131:4(330)
Das S, Das R, Mazumdar A (2016) Comparison of local scour characteristics around two eccentric piers of different shapes. Arab J Sci Eng 41(4):1199–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1817-4
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Moradi F, Gharabaghi B, Khozani ZS (2018) An integrated framework of Extreme Learning Machines for predicting scour at pile groups in clear water condition. Coast Eng 135(June 2017):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.12.012
Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Shamshirband S (2016) Extreme learning machine assessment for estimating sediment transport in open channels. Eng Comput 32(4):691–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-016-0446-1
Ehteram M, Ahmed AN, Latif SD, Huang YF, Alizamir M, Kisi O et al (2020) Design of a hybrid ANN multi-objective whale algorithm for suspended sediment load prediction. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10421-y
Etemad-Shahidi A, Bonakdar L, Jeng DS (2015) Estimation of scour depth around circular piers: applications of model tree. J Hydroinf 17(2):226–238. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2014.151
Harasti A, Gilja G, Potočki K, Lacko M (2021) Scour at bridge piers protected by the riprap sloping structure: A review. Water (Switzerland), 13(24). https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243606
Horata P, Chiewchanwattana S, Sunat K (2013) Robust extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 102:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.12.045
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2004) Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. IEEE Int Conf Neural Netw Conf Proc 2:985–990. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2004.1380068
Latif SD (2021a) Concrete compressive strength prediction modeling utilizing deep learning long short-term memory algorithm for a sustainable environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12877-y
Latif SD (2021b) Developing a boosted decision tree regression prediction model as a sustainable tool for compressive strength of environmentally friendly concrete. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15662-z
Latif SD, Ahmed AN (2021) Application of deep learning method for daily streamflow time-series prediction : a case study of the Kowmung River at Cedar Ford. Australia. Int J Sustain Dev Plan 16(3):497–501. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijsdp.160310
Latif SD, Ahmed AN, Sathiamurthy E, Huang YF, El-Shafie A (2021a) Evaluation of deep learning algorithm for inflow forecasting: a case study of Durian Tunggal Reservoir, Peninsular Malaysia. Nat Hazards, (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04839-x
Latif SD, Azmi MSBN, Ahmed AN, Fai CM, El-Shafie A (2020) Application of artificial neural network for forecasting nitrate concentration as a water quality parameter: a case study of Feitsui Reservoir, Taiwan. Int J Des Nat Ecodynamics. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijdne.150505
Latif SD, Birima AH, Najah A, Mohammed D, Al-ansari N, Ming C, El-shafie A (2021b) Development of prediction model for phosphate in reservoir water system based machine learning algorithms. Ain Shams Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.06.009
Liang F, Wang C, Huang M, Wang Y (2017) Experimental observations and evaluations of formulae for local scour at pile groups in steady currents. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 35(2):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2016.1147510
Liang NY, Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2006) A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 17(6):1411–1423. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2006.880583
Link O, Mignot E, Roux S, Camenen B, Escauriaza C, Chauchat J, et al (2019) Scour at bridge foundations in supercritical flows: an analysis of knowledge gaps. Water (Switzerland), 11(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081656
Melville B, Coleman S, Priestley S (2007) Local scour at complex piers. Examining the Confluence of Environmental and Water Concerns—Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2006, (Figure 1). https://doi.org/10.1061/40856(200)176
Moreno M, Maia R, Couto L (2016) Effects of relative column width and pile-cap elevation on local scour depth around complex piers. J Hydraul Eng 142(2):04015051. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hy.1943-7900.0001080
Muzzammil M, Alama J, Danish M (2015) Scour prediction at bridge piers in cohesive bed using gene expression programming. Aquatic Procedia, 4(Icwrcoe), 789–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.098
Najah A, Teo FY, Chow MF, Huang YF, Latif SD, Abdullah S et al (2021) Surface water quality status and prediction during movement control operation order under COVID-19 pandemic: case studies in Malaysia. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03139-y
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH, Latif SD (2021) Predictive modelling of piezometric head and seepage discharge in earth dam using soft computational models. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15029-4
Parsaie A, Haghiabi AH (2017) Mathematical expression of discharge capacity of compound open channels using MARS technique. J Earth Syst Sci 126(2):20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0807-1
Wang H, Tang H, Liu Q, Wang Y (2016a) Local scouring around twin bridge piers in open-channel flows. J Hydraul Eng 142(9):06016008. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hy.1943-7900.0001154
Wang H, Tang HW, Xiao JF, Wang Y, Jiang S (2016b) Clear-water local scouring around three piers in a tandem arrangement. SCIENCE CHINA Technol Sci 59(6):888–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-015-5905-1
Zhang K, Luo M (2015) Outlier-robust extreme learning machine for regression problems. Neurocomputing 151(P3):1519–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.09.022
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing original draft: MRGN; methodology: AF; analysis: AP; writing review and editing: SDL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nou, M.R.G., Foroudi, A., Latif, S.D. et al. Prognostication of scour around twin and three piers using efficient outlier robust extreme learning machine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 74526–74539 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20681-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20681-5