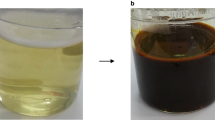
Abstract
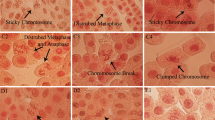
The genotoxicity of biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) obtained from three microbial mediators was assessed using the Allium cepa assay. Three clusters were differentiated for the highest frequency of end points of clastogenicity (stick-ends, fragments and bridges), end points of missegregation (C-metaphases and disorder anaphases), and lowest frequency of all the end points. In these clusters, the treatments were grouped respectively as I) positive control (GSF); II) silver nanoparticles form Aspergillus niger (AgNPs-An); and III) silver nanoparticles from both Cryptococcus laurentii (AgNPs-Cl) and Rhodotorula glutinis (AgNPs-Rg), Ag + , and negative control (NC). These results were in according to the principal component analisys (PCA) where treatments were associated to each component of the genotoxic effects. The statistical comparative analysis of the mitotic index (IM) and the abnormal mitosis frequency (AM) indicated that both GSF and AgNPsAn induce significant genotoxic effect. Low genotoxic effects were attributed to AgNPs-Cl and AgNPs-Rg, but mitogenic stimuli, similar to that obtained by the silver ions Ag + , were observed. Results suggested that different features of biogenic nanoparticles such as composition, size, and coating may be involved in the different cytological responses of the meristematic cells.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Akther T, Mathipi V, Kumar NS, Davoodbasha M, Srinivasan H (2019) Fungal-mediated synthesis of pharmaceutically active silver nanoparticles and anticancer property against A549 cells through apoptosis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):13649–13657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04718-w
Andrioli N (2011) Evaluación de agentes químicos con potencial genotóxico en células meristemáticas de Allium cepa. Tesis Doctoral 41–49
Andrioli NB, Mudry MD (2011) Cytological and cytogenetic effects induced by thiabendazole on Allium cepa root meristems. BAG - J Basic Appl Genet 22(2):17–23
Andrioli NB, Soloneski S, Larramendy ML, Mudry MD (2012) Cytogenetic and microtubule array effects of the zineb-containing commercial fungicide formulation Azzurro ® on meristematic root cells of Allium cepa L. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 742(1–2):48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.11.014
Andrioli NB, Soloneski S, Larramendy ML, Mudry MD (2014) Induction of microtubule damage in Allium cepa meristematic cells by pharmaceutical formulations of thiabendazole and griseofulvin. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 772:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.06.009
Asharani PV, Wu YL, Gong Z, Valiyaveettil S (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish models. 255102. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/25/255102
Babu K, Sabesan G (2012) Effect of Nano-Silver on Cell Division and Mitotic Chromosomes: A Prefatory Siren. Int J Nanotechnol 2(2). https://doi.org/10.5580/10eb
Bahadar H, Maqbool F, Niaz K, Abdollahi M (2016) Toxicity of nanoparticles and an overview of current experimental models. Iran Biomed J 20(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.7508/ibj.2016.01.001
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S, Chistensen (2014) Linear mixed-effects models using “Eigen” and S4.
Baymiller M, Huang F, Rogelj S (2017) Rapid one-step synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the ubiquitous coenzyme NADH. Matters 8–11 https://doi.org/10.19185/matters.201705000007
Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, Sutherland DS, Autrup H (2012) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles-Nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol Lett 208(3):286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.11.002
Bianchi CL, Ardizzone S, Capperelletti G (2006) Nanocrystalline Oxides : Surfactants-Assisted Growth. Encyclopedia Nanosci Nanotechnol January 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1081/E-ENN-120042107
Boonstra J, Post JA (2004) Molecular events associated with reactive oxygen species and cell cycle progression in mammalian cells. Gene 337(SUPPL):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.04.032
Campo A, Samaniego R, Giménez-Abián JF, Giménez-Martín G, López-Sáez JF, Díaz de la Espina SM, De la Torre C (2003) G2 checkpoint targets late replicating DNA. Biol Cell 95(8):521–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biolcel.2003.07.002
Carlson C, Hussein SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112(43):13608–13619. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp712087m
Charrad M, Ghazzali N, Boiteau V, Niknafs A (2014) NbClust: an R package for determining the relevant number of clusters in a data set. J Stat Softw 61:1–36
Deepak V, Kalishwaralal K (2011) Metal Nanoparticles in Microbiology. In Metal Nanoparticles in Microbiology (pp. 17–35). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18312-6
Dietz KJ, Herth S (2011) Plant nanotoxicology. Trends Plant Sci 16(11):582–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2011.08.003
Donaldson K, Poland CA, Schins RPF (2010) Possible genotoxic mechanisms of nanoparticles: Criteria for improved test strategies. Nanotoxicology 4(4):414–420. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2010.482751
Durán N, Marcato PD, Durán M, Yadav A, Gade A, Rai M (2011) Mechanistic aspects in the biogenic synthesis of extracellular metal nanoparticles by peptides, bacteria, fungi, and plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(5):1609–1624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3249-8
Feizi H, Kamali M, Jafari L, Rezvani Moghaddam P (2013) Phytotoxicity and stimulatory impacts of nanosized and bulk titanium dioxide on fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill). Chemosphere 91(4):506–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.012
Fenech M, Kirsch-Volders M, Natarajan AT, Surralles J, Crott JW, Parry J, Norppa H, Eastmond DA, Tucker JD, Thomas P (2011) Molecular mechanisms of micronucleus, nucleoplasmic bridge and nuclear bud formation in mammalian and human cells. Mutagenesis 26(1):125–132. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geq052
Fernandes TCC, Mazzeo DEC, Marin-Morales MA (2007) Mechanism of micronuclei formation in polyploidizated cells of Allium cepa exposed to trifluralin herbicide. Pestic Biochem Physiol 88(3):252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.12.003
Fernández JG, Almeida CA, Fernández-Baldo MA, Felici E, Raba J, Sanz MI (2015) Development of nitrocellulose membrane filters impregnated with different biosynthesized silver nanoparticles applied to water purification. Talanta 146:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.060
Fernández JG, Fernández-Baldo MA, Berni E, Camí G, Durán N, Raba J, Sanz MI (2016) Production of silver nanoparticles using yeasts and evaluation of their antifungal activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Process Biochem 51(9):1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.05.021
Fiskesjö G (1985) The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 102(1):99–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1985.tb00471.x
Gao D, Zhou H, Wang J, Miao S, Yang F, Wang G, Wang J, Bao X (2015) Size-Dependent Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 over Pd Nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 137(13):4288–4291. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b00046
Ghosh Chaudhuri R, Paria S (2012) Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev 112(4):2373–2433. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100449n
Gonzalez L, Cundari E, Leyns K-V (2017) Towards a New Paradigm in Nano-Genotoxicology: Facing Complexity of Nanomaterials’ Cellular Interactions and Effects. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 121:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12698
Granger CL, Cyr RJ, Mineyuki Y, Anraku Y, Chuong SDX, Park NIl, Freeman MC, Mullen RT, Muench DG, Yoneda A, Akatsuka M, Hoshino H, Kumagai F, Hasezawa S, Sawin KE, Nurse P, Dhonukshe P, Gadella TWJ, Hotta T, Bezanilla M (2004) Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: A molecular definition. J Cell Biol 23(1):10615–10623. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600916
Grant WF (1982) Chromosome aberration assays in allium: A report of the US environmental protection agency gene-tox program. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 99(3):273–291
Gudikandula K, Vadapally P, Singara Charya MA (2017) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from white rot fungi: Their characterization and antibacterial studies. OpenNano 2(June):64–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onano.2017.07.002
Harrison XA (2014) Using observation-level randomeffects to model overdispersion in count data in ecology and evolution. PeerJ 2014(1). https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.616
Jaidev LR, Narasimh G (2010) Fungal mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf, B 81(2):430–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.07.033
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: History, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9(1):1050–1074. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.98
Jorge de Souza TA, Rosa Souz LR, Franchi LP (2019) Silver nanoparticles: An integrated view of green synthesis methods, transformation in the environment, and toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171(May 2018):691–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.095
Kandlikar M, Ramachandran G, Maynard A, Murdock B, Toscano WA (2007) Health risk assessment for nanoparticles: A case for using expert judgment. J Nanopart Res 9(1):137–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5859-2_14
Karami MS, De Lima R (2016) Nanoparticles cyto and genotoxicity in plants: Mechanisms and abnormalities. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 6(1):184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016a.08.003
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12(7):908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Khoshnamvand M, Huo C, Liu J (2019) Silver nanoparticles synthesized using Allium ampeloprasum L. leaf extract: Characterization and performance in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and antioxidant activity. J Mol Struct 1175:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.089
Kirsch-Volders M, Vanhauwaert A, Eichenlaub-Ritter U, Decordier I (2003) Indirect mechanisms of genotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 140–141:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00498-8
Kumari M, Khan S, Pakrashi S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2011) Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on root cells of Allium cepa. J Hazard Mater 190(1–3):613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.095
Kumari M, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2009) Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa. Sci Total Environ 407(19):5243–5246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.06.024
Kuppusamy P, Yusoff MM, Maniam GP, Govindan N (2016) Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications – An updated report. Saudi Pharm J 24(4):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2014.11.013
Laurent A, Nicco C, Chéreau C, Goulvestre C, Alexandre J, Alves A, Lévy E, Goldwasser F, Pani Y, Soubrane O, Weill B, Batteux F (2005) Controlling tumor growth by modulating endogenous production of reactive oxygen species. Can Res 65(3):948–956
Leme DM, Marin-Morales MA (2009) Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 682(1):71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.06.002
Liu WJ, Qian TT, Jiang H (2014) Bimetallic Fe nanoparticles: Recent advances in synthesis and application in catalytic elimination of environmental pollutants. Chem Eng J 236:448–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.062
Ma X, Geiser-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: Phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408(16):3053–3061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.031
Metz KM, Sanders SE, Pender JP, Dix MR, Hinds DT, Quinn SJ, Ward AD, Duffy P, Cullen RJ, Colavita PE (2015) Green Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles via Natural Extracts: The Biogenic Nanoparticle Corona and Its Effects on Reactivity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3(7):1610–1617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00304
Mishima M (2017) Chromosomal aberrations, clastogens vs aneugens. Frontiers in Bioscience - Scholar 9(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.2741/S468
Mohamed AA, Fouda A, Abdel-Rahman MA, Hassan SED, El-Gamal MS, Salem SS, Shaheen TI (2019) Fungal strain impacts the shape, bioactivity and multifunctional properties of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101103
Mohanta YK, Nayak D, Biswas K, Singdevsachan SK, Abd Allah EF, Hashem A, Alqarawi AA, Yadav D, Mohanta TK (2018) Silver nanoparticles synthesized using wild mushroom show potential antimicrobial activities against food borne pathogens. Molecules 23(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030655
Mukherjee P, Ahmad A, Mandal D, Senapati S, Sainkar SR, Khan MI, Parishcha R, Ajaykumar PV, Alam M, Kumar R, Sastry M (2001) 0152.NanoLett.2001,1,515.pdf
Nagaonkar D, Shende S, Rai M (2015) Biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles and its effect on actively dividing cells of mitosis in Allium cepa. Biotechnol Prog 31(2):557–565. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2040
Ortega FG, Fernández-Baldo MA, Fernández JG, Serrano MJ, Sanz MI, Diaz-Mochón JJ, Lorente JA, Raba J (2015) Study of antitumor activity in breast cell lines using silver nanoparticles produced by yeast. Int J Nanomed 10:2021–2031. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S75835
Pakrashi S, Jain N, Dalai S, Jayakumar J, Chandrasekaran PT, Raichur AM, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A. (2014). In vivo genotoxicity assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by Allium cepa root tip assay at high exposure concentrations. PLoS ONE 9(2). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087789
Park K, Park EJ, Chun IK, Choi K, Lee SH, Yoon J, Le BC (2011) Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in rats. Arch Pharmacal Res 34(1):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0118-z
Raskar SV, Laware SL (2014) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on cytology and seed germination in onion. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 3(2):467–473 (http://www.ijcmas.com/vol-3-2/S.V.RaskarandS.L.Laware.pdf)
Rejeski D (2011) Public Policy on the Technological Frontier. In The Growing Gap Between Emerging Technologies and Legal-Ethical Oversight (pp. 47–59) Springer Dordrech. 7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1356-7
Scherer MD, Sposito JCV, Falco WF, Grisolia AB, Andrade LHC, Lima SM, Machado G, Nascimento VA, Gonçalves DA, Wender H, Oliveira SL, Caires ARL (2019) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles on meristematic cells of Allium cepa roots: A close analysis of particle size dependence. Sci Total Environ 660:459–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.444
Schrand AM, Rahman MF, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Smith DA, Syed AF (2010) Metal-based nanoparticles and their toxicity assessment. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 2(5):544–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.103
Shaymurat T, Gu J, Xu C, Yang Z, Zhao Q, Liu Y, Liu Y (2012) Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles on garlic (Allium sativum L.): A morphological study. Nanotoxicology 6(3):241–248. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.570462
Siddiqi KS, ur Rahman A, Tajuddin, Husen A (2018) Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Activity Against Microbes. Nanoscale Res Lett, 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2532-3
Singh P, Kim YJ, Zhang D, Yang DC (2016) Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 34(7):588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.006
Singh RP, Ramarao P (2012) Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 213(2):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.07.009
Zhu H, Han J, Xiao JQ, Jin Y (2008) Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of manufactured iron oxide nanoparticles by pumpkin plants. J Environ Monit 10(6):713–717. https://doi.org/10.1039/b805998e
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina (grant UBACyT 20020170200367BA) and by the Universidad Nacional de San Luis, Argentina (grant PRICO 02–2716).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nancy B. Andrioli: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing-Reviewing and Editing, Visualization. Stephany Solano Mendoza: Investigation, methodology. Jorge G Fernandez: Resources, Investigation. María I Sanz Ferramola: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing-Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
(Not applicable).
Consent to participate
(Not applicable).
Consent for publication
(Not applicable).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beatriz Andrioli, N., Mendoza, G.S.S., Fernández, J.G. et al. Mitotic and chromosomal effects induced for biosynthesized nanoparticles from three mediators on Allium cepa root cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 66716–66727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20363-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20363-2