Abstract
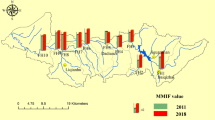
The aquatic ecological health status was focused on the Huai River Basin (HRB) from the aspects of water quantity, water quality, water ecology, river connectivity, and riparian habitat environment. Ten monitoring sections were set up in the middle and upper reaches of HRB, and 5 experiments of each section were conducted in July and December from 2012 to 2014. Thus, relevant data on the species, the density of phytoplankton, zooplankton and benthic animals, the concentration of water physicochemical variables, and riparian habitat quality were obtained. Eleven key impact factors were chosen using frequency statistics, theoretical analysis, and correlation analysis methods, forming the evaluation index system of aquatic ecological health. Then, the indicator weight value was determined by the combined weight method, and the health degree was evaluated by the comprehensive index method. On the whole, the aquatic ecological health degree of the upper sections (D1 ~ D3) of the Shaying River ranges from 0.334 to 0.927, which is generally in a “sub-healthy” state. The aquatic ecological health degree of the main section of the Huai River (D8 ~ D10) ranges from 0.362 to 0.777, which is in the “critical” or “sub-healthy” state. The Huaidian Sluice (D5) and Fuyang Sluice (D6) in the middle and lower reaches of the Shaying River had the worst aquatic ecological health. Its water ecological health range is 0.283–0.523, and most of them are under “sub-pathologic.” The research results have important theoretical and practical significance. They can enrich the evaluation theories and methods of river aquatic ecological health, help to grasp the aquatic ecological health status in HRB, and provide basic support for aquatic ecological protection and water pollution control in sluice-controlled rivers.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The main data have been reflected in the article. Please contact the author for detailed data.
References
Benítez-Mora A, Camargo JA (2014) Ecological responses of aquatic macrophytes and benthic macroinvertebrates to dams in the Henares River Basin (Central Spain). Hydrobiologia 728(1):167–178
Chen H, Zuo QT, Zhang YY (2017) Preliminary results of water quality assessment using phytoplankton and physicochemical approaches in the Huai River Basin China. Water Sci Technol 76(9):2554–2564
Chen H, Zuo QT, Zhang YY (2019) Impact factor analysis of aquatic species diversity in the Huai River Basin, China. Water Sci Technol-Water Supply 19(7):2061–2071
Chinese EPA (2002) Water and waste water monitoring and analysis method, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Kallis G, Butler D (2001) The EU water framework directive measures and implications. Water Policy 3(2):125–142
Kwang GA, Seok SP, Shin JY (2002) An evaluation of a river health using the index of biological integrity along with relations to chemical and habitat conditions. Environ Int 28:411–420
Ladson AR, White LJ, Doolan J, Finlayson B, Hart BT, Lake PS, Tilleard J (1999) Development and testing of an Index of Stream Condition for waterway management in Australia. Freshw Biol 41(2):453–468
Lin L, Wang FF, Chen H, Fang H, Zhang TY, Cao WZ (2021) Ecological health assessments of rivers with multiple dams based on the biological integrity of phytoplankton: A case study of North Creek of Jiulong River. Ecol Indic 121:106998
Liu CM, Liu XY (2008) Healthy river: essence and indicators. Acta Geogr Sin 63(7):683–692 (in Chinese)
Luo ZL, Zuo QT, Shao QX (2018) A new framework for assessing river ecosystem health with consideration of human srevice demand. Sci Total Environ 640–641:442–453
Ministry of Water Resources, P. R. China & National Bureau of Statistics, P. R. China (2013) Bulletin of First National Census for Water. China Water & Power Press, Beijing
Nikghalb S, Shokoohi A, Singh VP, Yu RH (2016) Ecological regime versus minimum environmental flow: comparison of results for a river in a semi Mediterranean region. Water Resour Manage 30(13):4969–4984
Rougier C, Pourriot R, Lamhoai T, Guiral D (2005) Ecological patterns of the rotifer communities in the Kaw River estuary (French Guiana), Estuarine. Coastal Shelf Sci 63:83–91
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:379–423
Sun J, Liu LY, Lin J, Lin BL, Zhao HP (2020) Vertical water renewal in a large estuary and implications for water quality. Sci Total Environ 710:135593
Suo LS (2005) Relationship between dam and gate with ecology. China Water Resour 16:5–7 (in Chinese)
Tao J, Sun XH, Cao Y, Ling MH (2022) Evaluation of water quality and its driving forces in the Shaying River Basin with the grey relational analysis based on combination weighting. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:18103–18115
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1(4):6–10
Tepe Y, Aydin H (2017) Water quality assessment of an urban water, Batlama Creek (Giresun), Turkey by applying multivariate statistical techniques. Fresenius Environ Bull 26:6413–6420
Terrado M, Sabater S, Chaplin-Kramer B, Mandle L, Ziv G, Acuña V (2016) Model development for the assessment of terrestrial and aquatic habitat quality in conservation planning. Sci Total Environ 540:63–70
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Taş B (2020) Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: a combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecological Indicators 113:105815
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Aydin H, Akbas A (2020b) Evaluation of surface water quality by multivariate statistical analyses and WQI: case of comlekci stream, (Giresun-Turkey). Fresenius Environ Bull 29(1):167–177
Villamagna AM, Murphy BR (2010) Ecological and socio-economic impacts of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): a review. Freshw Biol 55:282–298
Wang GS, Xia J (2010) Improvement of SWAT2000 modelling to assess the impact of dams and sluices on streamflow in the Huai River Basin of China. Hydrol Process 24(11):1455–1471
Wang L, Chen QW, Chen K, Liu X (2017) Establishment of target fishers for ecological flow in the main stream of Huaihe River. Acta Sci Circum 37(6):2379–2386 (in Chinese)
Wright JF, Sutcliffe DW, Furse MT (2000) Assessing the biological quality of fresh waters. RIVPACS and other techniques, Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside, England
Xia J, Zhao CS, Liu M, Wang GS, Zhang YY, Liu Y (2008) Impact assessment of dams & flood gates projects of Huaihe River on river ecosystem: a case study of the Bengbu Site. J Nat Resour 23(1):48–60
Yang T, Wang S, Li X, Wu T, Li L, Chen J (2018) River habitat assessment for ecological restoration of Wei River Basin China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(17):17077–17090
Zhang YY, Arthington AH, Bunn SE, Mackay S, Xia J, Kennard M (2012) Classification of flow regimes for environmental flow assessment in regulated rivers: the Huai River Basin China. River Res Appl 28(7):989–1005
Zhao CS, Shao NF, Yang ST, Ren H, Ge YR, Zhang ZS, Zhao Y, Yin X (2019) Integrated assessment of ecosystem health using multiple indicator species. Ecol Eng 130:157–168
Zuo QT, Chen H, Ming D, Zhang YY, Li DF (2015a) Experimental analysis of the impact of sluice regulation on water quality in the highly polluted Huai River Basin China. Environ Monit Assess 187(7):1–15
Zuo QT, Chen H, Zhang YY (2015b) Impact factors and health assessment of aquatic ecosystem in Upper and Middle Huai River Basin. J Hydraul Eng 46(9):1019–1027 (in Chinese)
Zuo QT, Chen H, Zhang YY, Dou M, Liu M (2017) Rotifers community structure analysis and water quality evaluation of upper and middle Huai River basin. Chinese J Environ Eng 11(1):165–173 (in Chinese)
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51779230, 41671024, 52109017, and 51909091), Scientific Research Project for High-level Talents of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (No. 40499), Key scientific research project of colleges and universities of Henan Province (Nos. 20A570003 and 18A570004), and Key R & D and extension projects in Henan Province (No. 182102310758).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Chen prepared article data, and contributed to preparing and writing the manuscript; Wen Li are mainly responsible for the language modification of articles; Shikui Liang, Qiting Zuo, and Yongyong Zhang conceived article frame structure, and modified article contents.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All listed authors have approved the manuscript before submission, including the names and order of authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, W., Zuo, Q. et al. Evaluation of aquatic ecological health of sluice-controlled rivers in Huai River Basin (China) using evaluation index system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 65128–65143 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20252-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20252-8