Abstract
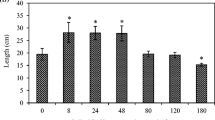
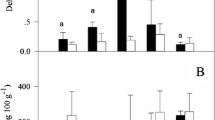
It has been well documented that polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) can be taken up from the environment by the plants and translocated into the shoots. However, the mechanisms underlying this process are poorly understood. Nelumbo nucifera L. (lotus) is a highly ornamental aquatic plant known to possess strong phytoremediation capability. In the present study, the association between phenanthrene (Phe) and nutrients, including nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), in lotus was investigated. Over 2 years, all eight lotus cultivars tested accumulated Phe to various degrees when grown in PAH-polluted sediment (0.46 mg/kg Phe). Cluster analysis showed N. nucifera 'Zhongguo Hong Beijing (ZHB)' was the one with the highest Phe levels in the leaves and petals in 2 years. The Phe concentrations in the tissues of 'ZHB' were 3.14 mg/kg and 1.63 mg/kg on average in the first and second year, respectively. Interestingly, 'ZHB' was also the cultivar with the lowest N and P levels considering 2 years and tissues. Hydroponic studies further revealed a negative association between the concentrations of Phe and those of N and P in the aerial tissues under 0.5 and 1.0 mg/L Phe treatments in 'ZHB'. Furthermore, the significant reductions of the roots number (72.6%), longest root length (75.8%), and petiolar height (34.6%) in 'ZHB' seedlings exposed to 1.0 mg/L Phe were observed, indicating that Phe retarded the growth of lotus. These results provide a new understanding of the accumulation of Phe in plants and the association with nutrients and enrich the basis of phytoremediation to the contaminated environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahammed GJ, Wang MM, Zhou YH, Xia XJ, Mao WH, Shi K, Yu JQ (2012) The growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant defense responses of five vegetable crops to phenanthrene stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.02.015
Alkio M, Tabuchi TM, Wang XC, Colón-Carmona A (2005) Stress responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Arabidopsis include growth inhibition and hypersensitive response-like symptoms. J Exp Bot 56:2983–2994. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri295
Bradstreet, (1954) Kjeldahl method for organic nitrogen. Anal Chem 26:185–187
Chen AQ, Hu J, Sun SB, Xu GH (2007) Conservation and divergence of both phosphate- and mycorrhiza-regulated physiological responses and expression patterns of phosphate transporters in solanaceous species. New Phytol 173:817–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01962.x
Desalme D, Binet P, Chiapusio G (2013) Challenges in tracing the fate and effects of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition in vascular plants. Environ Sci Technol 47:3967–3981. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304964b
Fan S, Liu H, Zheng G, Wang Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Liu X, Wan Y (2018) Differences in phytoaccumulation of organic pollutants in freshwater submerged and emergent plants. Environ Pollut 241:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.071
Gao YZ, Zhu LZ (2004) Plant uptake, accumulation and translocation of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils. Chemosphere 55:1169–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.037
Grandclement C, Seyssiecq I, Piram A, Wong-Wah-Chung P, Vanot G, Tiliacos N, Roche N, Doumenq P (2017) From the conventional biological wastewater treatment to hybrid processes, the evaluation of organic micropollutant removal: a review. Water Res 111:297–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.005
Han J, Liang Y, Zhao B, Wang Y, Xing F, Qin L (2019) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) geographical distribution in China and their source, risk assessment analysis. Environ Pollut 251:312–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.022
Houshani M, Salehi-Lisar SY, Motafakkerazad R, Movafeghi A (2019) Uptake and distribution of phenanthrene and pyrene in roots and shoots of maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:9938–9944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04371-3
Jiao XC, Xu FL, Dawson R, Chen SH, Tao S (2007) Adsorption and absorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to rice roots. Environ Pollut 148:230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.025
Keunen E, Schellingen K, Vangronsveldand J, Cuypers A (2016) Ethylene and metal stress: small molecule, big impact. Front Plant Sci 7:23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00023
Kummerová M, Zezulka S, Babula P, Váňová L (2013) Root response in Pisum sativum and Zea mays under fluoranthene stress: morphological and anatomical traits. Chemosphere 90:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.047
Lajayer BA, Moghadam NK, Maghsoodi MR, Ghorbanpour M, Kariman K (2019) Phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil, water and atmosphere using ornamental plants: mechanisms and efficiency improvement strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8468–8484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04241-y
Lavid N, Schwartz A, Yarden O, Tel-Or E (2001a) The involvement of polyphenols and peroxidase activities in heavy-metal accumulation by epidermal glands of the waterlily (Nymphaeaceae). Planta 212:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000400
Lavid N, Barkay Z, Tel-Or E (2001b) Accumulation of heavy metals in epidermal glands of the waterlily (Nymphaeaceae). Planta 212:313–322. https://doi.org/10.2307/23386117
Li CC, Huo SL, Yu ZQ, Xi BD, Yeager KM, He ZS, Ma CZ, Zhang JT, Wu FC (2017) National investigation of semi-volatile organic compounds (PAHs, OCPs, and PCBs) in lake sediments of China: occurrence, spatial variation and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 579:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.097
Liu AM, Tian DK, Xiang YC, Mo HB (2016) Effects of biochar on growth of Asian lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) and cadmium uptake in artificially cadmium-polluted water. Sci Hortic 198:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.11.030
Liu Y, Beckingham B, Ruegner H, Li Z, Ma LM, Schwientek M, Xie H, Zhao JF, Grathwohl P (2013) Comparison of sedimentary PAHs in the rivers of Ammer (Germany) and Liangtan (China): differences between early- and newly-industrialized countries. Environ Sci Technol 47:701–709. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3031566
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-473542-2.X5000-7
Meng Y, Liu X, Lu S, Zhang T, Jin B, Wang Q, Tang Z, Liu Y, Guo X, Zhou J, Xi B (2019) A review on occurrence and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes of China. Sci Total Environ 651:2497–2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.162
Mishra V, Pathak V, Tripathi B (2009) Accumulation of cadmium and copper from aqueous solutions using Indian lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Ambio 38:110–112. https://doi.org/10.1579/0044-7447-38.2.110
Mojiri A, Zhou JL, Ohashi A, Ozaki N, Kindaichi T (2019) Comprehensive review of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water sources, their effects and treatments. Sci Total Environ 696:133971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133971
Su YH, Zhu YG (2008) Uptake of selected PAHs from contaminated soils by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa) and influence of rhizosphere on PAH distribution. Environ Pollut 155:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.008
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xu Y, Wang L, Liang X (2011) Phytoremediation for co-contaminated soils of benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) and heavy metals using ornamental plant Tagetes patula. J Hazard Mater 186:2075–2082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.116
Sun YB, Zhou QX (2016) Uptake and translocation of benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) in two ornamental plants and dissipation in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 124:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.037
Shen Y, Gu RC, Sheng Y, Zeng ND, Zhan XH (2020) Acropetal translocation of phenanthrene in wheat seedlings: xylem or phloem pathway? Environ Pollut 260:114055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114055
Tao S, Jiao XC, Chen SH, Liu WX, Coveney RM, Zhu LZ, Luo YM (2006) Accumulation and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rice (Oryza sativa). Environ Pollut 140:406–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.004
Vajpayee P, Sharma SC, Tripathi RD, Rai UN, Yunus M (1999) Bioaccumulation of chromium and toxicity to photosynthetic pigments, nitrate reductase activity and protein content of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Chemosphere 39:2159–2169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00095-8
Váňová L, Kummerová M, Klemš M, Zezulka S (2009) Fluoranthene influences endogenous abscisic acid level and primary photosynthetic processes in pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants in vitro. Plant Growth Regul 57:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9318-z
Van Metre PC, Mahler BJ (2010) Contribution of PAHs from coal-tar pavement sealcoat and other sources to 40 US lakes. Sci Total Environ 409:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.014
Wang XW, Jain A, Huang X, Lan XX, Xu L, Zhao GM, Cong X, Zhang ZT, Fan XR, Hu F (2021) Reducing phenanthrene uptake and translocation, and accumulation in the seeds by overexpressing OsNRT2.3b in rice. Sci Total Environ 761:143690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143690
Wang YJ, Yuan M, Li ZX, Niu YQ, Jin QJ, Zhu B, Xu YC (2020) Effects of ethylene biosynthesis and signaling on oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system in Nelumbo nucifera G. under cadmium exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Re. 32:40156–40170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09918-3
Wieczorek JK, Wieczorek ZJ (2007) Phytotoxicity and accumulation of anthracene applied to the foliageand sandy substrate in lettuce and radish plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.10.002
Wild E, Dent J, Thomas GO, Jones KC (2005) Direct observation of organic contaminant uptake, storage, and metabolism within plant roots. Environ Sci Technol 39:3695–3702. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048136a
Wu FY, Tian K, Wang JF, Bao HY, Luo WQ, Zhang H, Hong HC (2019) Accumulation and translocation of phenanthrene, anthracene and pyrene in winter wheat affected by soil water content. Ecotoxicol Enviro Sa 183:109567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109567
Xiao N, Liu R, Jin C, Dai Y (2015) Efficiency of five ornamental plant species in the phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-contaminated soil. Ecol Eng 75:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.12.008
Xu X, Zhou Y, Han R, Song K, Zhou X, Wang G, Wang Q (2019) Eutrophication triggers the shift of nutrient absorption pathway of submerged macrophytes: implications for the phytoremediation of eutrophic waters. J Environ Manage 239:376–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.069
Yang QQ, Lu SK, Wang HJ, Li JF, Shen Y, Zhan XH (2016) Interaction of uptake and acropetal translocation between phenanthrene and phosphate in wheat roots. Asian J Ecotoxicol 11: 219–225 (in Chinese) https://doi.org/10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150922002
Zhan XH, Yuan JH, Yue L, Xu GH, Hu B, Xu RK (2015) Response of uptake and translocation of phenanthrene to nitrogen form in lettuce and wheat seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6280–6287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3834-3
Zhan XH, Ma HL, Zhou LX, Liang JR, Jiang TH, Xu GH (2010) Accumulation of phenanthrene by roots of intact wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings: passive or active uptake? BMC Plant Biol 10:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-52
Zhan XH, Zhu MD, Shen Y, Yue L, Li JF, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Xu GH (2018) Apoplastic and symplastic uptake of phenanthrene in wheat roots. Environ Pollut 233:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.056
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Tianheyuan Lotus Research Base for kindly providing all the lotus materials.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42107428, 31772346, 31971710, 32071829), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFD0900702), a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and an International Workshop on the nexus of food-energy-water (FEWS) systems, USA-China (20191J006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW: Methodology, performance of the experiments, data analysis, writing — original draft. YW, XZ1, BC, NK: Performance of the experiments, data analysis. LS, XZ2: Literature search, writing — review and editing. YX: Conceptualization, supervision, project administration, resources, writing — review and editing. FH: Conceptualization, supervision, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, X. et al. The association between phenanthrene and nutrients uptake in lotus cultivar 'Zhongguo Hong Beijing'. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 62272–62280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19996-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19996-0