Abstract
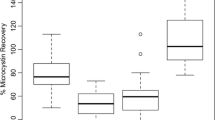
In this study, the contents of microcystin-LR (MC-LR) of Microcystis aeruginosa cultures in the laboratory and natural water samples from the Huangpu River in different seasons were detected through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), respectively. Excellent correlation between the two methods was obtained (R2 > 0.99). ELISA was a reliable and simple method with high reproducibility (coefficient of variation < 25%) and satisfactory recovery for the monitoring of low levels of MC-LR. MC-LR concentrations in Huangpu River varied with the seasonal variation, which peaked in August with the temperature over 30 °C and then gradually declined with the decreasing temperature after August. The highest MC-LR concentration in the Huangpu River was below the WHO drinking water quality standard (1 µg/L). These results indicated that warm temperature accelerated the MC-LR synthesis and release, and it is necessary to regularly monitor the MC-LR levels, especially during the high algae period in summer. ELISA can be applied to detect the low levels of MC-LR in the field without complex treatment, avoiding the samples from denaturation and degradation during the transportation. Hence, ELISA is a better alternative of HPLC when HPLC is unavailable, especially when rapid testing is required in routine MC-LR analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abe T, Lawson T, Weyers JDB et al (1996) Microcystin-LR inhibits photosynthesis of Phaseolus vulgaris primary leaves: Implications for current spray irrigation practice. New Phytol 133:651–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01934.x
Babica P, Kohoutek J, Bláha L et al (2006) Evaluation of extraction approaches linked to ELISA and HPLC for analyses of microcystin-LR, -RR and -YR in freshwater sediments with different organic material contents. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:1545–1551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0545-8
Budzyńska A, Rosińska J, Pełechata A et al (2019) Environmental factors driving the occurrence of the invasive cyanobacterium Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides (Nostocales) in temperate lakes. Sci Total Environ 650:1338–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.144
Campas M, Marty JL (2007) Highly sensitive amperometric immunosensors for microcystin detection in algae. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1034–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.04.025
Carmichael WW, Boyer GL (2016) Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 54:194–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.02.002
Corbel S, Mougin C, Bouaïcha N et al (2014) Cyanobacterial toxins: modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 96:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.056
Chik AHS, Giler MB, Servos M et al (2021) Comparison of approaches to quantify SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater using RT-qPCR: results and implications from a collaborative inter-laboratory study in Canada. J Environ Sci 107:218–229
Davis TW, Berry DL, Boyer GL et al (2009) The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 8:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2009.02.004
de Figueiredo DR, Azeiteiro UM, Esteves SM et al (2004) Microcystin-producing blooms - a serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.04.006
Foss AJ, Miles CO, Samdal IA et al (2018) Analysis of free and metabolized microcystins in samples following a bird mortality event. Harmful Algae 80:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2018.10.006
Gkelis S, Papadimitriou T, Zaoutsos N et al (2014) Anthropogenic and climate-induced change favors toxic cyanobacteria blooms: Evidence from monitoring a highly eutrophic, urban Mediterranean lake. Harmful Algae 39:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2014.09.002
Gupta N, Pant SC, Vijayaraghavan R et al (2003) Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 188:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00112-4
Gurbuz F, Metcalf JS, Karahan AG et al (2009) Analysis of dissolved microcystins in surface water samples from Kovada Lake, Turkey. Sci Total Environ 407:4038–4046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.02.039
Harke MJ, Steffen MM, Gobler CJ et al (2016) A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 54:4–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2015.12.007
Imai H, Chang KH, Kusaba M et al (2009) Temperature-dependent dominance of Microcystis (Cyanophyceae) species: M. aeruginosa and M. wesenbergii. J Plankton Res 31:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbn110
Jasionek G, Zhdanov A, John D et al (2010) Mitochondrial toxicity of microcystin-LR on cultured cells: application to the analysis of contaminated water samples. Environ Sci Technol 44:2535–2541. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903157h
Jiang Y, Ji B, Wong RNS et al (2008) Statistical study on the effects of environmental factors on the growth and microcystins production of bloom-forming cyanobacterium - Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 7:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2007.05.012
Johnk KD, Huisman J, Sharples J, Sommeijer B, Visser PM, Stroom JM (2008) Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Glob Change Biol 14(3):495–512
Lawton LA, Edwards C, Codd GA (1994) Extraction and high-performance liquid-chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst 119(7):1525–1530
Li X, Liu Y, Song L et al (2003) Responses of antioxidant systems in the hepatocytes of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) to the toxicity of microcystin-LR. Toxicon 42:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-0101(03)00104-1
Liu L, Xing C, Yan H et al (2014) Development of an ELISA and immunochromatographic strip for highly sensitive detection of microcystin-LR. Sensors 14:14672–14685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140814672
Mantzouki E, Lürling M, Fastner J et al (2018) Temperature effects explain continental scale distribution of cyanobacterial toxins. Toxins 10:24. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10040156
Máthé C, Beyer D, Erdodi F et al (2009) Microcystin-LR induces abnormal root development by altering microtubule organization in tissue-cultured common reed (Phragmites australis) plantlets. Aquat Toxicol 92:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.02.005
McElhiney J, Lawton LA (2005) Detection of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.06.002
McElhiney J, Lawton LA, Carlo L (2001) Investigations into the inhibitory effects of microcystins on plant growth, and the toxicity of plant tissues following exposure. Toxicon 39:1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-0101(01)00100-3
Merel S, Walker D, Chicana R et al (2013) State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ Int 59:303–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.06.013
Mitrovic SM, Allis O, Furey A (2005) Bioaccumulation and harmful effects of microcystin-LR in the aquatic plants Lemna minor and Wolffia arrhiza and the filamentous alga Chladophora fracta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 61:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.11.003
Mohamed ZA, Deyab MA, Abou-Dobara MI et al (2015) Occurrence of cyanobacteria and microcystin toxins in raw and treated waters of the Nile River, Egypt: implication for water treatment and human health. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11716–11727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4420-z
Mowe MAD, Porojan C, Abbas F et al (2015) Rising temperatures may increase growth rates and microcystin production in tropical Microcystis species. Harmful Algae 50:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2015.10.011
Nagata S, Tsutsumi T, Hasegawa A et al (1997) Enzyme immunoassay for direct determination of microcystins in environmental water. J AOAC Int 80:408–417
Pouria S, de Andrade A, Barbosa J et al (1998) Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 352:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(97)12285-1
Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G et al (2010) A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Environ Manage 45:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-009-9393-6
Rapala J, Erkomaa K, Kukkonen J et al (2002) Detection of microcystins with protein phosphatase inhibition assay, high-performance liquid chromatography-UV detection and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - Comparison of methods. Anal Chim Acta 466:213–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2670(02)00588-3
Rivasseau C, Racaud P, Deguin A et al (1999) Evaluation of an ELISA kit for the monitoring of microcystins (cyanobacterial toxins) in water and algae environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 33:1520–1527. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980460g
Samdal IA, Ballot A, Løvberg KE et al (2014) Multihapten approach leading to a sensitive ELISA with broad cross-reactivity to microcystins and nodularin. Environ Sci Technol 48:8035–8043. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5012675
Santos A, Rachid C, Pacheco AB et al (2020) Biotic and abiotic factors affect microcystin-LR concentrations in water/sediment interface. Microbiol Res 236:126452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126452
Su X, Xue Q, Steinman AD et al (2015) Spatiotemporal dynamics of microcystin variants and relationships with environmental parameters in Lake Taihu, China. Toxins 7:3224–3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083224
Tsuji K, Watanuki T, Kondo F et al (1994) Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria - effect of light on decomposition and isomerization. Environ Sci Technol 28:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00050a024
Umehara A, Tsutsumi H, Takahashi T (2012) Blooming of Microcystis aeruginosa in the reservoir of the reclaimed land and discharge of microcystins to Isahaya Bay (Japan). Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3257–3267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0835-y
Vezie C, Brient L, Sivonen K et al (1998) Variation of microcystin content of cyanobacterial blooms and isolated strains in Lake Grand-Lieu (France). Microb Ecol 35:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002489900067
Wu Y, Li L, Gan N et al (2014) Seasonal dynamics of water bloom-forming Microcystis morphospecies and the associated extracellular microcystin concentrations in large, shallow, eutrophic Dianchi Lake. J Environ Sci 26:1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.06.031
Wan X, Steinman AD, Gu Y et al (2020) Occurrence and risk assessment of microcystin and its relationship with environmental factors in lakes of the eastern plain ecoregion. China Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(36):45095–45107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10384-0
Ye J, Guan Y, Wu L et al (2020) Effects of glyphosate on microcystin-LR production and release fromMicrocystis aeruginosaat different temperatures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(33):41961–41969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10185-5
Zimba PV, Khoo L, Gaunt PS, Brittain S, Carmichael WW (2001) Confirmation of catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), mortality from Microcystis toxins. J Fish Dis 24(1):41–47
Zurawell RW, Chen H, Burke JM et al (2005) Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J Toxicol Environ Health - B: Crit Rev 8:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400590889412
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21307082), and the project of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China (18ZR1438000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. H. carried out the HPLC and ELISA detection and drafted the manuscript. J. C. took the water samples from Huangpu River and conducted the sample pre-treatment. L. W. participated in the HPLC detection. X. Y. participated in the design of the study and participated in the ELISA detection. J. Y. conceived of the study, designed the study, and helped to draft the manuscript. Y. L. developed the concept of this study in discussion. Y. Z. and F. T. performed the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, S., Chen, J., Wu, L. et al. The monthly variation tendency of microcystin-LR levels in the Huangpu River (China) by applications of ELISA and HPLC. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 56876–56884 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19791-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19791-x