Abstract
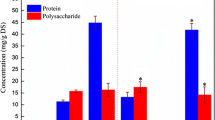
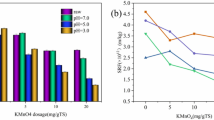
The water in sludge is trapped within the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) with gelatinous structure, greatly challenging the sludge deep dewatering. In this paper, the effect of the EPS viscoelasticity and the structural characteristics of sludge flocs on water distribution was revealed to provide a highly efficient approach in research on sludge dewatering. After biological, and physical method conditioning, the change of viscoelasticity and sludge network structure before/after EPS extraction was comprehensively explored, together with the sludge dewaterability and water distribution. The results suggested the proportion of capillary water and adsorption water carried in soluble EPS (S-EPS) was 59.17% and 40.83%, and that in tightly bound EPS (TB-EPS) was 54.77% and 45.23%, respectively. By contrast, the capillary water in loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS) accounted for as high as 99.99%. In comparison with raw sludge, adsorption water proportion in TB-EPS and S-EPS was reduced after lysozyme (LZM) or freezing-thaw conditioning, which was ascribed to reduction of EPS viscosity and the weakness of water adsorption capacity. Additionally, the sludge yield stress (τy) value first reduced and then increased with the extraction of EPS. Meanwhile, the consistency coefficient (k) also decreased from 4.23 Pa·sn to 0.006 Pa·sn and then slightly increased after LZM conditioning. This observation indicated the sludge system became sensitive to shearing, and its network structural strength as well as colloid elasticity first weakened and then slightly strengthened. In addition, after LZM or freezing-thaw conditioning, the sludge particle size significantly increased after TB-EPS extraction, while the sludge particle more easily absorbed water molecules, thereby increasing adsorption water and capillary water within the sludge flocs. This phenomenon also resulted in an increasing trend of capillary suction time (CST) after TB-EPS extraction, indicating the deterioration of sludge filtration performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai H, Zhu R, An H, Zhou G, Huang H, Ren H, Zhang Y (2018) Influence of wastewater sludge properties on the performance of electro-osmosis dewatering Environ Technol 0:1–11
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cai C, Liu H, Wang M (2017) Characterization of antibiotic mycelial residue (AMR) dewatering performance with microwave treatment. Chemosphere 174:20–27
Carrasco M, Gao W (2019) Sludge particle size and correlation with soluble organic matter and conditioning characteristics after freezing treatments. Water Air Soil Poll 230:1–9
Chakraborti RK, Gardner KH, Atkinson JF, Benschoten JE (2003) Changes in fractal dimension during aggregation. Water Res 37:873–883
Chen Z, Zhang WD, Wang MT, Bai R, Yu D (2016) Enhancement of waste activated sludge dewaterability using calcium peroxide pre-oxidation and chemical re-flocculation. Water Res 103:170–181
Chen L, Xiong Q, Li H, Hou H, Zhou M (2020) Enhancement of the sewage sludge dewaterability by using ethanol and Fe(III)-rice husk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:8696–8706
Chen Y, Li XH, W ZZ, Li F, Xie JH, Lin ZL, Xu ZH, Liu BZ, Li X, Zheng H, (2021) Research on a new cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) with a cationic microblock structure and its enhanced effect on sludge condition and dewatering. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:51865–51878
Eshtiaghi N, Markis F, Yap SD, Baudez JC, Slatter P (2013) Rheological characterization of municipal sludge: a review. Water Res 475:493–551
Farno E, Baudez JC, Parthasarathy R, Eshtiaghi N (2016) The viscoelastic characterization of thermally-treated waste activated sludge. Chem Eng J 304:362–368
Guo X, Liu J, Xiao B (2014) Evaluation of the damage of cell wall and cell membrane for various extracellular polymeric substance extractions of activated sludge. J Biotechnol 188:130–135
He DQ, Wang LF, Jiang H, Yu HQ (2015) A Fenton-Like Process for the Enhanced Activated Sludge Dewatering. Chem Eng J 272:128–134
Hui K, Song L, Yin Z, Song H, Wang Z, Gao W, Li X (2021) Freeze–thaw combined with activated carbon improves electrochemical dewaterability of sludge: analysis of sludge floc structure and dewatering mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-261233/v1
Li XY, Yang SF (2007) Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res 41:1022–1030
Li Y, Yuan X, Wu Z, Wang H, Xiao Z, Wu Y, Chen X, Zeng G (2016) Enhancing the Sludge Dewaterability by Electrolysis/Electrocoagulation Combined with Zero-Valent Iron Activated Persulfate Process. Chem Eng J 303:636–645
Liao BQ, Allen DG, Droppo IG, Leppard GG, Liss SN (2001) Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res 35:339–350
Lin F, Zhu X, Li J, Yu P, Luo Y, Liu M (2019) Effect of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) conditioned by combined lysozyme and cationic polyacrylamide on the dewatering performance of activated sludge. Chemosphere 235:679–689
Lin F, Li JG, Chai XS, Zhang ZB, Liu M (2020) Determination of Water Distribution in Sludge by A Multiple Headspace Extraction Analytical Technique. J Chromatogr A 1628:461449
Lin F, Li J, Liu M, Yu P, Zhu X (2020) New insights into the effect of extracellular polymeric substance on the sludge dewaterability based on interaction energy and viscoelastic acoustic response analysis. Chemosphere 261:127929
Liu H, Yang J, Zhu N, Zhang H, Li Y, He S, Yang C, Yao H (2013) A comprehensive insight into the combined effects of Fenton’s reagent and skeleton builders on sludge deep dewatering performance. J Hazard Mater 258–259:144–150
Liu J, Yu D, Zhang J, Yang M, Wang Y, Wei Y, Tong J (2016) Rheological properties of sewage sludge during enhanced anaerobic digestion with microwave-H2O2 pretreatment. Water Res 98:98–108
Mahmoud A, Olivier J, Vaxelaire J, Hoadley A (2011) Electro-dewatering of wastewater sludge: Influence of the operating conditions and their interactions effects. Water Res 45:2795–2810
Masihi H, Gholikandi GB (2018) Employing Electrochemical-Fenton process for conditioning and dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge: A novel approach. Water Res 144:373–382
Niu M, Zhang W, Wang D, Chen Y, Chen R (2013) Correlation of physicochemical properties and sludge dewaterability under chemical conditioning using inorganic coagulants. Bioresour Technol 144:337–343
Poxon TL, Darby JL (1997) Extracellular polyanions in digested sludge: Measurement and relationship to sludge dewaterability. Water Res 31:749–758
Ramachandra RH, Devatha CP (2020) Experimental investigation on sludge dewatering using granulated blast furnace slag as skeleton material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:11870–11881
Raunkjær K, Hvitved JT, Nielsen PH (1994) Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res 28:251–262
Sakohara S, Ochiai E, Kusaka T (2007) Dewatering of activated sludge by thermosensitive polymers. Sep Purif Technol 56:296–302
Seyssiecq I, Ferrasse JH, Roche N (2003) State-of-the-art: rheological characterization of wastewater treatment sludge. Biochem Eng J 16:41–56
Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Li XY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Biotechnol Adv 28:882–894
Suzuki M, Tsuge S, Takeuchi T (1970) Gas chromatographic estimation of occluded solvents in adhesive tape by periodic introduction method. Anal Chem 42:1705–1708
Vaxelaire J, Cezac P (2004) Moisture distribution in activated sludges: a review. Water Res 38:2215–2230
Wang BB, Liu XT, Chen JM, Peng DC, He F (2017a) Composition and functional group characterization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge: the impacts of polymerization degree of proteinaceous substrates. Water Res 129:133–142
Wang HF, Ma YJ, Wang HJ, Hu H, Zeng RJ (2017b) Applying rheological analysis to better understand the mechanism of acid conditioning on activated sludge dewatering. Water Res 122:398–406
Wang L, Li A, Chang Y (2017c) Relationship between enhanced dewaterability and structural properties of hydrothermal sludge after hydrothermal treatment of excess sludge. Water Res 112:72–82
Wang Z, Wang Y, Yu C, Zhao Y, Gao B (2018) The removal of silver nanoparticle by titanium tetrachloride and modified sodium alginate composite coagulants: floc properties, membrane fouling, and floc recycle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:21058–21069
Wu B, Zhou M, Dai XH, Chai X (2018) Mechanism insights into bio-floc bound water transformation based on synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography and viscoelastic acoustic response analysis. Water Res 142:480–489
Xiao K, Chen Y, Jiang X, Tyagi VK, Zhou Y (2016) Characterization of key organic compounds affecting sludge dewaterability during ultrasonication and acidification treatments. Water Res 105:470–478
Xiao J, Ge DD, Yuan HP, Zhu NW (2020) Waste activated sludge conditioning in a new Fe2+/persulfate/tannic acid process: Effectiveness and optimization study to enhance dewaterability. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103785
Xie S, Yu G, Li C, You F, Li J, Tian R, Wang Y (2019) Dewaterability enhancement and heavy metals immobilization by pig manure biochar addition during hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16537–16547
Ying W, Yang F, Bick A, Oron G, Herzberg M (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in a hybrid growth membrane bioreactor (HG-MBR): viscoelastic and adherence characteristics. Environ Sci Technol 44:8636–8643
You G, Wang P, Hou J, Wang C, Xu Y, Miao L, Lv B, Yang Y, Liu Z, Zhang F (2017) Insights into the short-term effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on sludge dewatering and related mechanism. Water Res 118:93–103
You G, Wang P, Hou J, Wang C, Miao L, Xu Y, Feng T (2018) Influence of CeO2 nanoparticles on viscoelastic properties of sludge: role of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ Res 167:34–41
Zhang SX, Chai XS, He L (2016) Accurate determination of fiber water retaining capability at process conditions by headspace gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1464:50–54
Zhang W, Dong B, Dai X (2019) Mechanism analysis to improve sludge dewaterability during anaerobic digestion based on moisture distribution. Chemosphere 227:247–255
Funding
The current study was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2016A020221011).
Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province,2016A020221011,Bingyun Li
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made contributions to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were carried out by FL and BL. The first draft of the manuscript was completed by FL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The final manuscript was read and approved by all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or explored during the current work are contained in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, F., Li, B. Changes of network structure and water distribution in sludge with the stratified extraction of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 48648–48660 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19075-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19075-4