Abstract
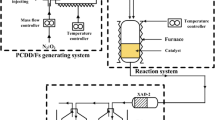
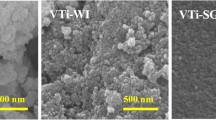
In this work, titania supported catalysts (V-W/Ti) with different vanadium-tungsten contents were prepared and evaluated in the catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene, which was used as the model compound of dioxins. The results showed that V2O5 is the main active component for chlorobenzene oxidation, and doping of WO3 affects the valence distributions of vanadium, contributing a bimetallic synergistic effect. The catalysts were investigated by XRD, SEM–EDS mapping, Raman, and XPS, and the changes in V element valence state and chlorine content on fresh and used catalysts were observed by XPS. Moreover, in situ FTIR studies and chlorine balance were also conducted, the addition of WO3 is helpful to the breakage of C–Cl, and a reaction mechanism for the catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene was proposed. 3 V-5 W/Ti catalyst with better catalytic activity was selected for catalytic oxidation of PCDD/Fs using a lab scale PCDD/Fs generating and decomposing system. The degradation efficiency was 66.5% at 200 °C and 62.2% at 300 °C, which indicated that the low reaction temperature of 200 °C was conducive to the catalytic degradation of PCDDs, while the high temperature of 300 °C was facilitated the degradation of PCDFs.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and materials
All data and materials generated or analyzed during this study were included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bell JG, Zhao XB, Uygur Y, Thomas KM (2011) Adsorption of chloroaromatic models for dioxins on porous carbons: the influence of adsorbate structure and surface functional groups on surface interactions and adsorption kinetics. J Phys Chem C 115:2776–2789. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1099893
Bist HD, Sarin VN, Ojha A, Jain YS (1970) The 2699 Å electronic band system of chlorobenzene-the in-plane vibrational modes in the excited state. Appl Spectrosc 24:292–294
Chang SH, Chi KH, Young CW, Hong BZ, Chang MB (2009) Effect of fly ash on catalytic removal of gaseous dioxins over V2O5-WO3 catalyst of a sinter plant. Environ Sci Technol 43:7523–7530. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901647t
Chen ZL, Lin XQ, Lu SY, Li XD, Yan JH (2019) Suppressing formation pathway of PCDD/Fs by S-N-containing compound in full-scale municipal solid waste incinerators. Chem Eng J 359:1391–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.039
Crihan D, Knapp M, Zweidinger S, Lundgren E, Weststrate CJ, Andersen JN, Seitsonen AP, Over H (2008) Stable deacon process for HCl oxidation over RuO2. Angew Chem 47:2131–2134. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200705124
De Jong V, Cieplik MK, Louw R (2004) Formation of dioxins in the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene and a micropollutant-like mixture on Pt/γ-Al2O3. Environ Sci Technol 38:5217–5223. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034820y
Demond A, Franzblau A, Garabrant D, Jiang X, Adriaens P, Chen Q, Gillespie B, Hao W, Hong B, Jolliet O, Lepkowski J (2012) Human exposure from dioxins in soil. Environ Sci Technol 46:1296–1302. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2022363
Fiedler H, Hutzinger O, Lau C, Cikryt P, Hosseinpour J (1995) Case study of a highly dioxin contaminated sports field: environmental risk assessment and human exposure. J Hazard Mater 43:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3894(95)00039-W
Fujimori T, Nishimoto Y, Shiota K, Takaoka M (2014) Contrasting effects of sulfur dioxide on cupric oxide and chloride during thermochemical formation of chlorinated aromatics. Environ Sci Technol 48:13644–13651. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503679c
Fujimori T, Nakamura M, Takaoka M, Shiota K, Kitajima Y (2016) Synergetic inhibition of thermochemical formation of chlorinated aromatics by sulfur and nitrogen derived from thiourea: multielement characterizations. J Hazard Mater 311:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.054
Goemans M, Clarysse P, Joannès J, De Clercq P, Lenaerts S, Matthys K, Boels K (2003) Catalytic NOx reduction with simultaneous dioxin and furan oxidation. Chemosphere 50:489–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00554-4
Hashimoto Y, Uemichi Y, Ayame A (2005) Low-temperature hydrodechlorination mechanism of chlorobenzenes over platinum-supported and palladium-supported alumina catalysts. Appl Catal A 287:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2005.03.039
Hsu WT, Hung PC, Chang SH, Young CW, Chen CL, Li HW, Pan KL, Chang MB (2018) Catalytic conversion of multipollutants (Hg0/NO/Dioxin) with V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:15195–15205. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b02804
Hung PC, Chang SH, Lin SH, Buekens A, Chang MB (2014) Pilot tests on the catalytic filtration of dioxins. Environ Sci Technol 48:3995–4001. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404926g
Jaegers NR, Lai JK, He Y, Walter E, Dixon DA, Vasiliu M, Chen Y, Wang CM, Hu MY, Mueller KT, Wachs IE, Wang Y, Hu JZ (2019) Tungsten oxide-promotion mechanism for supported V2O5/TiO2 catalysts during NOx abatement: structural effects revealed by 51VMAS NMR. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:12609–12616. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201904503
Kong M, Liu QC, Jiang LJ, Tong W, Yang J, Ren S, Li JL, Tian YM (2019) K+ deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: effect of vanadium content. Chem Eng J 370:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.156
Lavric ED, Konnov AA, Ruyck JD (2005) Surrogate compounds for dioxins in incineration. A Review Waste Manag 25:755–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2004.12.026
Li QQ, Li LW, Su GJ, Huang XC, Zhao YH, Li BK, Miao X, Zheng MH (2016) Synergetic inhibition of PCDD/F formation from pentachlorophenol by mixtures of urea and calcium oxide. J Hazard Mater 317:394–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.090
Liu ZG, Wall JC, Barge P, Dettmann ME, Ottinger NA (2011) Investigation of PCDD/F emissions from mobile source diesel engines: impact of copper zeolite SCR catalysts and exhaust aftertreatment configurations. Environ Sci Technol 45:2965–2972. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103933e
Liu XL, Wang J, Wang X, Zhu TY (2015) Simultaneous removal of PCDD/Fs and NOx from the flue gas of a municipal solid waste incinerator with a pilot plant. Chemosphere 133:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.009
Liu XL, Chen L, Zhu TY, Ning RL (2019) Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over noble metals (Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh) and the distributions of polychlorinated by-products. J Hazard Mater 363:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.074
Lomnicki S, Lichtenberger J, Xu Z, Waters M, Kosman J, Amiridis MD (2003) Catalytic oxidation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol over vanadia/titania-based catalysts. Appl Catal B 46:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00215-7
Long YP, Su YT, Xue YH, Wu ZB, Weng XL (2021) V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst for efficient synergistic control of NOx and chlorinated organics: insights into the arsenic effect. Environ Sci Technol 55:9317–9325. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c02636
Lu JY, Zhou ZY, Zhang HZ, Yang Z (2019) Influenced factors study and evaluation for SO2/SO3 conversion rate in SCR process. Fuel 245:528–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.02.077
Ma HT, Du N, Lin XY, Liu CF, Zhang JY, Miao ZZ (2018) Inhibition of element sulfur and calcium oxide on the formation of PCDD/Fs during co-combustion experiment of municipal solid waste. Sci Total Environ 633:1263–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.282
Okumura M, Akita T, Haruta M, Wang X, Kajikawa O, Okada O (2003) Multi-component noble metal catalysts prepared by sequential deposition precipitation for low temperature decomposition of dioxin. Appl Catal B 41:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00200-X
Peng YQ, Lu SY, Li XD, Yan JH, Cen KF (2020) Formation, measurement, and control of dioxins from the incineration of municipal solid wastes: recent advances and perspectives. Energy Fuels 34:13247–13267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c02446
Randrianandraina J, Deroche I, Bullot L, Stephan R, Hanf M-C, Chaplais G, Daou TJ, Simon-Masseron A, Patarin J, Sonnet P (2018) Adsorption of polychlorinated aromatics in EMT-type zeolites: a combined experimental-simulation approach. J Phys Chem C 122:12731–12741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b02115
Rordorf BF (1989) Prediction of vapor pressures, boiling points and enthalpies of fusion for twenty-nine halogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and fifty-five dibenzofurans by a vapor pressure correlation method. Chemosphere 18:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(89)90196-3
Sun Q, Fu YC, Liu JW, Auroux A, Shen JY (2008) Structural, acidic and redox properties of V2O5-TiO2-SO42− catalysts. Appl Catal A 334:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2007.09.023
Tang ZW, Huang QF, Yang YF (2013) PCDD/Fs in fly ash from waste incineration in China: a need for effective risk management. Environ Sci Technol 47:5520–5521. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401463s
Tang MH, Ye QL, Du CC, Peng YQ, Makwarimba CP, He Y (2021) Lu SY (2021) PCDD/F removal at low temperatures over vanadium-based catalyst: insight into the superiority of mechanochemical method. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15477-y)
Wang CZ, Yang SJ, Chang HZ, Peng Y, Li JH (2013) Dispersion of tungsten oxide on SCR performance of V2O5WO3/TiO2: acidity, surface species and catalytic activity. Chem Eng J 225:520–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.005
Wang J, Wang X, Liu XL, Zhu TY, Guo YY, Qi H (2015) Catalytic oxidation of chlorinated benzenes over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts: the effects of chlorine substituents. Catal Today 241:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.04.002
Wang QL, Hung PC, Lu SY, Chang MB (2016) Catalytic decomposition of gaseous PCDD/Fs over V2O5/TiO2-CNTs catalyst: effect of NO and NH3 addition. Chemosphere 159:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.072
Wang D, Chen QZ, Zhang X, Gao C, Wang B, Huang X, Peng Y, Li JH, Lu CM, Crittenden J (2021) Multipollutant control (MPC) of flue gas from stationary sources using scr technology: a critical review. Environ Sci Technol 55:2743–2766. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07326
Weckhuysen BM, Keller DE (2003) Chemistry, spectroscopy and the role of supported vanadium oxides in heterogeneous catalysis. Catal Today 78:25–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00323-1
Wu HM, Chen SA (1987) Dopant-polymer interaction: WCl6-doped polyacetylene. Synth Met 20:169–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(87)90556-X
Xiao X, Xiong SC, Li B, Geng Y, Yang SJ (2016) Role of WO3 in NO reduction with NH3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2: a new insight from the kinetic study. Catal Lett 146:2242–2251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-016-1852-0
Yu MF, Li WW, Li XD, Lin XQ, Chen T, Yan JH (2016) Development of new transition metal oxide catalysts for the destruction of PCDD/Fs. Chemosphere 156:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.011
Yu SH, Lu YY, Cao Y, Wang JM, Sun BW, Gao F, Tang CJ, Dong L (2018) Composite catalytic systems: A strategy for developing the low temperature NH3-SCR catalysts with satisfactory SO2 and H2O tolerance. Catal Today 327235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.043
Yu SH, Lu YY, Cao Y, Wang JM, Sun BW, Gao F, Tang CJ, Dong L (2019) Composite catalytic systems: a strategy for developing the low temperature NH3-SCR catalysts with satisfactory SO2 and H2O tolerance. Catal Today 327:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.043
Zhao RX, Jin DD, Yang HS, Lu SY, Potter PM, Du CC, Peng YQ, Li XD, Yan JH (2016) Low-temperature catalytic decomposition of 130 tetra- to octa-PCDD/Fs congeners over CuOx and MnOx modified V2O5/TiO2-CNTs with the assistance of O3. Environ Sci Technol 50:11424–11432. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02977
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the State Key Laboratory of Clean Energy Utilization, Institute for Thermal Power Engineering, Zhejiang University for the dioxin detection.
Funding
This work was supported by the Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (No. 20YDLZSN00100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Qin: investigation and original draft writing; Jun Gu: review and editing; Wentao Cai: review and editing; Zhaojia Wang: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Gu, J., Cai, W. et al. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene and PCDD/Fs over V2O5-WO3/TiO2: insights into the component effect and reaction mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 42809–42821 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18768-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18768-0