Abstract
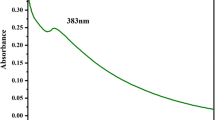
Borassus flabellifer leaf extract has been used for rapid biogenic synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) due to rich source of bioactive compounds. The synthesized ZnO-NPs were preliminarily confirmed by UV–visible spectroscopy adsorption peak range at 365 nm. The XRD (X-ray diffraction) confirms purity of ZnO-NPs that were crystalline in nature. The analysis of FT-IR (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy) confirms the presence of the following functional group such as alcohol, phenols, carboxylic acids, primary amides, secondary amides, and alkyl halide. The Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) analysis indicated that ZnO-NPs were in spherical shape, followed by EDX analysis which confirmed the presence of Zn-element. Antimicrobial effect of ZnO-NPs was investigated using different clinical pathogens like bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella Pneumonia, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and fungi Aspergillus flavus, Candida albicans, and Penicillium expansum which confirmed ZnO-NPs efficiency as an antimicrobial agent. ZnO-NP antimicrobial efficiency was observed in higher zone of inhibition at 50 μg/mL concentrations. Antioxidant activity was ascertained to be used for several biomedical applications. The ZnO-NPs efficiently degraded the environmental toxic dyes (methylene blue and crystal violet) under sunlight, and up to 95% higher degradation was achieved in both dyes. In support of photo light degradation, the study was progressed to understand the ZnO-dye interaction stability using molecular mechanism, and it shows efficient bonding features in the NPs environment. Overall, this investigation has great potential for being an effective and eco-friendly material used in environmental applications.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Abdullahi T, Harun Z, Othman MHD (2017) A review on sustainable synthesis of zeolite from kaolinite resources via hydrothermal process. Advan Pow Techno 28:1827–1840
Awwad M, Borhan A, L. Ahmad L( 2014) Green synthesis, characterization and optical properties of zinc oxide nanosheets using Oleaeuropea leaf extract, Adv. Mat. Lett. 5: 520–524.
Cittrarasu V, Balasubramanian B, Kaliannan D, Maluventhan V, Kaul T, Liu WC, Arumugam M (2019) Biological mediated Ag nanoparticles from Barleria longiflora for antimicrobial activity and photocatalytic degradation using methylene blue. Artif Cells Nanomedicin Biotechnol 47:2424–2430
Dalvand A, Nabizadeh R, Ganjali MR, Khoobi M, Nazmara S, Mahvi AH (2016) Modeling of Reactive Blue 19 azo dye removal from colored textile wastewater using L-arginine-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: optimization, reusability, kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Magn Magne Mater 404:179–189
Dhand C, Dwivedi N, Loh XJ, Ying ANJ, Verma NK, RW, (2015) Beuerman, Ramakrishna. Methods and Strategies for the Synthesis of Diverse Nanoparticles and Their Applications: a Comprehensive Overview, Rsc Advances Rsc Advances 5:105003–105037
Duffy EM, Jorgensen WL (2000) Prediction of properties from simulations: free energies of salvation in Hexa decane, octanol, and water. J Am Chem 122:2878–2888
Elumalai EK, Prasad TNVKV, Kambala V, Nagajyothi PC, David E (2010) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Euphorbia hirta L and their antifungal activities. Arch Appl Sci Res 2:76–81
Ibrahim MB, Abdullahi SH (2017) Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles using Ipomoea asarifolia leaves extract and its adsorption properties for the removal of dyes. J Pure Appl Sci 10:7–14
Jamdagni P, Khatri P, Rana JS (2018) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthesarbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J Kin Sau Univer Sci 30:168–175
Jamdagni P, Rana JS, Khatri P (2019) Antioxidant activity and antifungal fractional inhibitory concentration indices of zinc oxide nanoparticles in combination with carbendazim, mancozeb, and thiram. Micro Nano Let 14(10):1037–1040
Kalaimurugan D, Vivekanandhan P, Sivasankar P, Durairaj K, Senthilkumar P, Shivakumar MS, Venkatesan S (2019a) Larvicidal activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Pseudomonas fluorescens YPS3 isolated from the Eastern Ghats of India. J Clus Sci 30:225–233
Kalaimurugan D, Sivasankar P, Lavanya K, Shivakumar MS, Venkatesan S (2019b) Antibacterial and larvicidal activity of Fusarium proliferatum (YNS2) whole cell biomass mediated copper nanoparticles. J Clu Sci 30:1071–1080
Mahdavi B, Saneei S, Qorbani M, Zhaleh M, Zangeneh A, Zangeneh MM, Ghaneialvar H (2019) Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam leaves aqueous extract mediated synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their antibacterial, antifungal, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and cutaneous wound healing properties under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Appl Organomet Chemi 33:5164
Mirza AU, Kareem A, Nami SA, Bhat SA, Mohammad A, Nishat N (2019) Malus pumila and Juglen regia plant species mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, spectral characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial studies. Microb Pathog 129:233–241
Piccinno F, Gottschalk F, Seeger S, Nowack, B( 2012) Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J Nanoparti Resear. 14: 1–11.
Reddy KM, Feris K, Bell J, Wingett DG, Hanley C, Punnoose A ( 2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90.
Safawo T, Sandeep BV, Pola S, Tadesse A (2018) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using tuber extract of anchote (Cocciniaabyssinica (Lam.) Cong.) for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity assessment. Open Nano 3:56–63
Saravanan M, Gopinath V, Chaurasia MK, Syed A, Ameen F, Purushothaman N (2018) Green synthesis of anisotropic zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and cytofriendly properties. Microb Pathog 115:57–63
Singh A, Dutta PK (2020) Green synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of chitin glucan based zinc oxide nanoparticles and its curcumin conjugation. Interna J Biologi Macromole 156:514–521
Sunghwan K, Paul AT, Evan EB, Chen J, Gang F (2016) PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1202–D1213
Suresh D, Nethravathi PC, Udayabhanu H, Rajanaika H, NagabhushanaSC SC (2015) Green synthesis of multifunctional zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Cassia fistula plantextract and their photodegradative, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Mater Sci Semicond Process 31:446–454
Xie YP, He YP, Irwin PL, JinT SXM (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2325–2331
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Periyar University, India, for providing the necessary facility and also grateful to the Sejong University, Republic of Korea, for their support of instrumental analysis facility. All the authors were grateful and extended their appreciation to the authorities for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: B.B. and S.V.
Methodology: D.K., K.L., K.D., P.S., and K.N.
Analysis: K.D. and M.S.S.
Data curation: P.S., D.K., B.B., and D.K.
Writing-original draft preparation: D.K. and B.B.
Data interpretation and review: S.P. and W.L.
Writing-review and editing: B.B. and S.V.
Supervision and project administration: S.V.
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors agree to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
All authors allow the publication of the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Borassus flabellifer leaf is used for synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs).
• The ZnO-NPs synthesized material was characterized by UV spectra, XRD, FE-SEM, and EDX.
• B. flabellifer leaf extract and its derived Zn-NPs have been tested for their antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activity.
• In backing of photocatalytic study, proceeded to in silico docking analysis.
• These simple biological approaches are non-toxic, environmentally safe, and cost efficient.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalaimurugan, D., Lalitha, K., Durairaj, K. et al. Biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles mediated from Borassus flabellifer (Linn): antioxidant, antimicrobial activity against clinical pathogens, and photocatalytic degradation activity with molecular modeling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 86308–86319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18074-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18074-1