Abstract
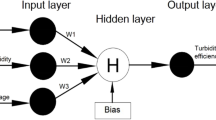
In this study, an enhanced coagulation-flocculant process incorporating magnetic powder was used to further treat the secondary effluent of domestic wastewater from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. The purpose of this work was to improve the discharged water quality to the surface water class IV standard of China. A novel approach using a combination of the response surface methodology and an artificial neural network (RSM-ANN) was used to optimize and predict the total phosphorus (TP) pollutant removal and turbidity. This work was first evaluated by RSM using the concentrations of coagulant, magnetic powder, and flocculant as the controllable operating variables to determine the optimal TP removal and turbidity. Next, an ANN model with a back-propagation algorithm was constructed from the RSM data along with the non-controllable variables, raw TP concentration, and raw water turbidity. Under the optimized experimental conditions (28.42 mg/L coagulant, 623 mg/L magnetic powder, and 0.18 mg/L flocculant), the TP and turbidity removal reached 88.79 ± 5.45% and 63.48 ± 9.60%, respectively, compared with 83.28% and 59.80%, predicted by the single RSM model, and 87.71 ± 5.74% and 64.62 ± 10.75%, predicted by the RSM-ANN model. The treated water were 0.17 ± 6.69% mg/L of TP and 2.46 ± 5.09% NTU of turbidity, respectively, which completely met the surface water class IV standard (TP < 0.3 mg/L; turbidity < 3 NTU). Therefore, this work demonstrated that the discharged water quality was completely improved using the magnetic coagulation process. In addition, the combined RSM-ANN approach could have potential application in municipal wastewater treatment plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barekati-Goudarzi M, Mehrnia MR, Roudsari FP, Boldor D (2016) Rapid separation of microalga Chlorella vulgaris using magnetic chitosan: process optimization using response surface methodology. Particul Sci Technol 34:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2015.1054973
Beltrán Heredia J, Sánchez Martín J (2009) Removing heavy metals from polluted surface water with a tannin-based flocculant agent. J Hazard Mater 165:1215–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.104
Bogunovi M, Ivanev-Tumbas I, Česen M, Esen M, Sekulić TD, Prodanović J, Tubić A, Heath D, Heath E (2021) Removal of selected emerging micropollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluent by advanced non-oxidative treatment - a lab-scale case study from Serbia. Sci Total Environ 765:142764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142764
Dai LY (2017) Application of magnetic coagulation technology in high phosphorus wastewater treatment. Phosphate & Compd. Fertil. 032(010):47–49 ((in Chinese))
Ding N, Wang X, Jiang L, Geng Y, Dong LM, Liu H (2021) Enhancement of sludge dewaterability by a magnetic field combined with coagulation/flocculation: a comparative study on municipal and citric acid–processing waste-activated sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13278-x
Gadekar MR, Ahammed MM (2019) Modelling dye removal by adsorption onto water treatment residuals using combined response surface methodology-artificial neural network approach. J Environ Manage 231(FEB.1):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.017
Ganapathy S, Balasubramanian P, Vasanth B (2020) Comparative investigation of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Response Surface Methodology (RSM) expectation in EDM parameters. Materials Today: Proceedings 46(19):9592–9596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.499
Ghritlahre HK, Prasad RK (2018) Application of ANN technique to predict the performance of solar collector systems - a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 84:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.01.001
Hafeez A, Taqvi SAA, Fazal T, Javed F, Khan Z, Amjad US, Bokhari A, Shehzad N, Rashid N, Rehman S, Rehman F (2020) Optimization on cleaner intensification of ozone production using artificial neural network and response surface methodology: parametric and comparative study. J Clean Prod 252:119833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119833
Ho N, Babel S (2020) Bioelectrochemical technology for recovery of silver from contaminated aqueous solution: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10065-y
Huangfu XL, Ma C, Ma J, He Q, Yang C, Jiang J, Wang Y, Wu Z (2017) Significantly improving trace thallium removal from surface waters during coagulation enhanced by nanosized manganese dioxide. Chemosphere 168:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.054
Igwegbe CA, Mohammadi L, Ahmadi S (2019) Modeling of adsorption of methylene blue dye on Ho-CaWO4 nanoparticles using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) techniques. MethodsX 6:1779–1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.07.016
Jiang W, Xu H, Wang DS, Xiao F (2014) The characteristics of flocs and zeta potential in nano-TiO2 system under different coagulation conditions. Colloids Surf, A 452:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.03.073
Katz I, Dosoretz CG (2008) Desalination of domestic wastewater effluents: phosphate removal as pretreatment. Desalination 222:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.160
Khalid AAH, Yaakob Z, Abdullah SRS (2019) Analysis of the elemental composition and uptake mechanism of Chlorella sorokiniana for nutrient removal in agricultural wastewater under optimized response surface methodology (RSM) conditions. J Clean Prod 210:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.095
Krupińska I (2020) The effect of the type of hydrolysis of aluminium coagulants on the effectiveness of organic substances removal from water. Desalin Water Treat 186:171–180. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25248
Kumari M, Gupta SK (2020) A novel process of adsorption cum enhanced coagulation-flocculation spiked with magnetic nano adsorbents for the removal of aromatic and hydrophobic fraction of natural organic matter along with turbidity from drinking water. J Clean Prod 244:118899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118899
Li C, Ma J, Shen J, Peng W (2009) Removal of phosphate from secondary effluent with Fe2+ enhanced by H2O2 at nature pH/neutral pH. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):891–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.111
Li RH, Guo BY, Sun JZ, Yue QY (2018) Coagulation behavior of kaolin-anionic surfactant simulative wastewater by polyaluminum chloride-polymer dual coagulant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7382–7390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1073-0
Liu D, Wang P, Wei GR, Dong WB, Hui F (2013a) Removal of algal blooms from freshwater by the coagulation-magnetic separation method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1052-4
Liu YY, Zhang WJ, Yang XY, Xiao P, Wang DS, Song YQ (2013b) Advanced treatment of effluent from municipal WWTP with different metal salt coagulants: contaminants treatability and floc properties. Sep Purif Technol 120:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.09.046
Lohwacharin J, Phetrak A, Oguma K, Takizawa S (2014) Flocculation performance of magnetic particles with high-turbidity surface water. Water Supply 14(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2014.015
Lv M, Zhang Z, Zeng J, Liu JF, Sun MC, Yadav RS, Feng YJ (2019) Roles of magnetic particles in magnetic seeding coagulation-flocculation process for surface water treatment. Sep Purif Technol 212:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.011
Lv M, Li D, Zhang Z (2020) Feng Y (2020) Magnetic seeding coagulation: effect of Al species and magnetic particles on coagulation efficiency, residual Al, and floc properties. Chemosphere 268(1):129363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129363
Mahmoodi-Babolan N, Heydari A, Nematollahzadeh A (2019) Removal of methylene blue via bioinspired catecholamine/starch superadsorbent and the efficiency prediction by response surface methodology and artificial neural network-particle swarm optimization. Bioresour Technol 294:122084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122084
Mohammad R, Hamed T, Mohammad RR (2019) Degradation of crystal violet in water solution using post discharge DBD plasma treatment: factorial design experiment and modeling. Chemosphere 232:213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.153
Momeni MM, Kahforoushan D, Abbasi F, Ghanbarian S (2018) Using chitosan/chpatc as coagulant to remove color and turbidity of industrial wastewater optimization through RSM design. J Environ Manage 211(APR.1):347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.031
Mortadi A, Chahid EG, Abderrahmane E, Chahbi M, Moznine, RE (2020) Complex electrical conductivity as a new technique to monitor the coagulation-flocculation processes in the wastewater treatment of the textile industry. Water Resour Ind 24:100130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2020.100130
Pambi RL, Musonge P (2016) Application of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) In the treatment of final effluent from the sugar industry using Chitosan. Water Pollution 209:209–219. https://doi.org/10.2495/WP160191
Qasim M, Park S, Lee J, Kim JO (2019) Evaluation of floc settling velocity models through image analysis for ballasted flocculation. Desalin Water Treat 144:370–383. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23586
Rizzo L, Gennaro AD, Gallo M (2008) Coagulation/chlorination of surface water: a comparison between chitosan and metal salts. Sep Purif Technol 62(1):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.12.020
Rizzo L, Malato S, Antakyali D, Beretsou VG, Đolić MB, Gernjak W, Heath E, Ivancev-Tumbas I, Karaolia P, Ribeiro ARL, Mascolo G, McArdell CS, Schaar H, Silva AMT, Fatta-Kassinos D (2019) Consolidated vs new advanced treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern from urban wastewater. Sci Total Environ 655:986–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.265
Santos TRT, Silva MF, Nishi L, Vieira AMS, Klein MRF, Andrade MB, Vieira MF, Bergamasco R (2016) Development of a magnetic coagulant based on Moringa oleifera seed extract for water treatment. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:7692–7700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6029-7
Tetteh EK, Rathilal S (2018) Evaluation of the coagulation floatation process for industrial mineral oil wastewater treatment using response surface methodology (RSM). Int J Environ Impacts 1(4):491–502. https://doi.org/10.2495/EI-V1-N4-491-502
Usefi S, Asadi-Ghalhari M (2019) Optimization of turbidity removal by coagulation and flocculation process from synthetic stone cutting wastewater. International J Energy Wat Resour 3:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-019-00010-2
Wang JP, Chen YZ, Wang Y, Yuan SJ, Yu HQ (2011) Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process for pulp mill wastewater treatment using a combination of uniform design and response surface methodology. Water Res 45:5633–5640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.023
Wang P, Ding S, An G (2021) Removal of disinfection by-product precursors by Al-based coagulants: a comparative study on coagulation performance. J Hazard Mater 420:126558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126558
Xu Q, Xiao KK, Wang H, Wu QX, Liang S, Yu WB, Hou HJ, Liu BC, Hu JP, Yang JK (2020) Insight into effects of organic and inorganic phosphorus speciations on phosphorus removal efficiency in secondary effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):11736–11748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07774-9
Yao M, Nan J, Chen T (2014) Effect of particle size distribution on turbidity under various water quality levels during flocculation processes. Desalination 354:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.09.029
Zhang X, Yao J, Peng W, Xu W, Li Z, Zhou C (2018) Degradation of dichloroacetonitrile by a UV/peroxymonosulfate process: modeling and optimization based on response surface methodology (RSM). RSC Adv 8(59):33681–33687. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra07009a
Zhou G, Wang Q, Li J, Li QS, Xu H, Ye Q, Wang YQ, Shu SH, Zhang J (2021) Removal of polystyrene and polyethylene microplastics using PAC and FeCl3 coagulation: performance and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 752:141837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141837
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Alan K Chang (Wenzhou University) for valuable discussion and for revising the language of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFE0103700); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61901303 and 61871293); the Science and Technology Program of Cangnan, China (Grant No: 2018G29); and the Science and Technology Major Program of Wenzhou, China (Grant No: 2018ZG002).
national key research and development program of china,No. 2018YFE0103700,Qi Wang,National Natural Science Foundation of China,Nos. 61901303,Qi Wang,61871293,Qi Wang,science and technology program of Cangnan,China,No: 2018G29,Qi Wang,science and technology major program of wenzhou,China,No: 2018ZG002,Qi Wang
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KW established the models, analyzed and interpreted the experimental data, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. YM designed the experiments, performed the water quality measurements along with KW, and was a contributor on graphical processing. CW did the literature research. QK downloaded and installed the required software. MZ provided the vehicles for the experimental condition. QW came up with the idea, consulted the literatures, and contacted with the management of the multiple wastewater treatment plants. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Mao, Y., Wang, C. et al. Application of a combined response surface methodology (RSM)-artificial neural network (ANN) for multiple target optimization and prediction in a magnetic coagulation process for secondary effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 36075–36087 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18060-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18060-7