Abstract
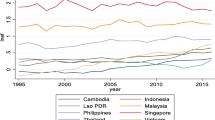
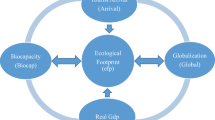
Several studies have investigated the relationship between tourism, consumption of energy, globalization, and ecological footprint. However, the role of biocapacity alongside tourism development in environmental sustainability is yet to be documented in the extant literature. No doubt, the biocapacity of a country, its level of tourist’s arrival, as well as globalization all contribute immensely to ecological footprint. Consequently, this study looks at long-run and causality connections with a special focus on bio-capacity. The study uses the pooled mean group-autoregressive distributed lag model (PMG-ARDL) methodology to test the causality relationship during 2016 international tourists’ receipt from world tourism organization data files for 10 tourism destinations. Empirical result based on the panel PMG-ARDL confirms the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis for the 10 tourism destinations countries investigated. Furthermore, the panel ARDL estimator was used to estimate the short-run and long-run relationships simultaneously between biocapacity, tourist arrivals, GDP per capita, globalization, and ecological footprints. While the Dumitrescu and Hurlin panel causality test was used to establish causality relationships among the highlighted variables. The trade-off between economic growth and environmental quality suggests that tourist arrival dampens environmental quality. In addition, the study finds that growing biocapacity affects ecological footprints negatively. Furthermore, an increase in tourism-related activities, globalization, and economic production has the potential to damage the quality of the environment. To this end, given the study results, there is a need to pursue green tourism which can reduce environmental degradation and destruction of land caused by multiple tourism-related transportation and construction of tourist facilities respectively in the top ten tourist destination countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data for this present study are sourced from the World Development Indicators (https://data.worldbank.org/). The current data specific data can be made available upon request but all available and downloadable at the earlier mentioned database and weblink.
References
Acheampong AO, Adams S, Boateng E (2019) Do globalization and renewable energy contribute to carbon emissions mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa? Sci Total Environ 677:436–446
Adedoyin FF, Bekun FV (2020) Modelling the interaction between tourism, energy consumption, pollutant emissions and urbanization: renewed evidence from panel VAR. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(31):38881–38900
Adedoyin FF, Alola AA, Bekun FV (2020a) An assessment of environmental sustainability corridor: the role of economic expansion and research and development in EU countries. Sci Total Environ 713:136726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136726
Adedoyin FF, Gumede MI, Bekun FV, Etokakpan MU, Balsalobre-lorente D (2020b) Modelling coal rent, economic growth and CO2 emissions: does regulatory quality matter in BRICS economies? Sci Total Environ 710:136284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136284
Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Yang X, Hussain N, Sinha A (2021a). Financial development and environmental degradation: Do human capital and institutional quality make a difference? Gondwana Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2021.09.012 (early view)
Ahmad M, Işık C, Jabeen G, Ali T, Ozturk I, Atchike DW (2021b) Heterogeneous links among urban concentration, non-renewable energy use intensity, economic development, and environmental emissions across regional development levels. Sci Total Environ 765:144527
Akadiri SS, Akadiri AC, Alola UV (2019) Is there growth impact of tourism? Evidence from selected small island states. Curr Issue Tour 22(12):1480–1498
Akadiri SS, Lasisi TT, Uzuner G, Akadiri AC (2020) Examining the causal impacts of tourism, globalization, economic growth and carbon emissions in tourism island territories: bootstrap panel Granger causality analysis. Curr Issue Tour 23(4):470–484
Alola UV, Cop S, Adewale Alola A (2019a) The spillover effects of tourism receipts, political risk, real exchange rate, and trade indicators in Turkey. Int J Tour Res 21(6):813–823
Alola AA, Eluwole KK, Alola UV, Lasisi TT, Avci T (2019b) Environmental quality and energy import dynamics: the tourism perspective of the coastline Mediterranean countries (CMCs). Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal.
Baek J, Cho Y, Koo WW (2009) The environmental consequences of globalization: a country-specific time-series analysis. Ecol Econ 68(8–9):2255–2264
Balli E, Sigeze C, Manga M, Birdir S, Birdir K (2019) The relationship between tourism, CO2 emissions and economic growth: a case of Mediterranean countries. Asia Pac J Tour Res 24(3):219–232
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Adedoyin FF (2021) The asymmetric impact of air transport on economic growth in Spain: fresh evidence from the tourism-led growth hypothesis. Curr Issues Tour 24(4):503–519
Brida JG, Pereyra JS, Risso WA, Devesa MJS, Aguirre SZ (2008) The tourism-led growth hypothesis: empirical evidence from Colombia
Cadarso MÁ, Gómez N, López LA, Tobarra MÁ (2016) Calculating tourism’s carbon footprint: measuring the impact of investments. J Clean Prod 111:529–537
Cai W, Song X, Zhang P, Xin Z, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wei W (2020) Carbon emissions and driving forces of an island economy: a case study of Chongming Island, China. J Clean Prod 254:120028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120028
Cheng Y, Sinha A, Ghosh V, Sengupta T, Luo H (2021) Carbon tax and energy innovation at crossroads of carbon neutrality: designing a sustainable decarbonization policy. J Environ Manag 294:112957
Chu X, Deng X, Jin G, Wang Z, Li Z (2017) Ecological security assessment based on ecological footprint approach in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 101:43–51
Churchill SA, Inekwe J, Ivanovski K, Smyth R (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve in the OECD: 1870–2014. Energy Econ 75:389–399
Danish HS, Baloch MA, Mahmood N, Zhang JW (2019) Linking economic growth and ecological footprint through human capital and biocapacity. Sustain Cities Soc 47:101516
Eluwole KK, Saint Akadiri S, Alola AA, Etokakpan MU (2020) Does the interaction between growth determinants a drive for global environmental sustainability? Evidence from world top 10 pollutant emissions countries. Sci Total Environ 705:135972
Etokakpan MU, Bekun FV, Abubakar AM (2019) Examining the tourism-led growth hypothesis, agricultural-led growth hypothesis and economic growth in top agricultural producing economies. Eur J Tour Res 21:132–137
Gössling S, Peeters P (2015) Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. J Sustain Tour 23(5):639–659
Guan D, Meng J, Reiner DM, Zhang N, Shan Y, Mi Z, ... Davis SJ (2018) Structural decline in China’s CO2 emissions through transitions in industry and energy systems. Nat Geosci 11(8):551–555
Jorgenson AK, Clark B (2011) Societies consuming nature: a panel study of the ecological footprints of nations, 1960–2003. Soc Sci Res 40(1):226–244
Katircioglu S, Gokmenoglu KK, Eren BM (2018) Testing the role of tourism development in ecological footprint quality: evidence from top 10 tourist destinations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(33):33611–33619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3324-0
Khan MK, Teng JZ, Khan MI, Khan MO (2019a) Impact of globalization, economic factors and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 688:424–436
Khan MTI, Yaseen MR, Ali Q (2019b) Nexus between financial development, tourism, renewable energy, and greenhouse gas emission in high-income countries: a continent-wise analysis. Energy Economics 83:293–310
Koçak E, Ulucak ZŞ (2019) The effect of energy R&D expenditures on CO2 emission reduction: estimation of the STIRPAT model for OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14328–14338
Koçak E, Ulucak R, Ulucak ZŞ (2020) The impact of tourism developments on CO2 emissions: an advanced panel data estimation. Tour Manag Perspect 33:100611
Kongbuamai N, Bui Q, Yousaf HMAU, Liu Y (2020) The impact of tourism and natural resources on the ecological footprint: a case study of ASEAN countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19251–19264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08582-x
Meng W, Xu L, Hu B, Zhou J, Wang Z (2016) Quantifying direct and indirect carbon dioxide emissions of the Chinese tourism industry. J Clean Prod 126:586–594
Meo M, Nathaniel S, Shaikh G, Kumar A (2021) Energy consumption, institutional quality and tourist arrival in Pakistan: Is the nexus (a) symmetric amidst structural breaks? J Public Affairs 21(2):e2213
Nathaniel SP (2021a) Ecological footprint and human well-being nexus: accounting for broad-based financial development, globalization, and natural resources in the Next-11 countries. Future Bus J 7(1):1–18
Nathaniel SP (2021b) Economic complexity versus ecological footprint in the era of globalization: evidence from ASEAN countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15360-w (early view)
Nathaniel SP (2021c) Natural resources, urbanisation, economic growth and the ecological footprint in South Africa: the moderating role of human capital. Quaestiones Geograph 40(2):63–76
Nathaniel SP, Adedoyin FF (2020) Tourism development, natural resource abundance, and environmental sustainability: another look at the ten most visited destinations. J Public Affairs e2553. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2553 (early view)
Nathaniel SP, Barua S, Ahmed Z (2021) What drives ecological footprint in top ten tourist destinations? Evidence from advanced panel techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13389-5 (early view)
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development OECD (2018) Available at OECD Tourism Trends and Policies 2018 | OECD Tourism Trends and Policies | OECD iLibrary. oecd-ilibrary.org. Accessed 2 Jan 2020
Ozcan CC, Bekun FV, Nazlioglu S (2021) Tourism-induced pollutant emissions in Mediterranean countries: evidence from panel causality analysis. Int Soc Sci J 71(241–242):261–281
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RP (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Stat Assoc 94(446):621–634
Saint Akadiri S, Alkawfi MM, Uğural S, Akadiri AC (2019a) Towards achieving environmental sustainability target in Italy. The role of energy, real income and globalization. Sci Total Environ 671:1293–1301
Saint Akadiri S, Alola AA, Akadiri AC (2019b) The role of globalization, real income, tourism in environmental sustainability target. Evidence from Turkey. Sci Total Environ 687:423–432
Saint Akadiri S, Lasisi TT, Uzuner G, Akadiri AC (2019c) Examining the impact of globalization in the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the case of tourist destination states. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):12605–12615
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Shahzad SJH, Shahbaz M, Ferrer R, Kumar RR (2017) Tourism-led growth hypothesis in the top ten tourist destinations: New evidence using the quantile-on-quantile approach. Tourism Management 60:223–232
Shahbaz M, Sharma R, Sinha A, Jiao Z (2021) Analyzing nonlinear impact of economic growth drivers on CO2 emissions: designing an SDG framework for India. Energy Policy 148:111965
Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P (2021) Does renewable energy consumption reduce ecological footprint? Evidence from eight developing countries of Asia. J Clean Product 285:124867
Sun YY (2016) Decomposition of tourism greenhouse gas emissions: revealing the dynamics between tourism economic growth, technological efficiency, and carbon emissions. Tour Manage 55:326–336
Tang Z, Shang J, Shi C, Liu Z, Bi K (2014) Decoupling indicators of CO2 emissions from the tourism industry in China: 1990–2012. Ecol Ind 46:390–397
Tecel A, Katircioğlu S, Taheri E, Bekun FV (2020) Causal interactions among tourism, foreign direct investment, domestic credits, and economic growth: evidence from selected Mediterranean countries. Port Econ J 19(3):195–212
Udi J, Bekun FV, Adedoyin FF (2020) Modeling the nexus between coal consumption, FDI inflow and economic expansion: does industrialization matter in South Africa? Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07691-x
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Ahmad W (2021) Do technological innovations have symmetric or asymmetric effects on environmental quality? Evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Product 316:128239
United Nations World Tourism Organization (2019) International tourism highlights. https://www.eunwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/9789284421152. Accessed 2 Jan 2020
Wang X, Shao Q (2019) Non-linear effects of heterogeneous environmental regulations on green growth in G20 countries: evidence from panel threshold regression. Sci Total Environ 660:1346–1354
Wang N, Zhu H, Guo Y, Peng C (2018) The heterogeneous effect of democracy, political globalization, and urbanization on PM2. 5 concentrations in G20 countries: evidence from panel quantile regression. J Clean Prod 194:54–68
World Travel and Tourism Council (2017) Travel and tourism economic impact 2017 Cuba. https://www.wttc.org/-/media/files/reports/economic-impact-research/archived/countries-2017-old/cuba2017.pdf. Accessed 2 Jan 2020
Wu L, Liu S, Liu D, Fang Z, Xu H (2015) Modelling and forecasting CO2 emissions in the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) countries using a novel multi-variable grey model. Energy 79:489–495
Xue GAO, Chang HL, Chi-Wei SU (2018) Does exchange rate always affect the number of inbound tourists significantly in China? Theoret Appl Econ 25(1):55–72
You W, Lv Z (2018) Spillover effects of economic globalization on CO2 emissions: a spatial panel approach. Energy Econ 73:248–257
Zafar MW, Sinha A, Ahmed Z, Qin Q, Zaidi SAH (2021) Effects of biomass energy consumption on environmental quality: the role of education and technology in Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 142:110868
Zaman K, Shahbaz M, Loganathan N, Raza SA (2016) Tourism development, energy consumption and environmental Kuznets curve: trivariate analysis in the panel of developed and developing countries. Tour Manage 54:275–283
Zhang S, Liu X (2019) The roles of international tourism and renewable energy in environment: new evidence from Asian countries. Renew Energy 139:385–394
Acknowledgements
Author gratitude is extended to the prospective editor(s) and reviewers that will/have spared time to guide toward a successful publication.
The authors of this article also assures that they follow the springer publishing procedures and agree to publish it as any form of access article confirming to subscribe access standards and licensing.
Many thanks in advance look forward to your favorable response
Yours truly,
Authors
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first authors Dr. Festus Fatai Adedoyin were responsible for the conceptual construction of the study’s idea and also handled the literature section while the third authors Asst. Prof. Dr. Uju Violet Alola managed the data gathering and preliminary analysis, and Dr. Festus Victor Bekun was responsible for proofreading and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Authors mentioned in the manuscript have agreed for authorship read and approved the manuscript, and given consent for submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1. Summary of literature
Table 10
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adedoyin, F.F., Alola, U.V. & Bekun, F.V. On the nexus between globalization, tourism, economic growth, and biocapacity: evidence from top tourism destinations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 24995–25005 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17651-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17651-8