Abstract
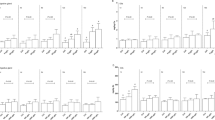
Antibiotic toxicity and antibiotic resistance have become significant challenges to human health. However, the potential ecotoxicity of sediment-associated antibiotics remains unknown. In this study, biochemical responses, histological changes, and behavioral responses of Corbicula fluminea exposed to sediment-associated ciprofloxacin (CIP) were systemically investigated. Special attention was paid to the influence of different substrate types. Biochemical analyses revealed that the balance of the antioxidant system was disrupted, eventually leading to oxidative damage to the gills and digestive gland with increasing CIP concentration. Severe histopathological changes appeared along with the oxidative damage. An enlargement of the tubule lumen and thinning of the epithelium in the digestive gland were observed under exposure to high CIP concentrations (0.5 and 2.5 μg/g CIP). In a behavioral assay, the filtration rate of C. fluminea in high concentration exposure groups was clearly inhibited. Moreover, from the integrated biomarker response (IBR) index, the toxicity response gradients of the digestive gland (no substrate--NOS > Sand > Sand and kaolinite clay-- SKC > Sand, kaolinite clay, and organic matter--SCO) and gills (NOS > SCO > SKC > Sand) were different among substrate exposure groups. The most serious histopathological damage and highest siphoning inhibition were observed in the NOS group. The changes in the morphological structure of digestive gland cells in C. fluminea were similar in the other three substrate groups. The inhibition of the filtration rate in the higher concentration groups decreased in the order Sand > SKC > SCO.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arini A, Daffe G, Gonzalez P, Feurtet-Mazel A, Baudrimont M (2014) Detoxification and recovery capacities of Corbicula fluminea after an industrial metal contamination (Cd and Zn): a one-year depuration experiment. Environ Pollut 192:74–82
Aguirre-Martínez GV, DelValls AT, Laura Martín-Díaz M (2015) Yes, caffeine, ibuprofen, carbamazepine, novobiocin and tamoxifen have an effect on Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:142–154
Beliaeff B, Burgeot T (2002) Integrated biomarker response: a useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1316–1322
Boening D (1999) An evaluation of bivalves as biomonitors of heavy metals pollution in marine waters. Environ Monit Assess 55:459–470
Wilson C, Clarke R, D’Arcy BC et al (2005) Persistent pollutants urban rivers sediment survey: implications for pollution control. Water Sci Technol 51(3-4):217–224
Carvalho IT, Santos L (2016) Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of the European scenario. Environ Int 94:736–757
Coughlan J (1969) The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Mar Biol 2:356–358
Chen H, Zha J, Liang X, Li J, Wang Z (2014) Effects of the human antiepileptic drug carbamazepine on the behavior, biomarkers, and heat shock proteins in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Aquat Toxicol 155:1–8
Chen H, Zha J, Yuan L, Wang Z (2015) Effects of fluoxetine on behavior, antioxidant enzyme systems, and multixenobiotic resistance in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Chemosphere 119:856–862
Chen K, Zhou JL (2014) Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 95:604–612
Cid A, Picado A, Correia JB, Chaves R, Silva H, Caldeira J, de Matos APA, Diniz MS (2015) Oxidative stress and histological changes following exposure to diamond nanoparticles in the freshwater Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774). J Hazard Mater 284:27–34
Crawford SE, Liber K (2015) Effects of clay minerals and organic matter in formulated sediments on the bioavailability of sediment-associated uranium to the freshwater midge, Chironomus dilutus. Sci Total Environ 532:821–830
Csiszár J, Horváth E, Bela K, Gallé Á (2016) Glutathione-Related enzyme system: glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione transferases (GSTs) and Glutathione peroxidases (GPXs). In: Gupta DK, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (eds) Redox State as a Central Regulator of Plant-Cell Stress Responses. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 137–158
Doherty FG (1990) The Asiatic clam, Corbicula spp., as a biological monitor in freshwater environments. Environ Monit Assess 15:143
Esperanza M, Seoane M, Servia MJ, Cid Á (2020) Effects of Bisphenol A on the microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and the clam Corbicula fluminea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110609
Feng C, Guo X, Yin S, Tian C, Li Y, Shen Z (2017) Heavy metal partitioning of suspended particulate matter–water and sediment–water in the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 185:717–725
Feng C, Zhao S, Wang D, Niu J, Shen Z (2014) Sedimentary records of metal speciation in the Yangtze Estuary: role of hydrological events. Chemosphere 107:415–422
Fournier E, Adam C, Massabuau JC, Garnierlaplace J (2005) Bioaccumulation of waterborne selenium in the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea: influence of feeding-induced ventilatory activity and selenium species. Aquat Toxicol 72:251–260
Fu L, Huang T, Wang S, Wang X, Su L, Li C, Zhao Y (2017) Toxicity of 13 different antibiotics towards freshwater green algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and their modes of action. Chemosphere 168:217–222
Graney RL, Cherry DS, Cairns J (1984) The influence of substrate, pH, diet and temperature upon cadmium accumulation in the asiatic clam (Corbicula fluminea) in laboratory artificial streams. Water Res 18:833–842
Guilhermino L, Vieira LR, Ribeiro D, Tavares AS, Cardoso V, Alves A, Almeida JM (2018) Uptake and effects of the antimicrobial florfenicol, microplastics and their mixtures on freshwater exotic invasive bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Sci Total Environ 622-623:1131–1142
Guo X, Feng C (2018) Biological toxicity response of Asian Clam (Corbicula fluminea) to pollutants in surface water and sediment. Sci Total Environ 631-632:56–70
Guo X, Feng C, Gu E, Tian C, Shen Z (2019) Spatial distribution, source apportionment and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Sci Total Environ 671:548–557
Herrero A, Vila J, Eljarrat E, Ginebreda A, Sabater S, Batalla RJ, Barceló D (2018) Transport of sediment borne contaminants in a Mediterranean river during a high flow event. Sci Total Environ 633:1392–1402
Ho KT, Burgess RM, Pelletier MC, Serbst JR, Ryba SA, Cantwell MG, Kuhn A, Raczelowski P (2002) An overview of toxicant identification in sediments and dredged materials. Mar Pollut Bull 44:286–293
Huang Y, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhang L, Ye F, Wang J, Shang J, Liao Q (2020) Impact of sediment characteristics on adsorption behavior of typical antibiotics in Lake Taihu Chinau. Sci Total Environ 718:137329
Jiang Y, Li M, Guo C, An D, Xu J, Zhang Y, Xi B (2014) Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent–receiving river (Wangyang River) in north China. Chemosphere 112:267–274
Jr. G. Allen Burton (2002) Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Jpn J Limnol 3, 65-76
Kaeseberg T, Zhang J, Schubert S, Oertel R, Siedel H, Krebs P (2018) Sewer sediment-bound antibiotics as a potential environmental risk: adsorption and desorption affinity of 14 antibiotics and one metabolite. Environ Pollut 239:638–647
Legeay A, Achard-Joris M, Baudrimont M, Massabuau J, Bourdineaud J (2005) Impact of cadmium contamination and oxygenation levels on biochemical responses in the Asiatic clam Corbicula fluminea. Aquat Toxicol 74:242–253
Li D, Wang P, Wang C, Fan X, Hu B (2018) Combined toxicity of organophosphate flame retardants and cadmium to Corbicula fluminea in aquatic sediments. Environ Pollut 243:S597672460
Liu Y, Junaid M, Xu P, Zhong W, Pan B, Xu N (1987) (2020) Suspended sediment exacerbates perfluorooctane sulfonate mediated toxicity through reactive oxygen species generation in freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea. Environ Pollut 267:115671
Lubecki L, Kowalewska G (2019) Plastic-derived contaminants in sediments from the coastal zone of the southern Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 146:255–262
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and Transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1833
Matić Bujagić I, Grujić S, Laušević M, Hofmann T, Micić V (2019) Emerging contaminants in sediment core from the Iron gate i reservoir on the Danube River. Sci Total Environ 662:77–87
Naylor C, Rodrigues C (1995) Development of a test method for Chironomus riparius using a formulated sediment. Chemosphere 31:3291–3303
Ortmann C (2003) (2003) Energy metabolism and valve closure behaviour in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. J Exp Biol 206(22):4167–4178
Qi W, Müller B, Pernet-Coudrier B, Singer H, Liu H, Qu J, Berg M (2014) Organic micropollutants in the Yangtze River: seasonal occurrence and annual loads. Sci Total Environ 472:789–799
Ren J, Luo J, Ma H, Wang X, Ma LQ (2013) Bioavailability and oxidative stress of cadmium to Corbicula fluminea. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:86–869
Riaz L, Mahmood T, Khalid A, Rashid A, Ahmed Siddique MB, Kamal A, Coyne MS (2018) Fluoroquinolones (FQs) in the environment: a review on their abundance, sorption and toxicity in soil. Chemosphere 191:704–720
Roman YE, De Schamphelaere KAC, Nguyen LTH, Janssen CR (2007) Chronic toxicity of copper to five benthic invertebrates in laboratory-formulated sediment: sensitivity comparison and preliminary risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 387:128–140
Rusina TP, Smedes F, Brborić M, Vrana B (2019) Investigating levels of organic contaminants in Danube River sediments in Serbia by multi–ratio equilibrium passive sampling. Sci Total Environ 696:133935
Saidani W, Sellami B, Khazri A, Mezni A, Dellali M, Joubert O, Sheehan D, Beyrem H (2019) Metal accumulation, biochemical and behavioral responses on the Mediterranean clams Ruditapes decussatus exposed to two photocatalyst nanocomposites (TiO2 NPs and AuTiO2NPs). Aquat Toxicol 208:71–79
Sajjad. Zare, H.P. (2012) Changes activities of antioxidant enzymes in oilseed rape in response to salinity stress. Int JAgricult Crop Sci 7:398–403
Sanchez W, Burgeot T, Porcher JM (2012) A novel “integrated biomarker response” calculation based on reference deviation concept. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2721–2725
Santos KCD, Martinez CBR (2014) Genotoxic and biochemical effects of atrazine and Roundup ®; alone and in combination, on the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:7–14
Shan Y, Yan S, Hong X, Zha J, Qin J (2020) Effect of imidacloprid on the behavior, antioxidant system, multixenobiotic resistance, and histopathology of Asian freshwater clams (Corbicula fluminea). Aquat Toxicol 218:105333
Suzuki J, Nakano D, Imamura M, Yamamoto R, Fujita M (2019) Assessing a polluted river environment by oxidative stress biomarker responses in caddisfly larvae. Sci Total Environ 696:134005
Sheehan D, Meade G, Foley VM, Dowd CA (2001) Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem J 360:1–16
Silva SN, Azevedo AP, Teixeira V, Pina JE, Rueff J, Gaspar JF (2009) The role of GSTA2 polymorphisms and haplotypes in breast cancer susceptibility: a case-control study in the Portuguese population. Oncol Rep 22:593–598
Su T, Shao Q, Wang P, Ma C (2016) Oxidative Stress and its role in peroxisome homeostasis in plants. In: Gupta DK, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (eds) Redox state as a central regulator of plant-cell stress responses. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 117–136
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406
Trchounian A, Petrosyan M, Sahakyan N (2016) Plant Cell redox homeostasis and reactive oxygen species. In: Gupta DK, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (eds) Redox State as a Central Regulator of Plant-Cell Stress Responses. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 25–50
US Environmental Protection Agency (2007) Sediment toxicity identification evaluation (TIE) phases I, II, and III guidance document. EPA 600/R-07/080. Final Report, Washington DC
Vale G, Franco C, Diniz MS, Santos MMCD, Domingos RF (2014) Bioavailability of cadmium and biochemical responses on the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea–the role of TiO2 nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:161–168
Wang D, Ning Q, Dong J, Brooks BW, You J (2020) Predicting mixture toxicity and antibiotic resistance of fluoroquinolones and their photodegradation products in Escherichia coli. Environ Pollut 262:114275
Wang Q, Hong X, Chen H, Yuan L, Zha J (2018) The neuropeptides of Asian freshwater clam (Corbicula fluminea) as new molecular biomarker basing on the responses of organophosphate chemicals exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:52–59
Wu Y, Gu E, Li H, Tian C, Feng C (2019) Oxidative stress and histological changes in Corbicula fluminea exposed to nano-Al13 and monomeric Al coagulants. Environ Sci Nano 6:2736–2748
Xu J, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Guo C, Wang D, Du P, Luo Y, Wan J, Meng W (2014) Distribution, sources and composition of antibiotics in sediment, overlying water and pore water from Taihu Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 497-498:267–273
Yan S, Wu H, Qin J, Zha J, Wang Z (2017) Halogen-free organophosphorus flame retardants caused oxidative stress and multixenobiotic resistance in Asian freshwater clams (Corbicula fluminea). Environ Pollut 225:559–568
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Chen F (2010) Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC-MS/MS. Sci Total Environ 408:3424–3432
Zhang H, Hong X, Yan S, Zha J, Qin J (2020) Environmentally relevant concentrations of bifenthrin induce changes in behaviour, biomarkers, histological characteristics, and the transcriptome in Corbicula fluminea. Sci Total Environ 728:138821
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606:135–150
Zhou J, Broodbank N (2014) Sediment-water interactions of pharmaceutical residues in the river environment. Water Res 48:61–70
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42007368), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2021A1515011863), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFF0204502, 2016YFF0204500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoyu Guo: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing - original draft. Chenghong Feng: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing - review & editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. Zhe Bi: review & editing. Akhtar Islam: review & editing. Yanpeng Cai: review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Beijing Normal University. The benthic bivalve- Corbicula fluminea used in this study was not listed as a protected species in China.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2599 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Feng, C., Bi, Z. et al. Toxicity effects of ciprofloxacin on biochemical parameters, histological characteristics, and behaviors of Corbicula fluminea in different substrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 23700–23711 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17509-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17509-z