Abstract
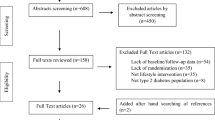
Study was conducted utilizing a confirmed medication adherence scale to measure the socio-demographic profile, self-care, and medication adherence among Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients. The Fisher exact test was used to calculate the level of significance (P) using SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) Version 21.0. The research presented in this paper uses statistical evidence to assess the numerous aspects that may be linked to medication adherence. A prospective observational study was undertaken on participants visiting the outpatient department for 6 months at a North Indian tertiary care hospital to investigate the pattern and quality of life associated with T2DM. The study examined those who had T2DM for more than 2 years. At the time of the visit, subjects were interviewed using socio demographic information and a structured verified questionnaire. Fisher exact test was used to identify the parameters that were linked to medication adherence, with P0.05 being regarded statistically significant. A total of 350 T2DM outpatients were followed up on, with a male-to-female ratio of 1:0.95. A 13-item medication adherence scale was created and tested, revealing that approximately 32% of participants demonstrated high adherence to anti-diabetic drugs (score = 13). The P value was obtained using Fisher exact test for educational status, occupation, marital status, and the quantity and kind of anti-diabetic drugs was found to be 0.05. Only 32% of the respondents took their diabetes medication as prescribed, indicating the need to improve adherence among T2DM patients. The quantity and kind of anti-diabetic drugs, as well as the patients’ educational status, occupation, and marital status, all demonstrated a statistically significant relationship with medication adherence.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Adelufosi AO, Adebowale TO, Abayomi O, Mosanya JT (2012) Medication adherence and quality of life among Nigerian outpatients with schizophrenia. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 34:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2011.09.001
Ali M, Alemu T, Sada O (2017) Medication adherence and its associated factors among diabetic patients at Zewditu Memorial Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes 10(1):676. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-3025-7
Alqarni AM, Alrahbeni T, Qarni AA, Qarni HMA (2019) Adherence to diabetes medication among diabetic patients in the Bisha governorate of Saudi Arabia - a cross-sectional survey. Patient Prefer Adherence 13:63–71. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S176355
Arifulla M, John LJ, Sreedharan J, Muttappallymyalil J, Basha SA (2014) Patients’ adherence to anti-diabetic medications in a hospital at ajman, UAE. Malays J Med Sci 21:44–49
Arulmozhi S, Mahalakshmy T (2014) Self care and medication adherence among type 2 diabetics in Puducherry, southern India: a hospital based study. J Clin Diagn Res 8:UC01-3. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/7732.4256
Asiimwe D, Mauti GO, Kiconco R (2020) Prevalence and risk factors associated with type 2 diabetes in elderly patients aged 45–80 years at Kanungu District. J Diabetes Res 2020:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5152146
Baghikar S, Benitez A, FernandezPiñeros P, Gao Y, Baig AA (2019) Factors impacting adherence to diabetes medication among urban, low income Mexican-Americans with diabetes. J Immigr Minor Health 21:1334–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10903-019-00867-9
Basu S, Khobragade M, Kumar A, Raut DK (2015) Medical adherence and its predictors in Diabetes Mellitus patients attending government hospitals in the Indian Capital, Delhi, 2013: a cross sectional study. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 35:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-014-0232-9
Basu S, Garg S, Sharma N, Singh MM (2019) Enhancing medication adherence through improved patient-provider communication: The 6A’s of intervention. J Assoc Physicians India 67:69–71
de la Cruz JPS, Morales DLG, González-Castro TB, Tovilla-Zárate CA, Juárez-Rojop IE, López-Narváez L, Hernández-Díaz Y, Ble-Castillo JL, Pérez-Hernández N, Rodriguez-Perez JM (2020) Quality of life of Latin-American individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Prim Care Diabetes 14:317–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2019.09.003
Fadare J, Olamoyegun M, Gbadegesin BA (2015) Medication adherence and direct treatment cost among diabetes patients attending a tertiary healthcare facility in Ogbomosho, Nigeria. Malawi Med J 27:65–70. https://doi.org/10.4314/mmj.v27i2.7
Ghanbari A, Yekta ZP, Roushan ZA, Lakeh NM (2005) Assessment of factors affecting quality of life in diabetic patients in Iran. Public Health Nurs 22:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0737-1209.2005.220406.x
Goyal A, Kumar S, Nagpal M, Singh I, Arora S (2015) Potential of novel drug delivery systems for herbal drugs. Indian J Pharm Res Educ 45(3):225-235
Gu L, Wu S, Zhao S, Zhou H, Zhang S, Gao M, Qu Z, Zhang W, Tian D (2017) Association of social support and medication adherence in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(12):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121522
Horii T, Momo K, Yasu T, Kabeya Y, Atsuda K (2019) Determination of factors affecting medication adherence in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients using a nationwide claim-based database in Japan. PLoS ONE 14(10):e0223431. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223431
Mutyambizi C, Pavlova M, Hongoro C, Groot W (2020) Inequalities and factors associated with adherence to diabetes self-care practices amongst patients at two public hospitals in Gauteng, South Africa. BMC Endocr Disord 20:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-020-0492-y
Palathingal JT, Tom R, Naresh Babu V, Chacko SE, Kumar AS, Saravanan M (2020) Assessment of medication adherence in rural population with type 2 diabetes: study in a tertiary care hospital in south India. Int J Biomed Sci 16:21–29
Presley B, Groot W, Pavlova M (2019) Pharmacy-led interventions to improve medication adherence among adults with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Res Social Adm Pharm 15:1057–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2018.09.021
Sankar UV, Lipska K, Mini GK, Sarma PS, Thankappan KR (2015) The adherence to medications in diabetic patients in rural Kerala, India. Asia Pac J Public Health 27:NP513-23. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539513475651
Sankhyan A, Pawar PK (2013) Metformin loaded non-ionic surfactant vesicles: optimization of formulation, effect of process variables and characterization. Daru 21:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-7
Sinclair A, Saeedi P, Kaundal A, Karuranga S, Malanda B, Williams R (2020) Diabetes and global ageing among 65–99-year-old adults: findings from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 162:108078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108078
Tandon S, Chew M, Eklu-Gadegbeku CK, Shermock KM, Morisky DE (2015) Validation and psychometric properties of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in Type 2 diabetes patients in sub-Saharan Africa. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 110:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2015.10.001
Wu P, Liu N (2016) Association between patients’ beliefs and oral antidiabetic medication adherence in a Chinese type 2 diabetic population. Patient Prefer Adherence 10:1161–1167. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S105600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This collaboration work was carried out among all the authors. RS, PS, OS, and VS designed the study; OS and VS collected the data and performed the analysis; and OS with AP interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institution Ethics Committee, Chitkara University, Punjab (Ref No – IHEC/DHR/CU/PB/20/03/17).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Kumari, P., Prashar, A. et al. Assessment of medication adherence among type-2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care hospital of North India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 24951–24955 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17434-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17434-1