Abstract
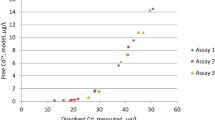
For the prediction of metal mixture ecotoxicity, the BLM approach is promising since it evaluates the amount of metals accumulated on the biotic ligand on the basis of water chemistry, i.e., species (major cations) competing with metals, and related toxicity. Based on previous work by Farley et al. (2015) (MMME research project), this study aimed at modeling toxicity of Cd:Cu mixtures (0:1 - 1:1 - 1:0 - 1:2 - 1:3 - 2:1 - 3:1 - 4:1 - 5:1 - 6:1) to the crustacean Daphnia magna(48-h immobilization tests) and the microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata (72-h growth inhibition tests). The 2012 version of the USGS model was chosen, assuming additivity of effects and accumulation of metals on a single site. The assumption that EDTA could contribute to toxicity through metals complexing was also tested, and potential effects due to reduction of ions Ca2+ absorption by metals were considered. Modeling started with parameter values of Farley et al. (2015) and some of these parameters were adjusted to fit modeled data on observed data. The results show that toxicity can be correctly predicted for the microalgae and that the hypothesis of additivity is verified. For daphnids, the prediction was roughly correct, but taking into account CuEDTA led to more realistic parameter values close to that reported by Farley et al. (2015). However, It seems that, for daphnids responses, metals interact either antagonistically or synergistically depending on the Cu:Cd ratio. Furthermore, synergy could not be explained by additional effects linked to a reduction of Ca absorption since this reduction, mainly due to Cd, increased inversely to synergy. Finally, the USGS model applied to our data was able to predict Cu:Cd mixture toxicity to microalgae and daphnids, giving rise to estimated EC50s roughly reflecting EC50s calculated from observed toxicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon request from the first author.
References
Balistrieri LS, Mebane CA (2014) Predicting the toxicity of metal mixtures. Sci Total Environ 466–467:788–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.034
Balistrieri LS, Mebane CA, Schmidt TS, Keller WB (2015) Expanding metal mixture toxicity models to natural stream and lake invertebrate communities. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:761–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2824
Barata C, Baird DJ, Nogueira AJA, Soares AMVM, Riva MC (2006) Toxicity of binary mixtures of metals and pyrethroid insecticides to Daphnia magna Straus. Implications for multi-substance risks assessment. Aquat Toxicol 78:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.01.013
Baudrot V, Peux S, Ducrot V, Pavé A, Charles S (2018) Nouvelles perspectives pour comparer et choisir les modèles TKTD pour la survie basés sur une étude interlaboratoire pour Lymnaea stagnalis exposée au Cd. Environ Sci Technol 52:1582–1590. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05464
Breault RF, Colman JA, Aiken GR, McKnight DM (1996) Copper speciation and binding by organic matter in copper-contaminated streamwater. Environ Sci Technol 30:3477–3486. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9601301
Campbell PG, Errécalde O, Fortin C, Hiriart-Baer VP, Vigneault B (2002) Metal bioavailability to phytoplankton—applicability of the biotic ligand model. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol 133:189–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1532-0456(02)00104-7
Charles S, Veber P, Delignette-Muller ML (2018) MOSAIC:a web-interface for statistical analyses in ecotoxicology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:11295–11302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9809-4
Clément B, Triffault-Bouchet G, Delhaye H (2013) Development and optimisation of an aquatic laboratory microcosm for ecotoxicological risk assessment. In: Microcosms: Ecology, Biological Implications and Environmental Impact. Nova Publishers. https://novapublishers.com/shop/microcosms-ecology-biological--implications-and-environmental-impact/
Clément B, Triffault-Bouchet G, Delhaye H (2014) Comparison of laboratory batch and flow-through microcosm bioassays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 108:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.07.015
Clifford M, McGeer JC (2010) Development of a biotic ligand model to predict the acute toxicity of cadmium to Daphnia pulex. Aquat Toxicol 98:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.01.001
De Laender F, Janssen CR, De Schamphelaere KAC (2009)Non-simultaneous ecotoxicity testing of single chemicals and their mixture results in erroneous conclusions about the joint action of the mixture. Chemosphere 76:428–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.01.001
De Schamphelaere KAC, Heijerick DG, Janssen CR (2002) Refinement and field validation of a biotic ligand model predicting acute copper toxicity to Daphnia magna. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 133:243–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(02)00087-X
De Schamphelaere KAC, Vasconcelos FM, Heijerick DG, Tack FMG, Delbeke K, Allen HE, Janssen CR (2003) Development and field validation of a predictive copper toxicity model for the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:24–54. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-499
Di Toro DM, Allen HE, Bergman HL, Meyer JS, Paquin PR, Santore RC (2001) Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals. 1. Technical basis. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2383–2396. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620201034
Elendt BP, Bias WR (1990) Trace nutrient deficiency in Daphnia magna cultured in standard medium for toxicity testing. Effects of the optimization of culture conditions on life history parameters of D. magna. Water Res 24:1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(90)90180-E
Farley KJ, Meyer JS (2015) Metal mixture modeling evaluation project:3. Lessons learned and steps forward. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:821–832. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2837
Farley KJ, Meyer JS, Balistrieri LS, De Schamphelaere KAC, Iwasaki Y, Janssen CR, Kamo M, Lofts S, Mebane CA, Naito W, Ryan A, Santore R, Tipping E (2015) Metal mixture modeling evaluation project:2. Comparison of four modeling approaches. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:741–753. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2820
Gessner PK (1995) Isobolographic analysis of interactions: an update on applications and utility. Toxicology. 105:161–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(95)03210-7
Gopalapillai Y, Hale B (2015) Evaluating the concentration addition approach for describing expected toxicity of a ternary metal mixture (Ni, Cu, Cd) using metal speciation and response surface regression. Environ Chem 13:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN15124_AC
Guilhermino L, Diamantino TC, Ribeiro R, Gonçalves F, Soares AMVM (1997) Suitability of test media containing EDTA for the evaluation of acute metal toxicity to Daphnia magna Straus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:292–295. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1997.1599
Hatano A, Shoji R (2008) Toxicity of copper and cadmium in combinations to duckweed analyzed by the biotic ligand model. Environ Toxicol 23:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox
Hollis L, McGeer JC, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2000) Protective effects of calcium against chronic waterborne cadmium exposure to juvenile rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2725–2734. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620191117
ISO (2012a) Qualité de l’eau. Essai d’inhibition de la croissance des algues d’eau douce avec des algues vertes unicellulaires. NF EN ISO 8692, 23 p.
ISO (2012b) Qualité de l’eau. Détermination de l’inhibition de la mobilité de Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea) — Essai de toxicité aiguë. NF EN ISO 6341, 24 p.
Iwasaki Y, Kamo M, Naito W (2015) Testing an application of the biotic ligand model to predict acute toxicity of metal mixtures to rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:754–760. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2780
Jho EH, An J, Namand K (2011) Extended biotic ligand model for prediction of mixture toxicity of Cd and Pb using single metal toxicity data. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:1697–1703. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.556
Meyer JS, Farley KJ, Garman ER (2015a) Metal mixture modeling evaluation: 1. Background. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:726–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2792
Meyer JS, Ranville JF, Pontasch M, Gorsuch JW, Adams WJ (2015b) Acute toxicity of binary and ternary mixtures of Cd, Cu, and Zn to Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:799–808. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2787
Morel FMM (1983) Principles of Aquatic Chemistry. Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY, pp 301–308
Niyogi S, Wood CM (2004) Biotic ligand model, a flexible tool for developing site-specific water quality guidelines for metals. Environ Sci Technol 38:6177–6192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0496524
Paquin PR, Santore RC, Wu KB, Kavvadas CD, Di Toro DM (2000) The biotic ligand model: a model of the acute toxicity of metals to aquatic life. Environ Sci Pol 3:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1462-9011(00)00047-2
Playle RC, Dixon DG, Burnison K (1993) Copper and cadmium binding to fish gills: estimates of metals-gill stability constants and modelling of metal accumulation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:2678–2687. https://doi.org/10.1139/f93-291
Rodea-Palomares I, Gonzalez-Garcia C, Leganes F, Fernandez-Pinas F (2009) Effect of pH, EDTA, and anions on heavy metal toxicity toward a bioluminescent cyanobacterial bioreporter. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9280-9
Santore RC, Ryan AC (2015) Development and application of a multimetal multibiotic ligand model for assessing toxicity of metal mixtures. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:777–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(02)00106-0
Sillanpää M, Oikari A (1996) Assessing the impact of complexation by EDTA and DTPA on heavy metal toxicity using microtox bioassay. Chemosphere 32:1485–1497. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(96)00057-4
Sørensen H, Cedergreen N, Skovgaard IM, Streibig JC (2007) An isobole-based statistical model and test for synergism/antagonism in binary mixture toxicity experiments. Environ Ecol Stat 14:383–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-007-0022-3
Tan QG, Wang WX (2008) The influences of ambient body calcium on cadmium and zinc accumulation in Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1605–1613. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-592.1
Tubbing DMJ, Admiraal W, Cleven RFMJ, Iqbal M, van de Meent D, Verweij W (1994) The contribution of complexed copper to the metabolic inhibition of algae and bacteria in synthetic media and river water. Water Res 28:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90117-1
Verbost P, Flik G, Lock RA, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1987) Cadmium inhibition of Ca2+ uptake in rainbow trout gills. Am J Physiol Regul 253:216–221. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.2.R216
Verbost PM, Flik G, Lock RA, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1988) Cadmium inhibits plasma membrane calcium transport. J Membr Biol 102:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870448
Verbost PM, Van Rooij J, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1989) The movement of cadmium through freshwater trout branchial epithelium and its interference with calcium transport. J Exp Biol 145:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870448
Acknowledgements
This work was performed within the framework of the EUR H2O’Lyon (ANR-17-EURE-0018) of Université de Lyon (UdL), within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR). The authors thank Denise BLANC-BISCARAT(DEEP-INSA, Lyon, France) for her contribution on chemical modeling.
Funding
This work was funded by ENTPE and the French Ministry of Ecology (salaries, experimental environment).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Experimental work and preliminary data analyses were carried out by Valentin Bertrand and Bernard Clement. Modeling was done by Vincent Felix and Bernard Clement. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Bernard Clement and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that they submit original work as a whole, not published elsewhere, that the results are not falsified, and that proper acknowledgements to other works have been given.
Consent to participate
All listed authors are volunteer to participate to this publication.
Consent to publication
All listed authors have approved the manuscript before submission.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bruno Nunes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clément, B., Felix, V. & Bertrand, V. The toxicity of cadmium-copper mixtures on daphnids and microalgae analyzed using the Biotic Ligand Model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 29285–29295 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16516-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16516-4