Abstract
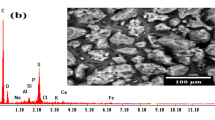
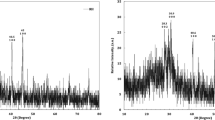
Development of efficient sorbents for selective removing and recovery of uranium from radioactive wastewaters is highly important in nuclear fuel industries from the standpoint of resource sustainability and environmental safety issues. In this study, carbon powder waste was modified by various chemical activating agents under atmosphere of nitrogen gas at 725 °C to prepare an efficient sorbent for removal and recovery of uranium ions from radioactive wastewaters of nuclear fuel conversion facility. Activation of the carbon powder with KOH, among different activators, provided maximum porosity and surface area. The activated samples were modified by reacting with ammonium persulfate in sulfuric acid solution to generate surface functional groups. The synthetized sorbents were characterized with FT-IR, XRD, BET, and SEM-EDS techniques. The effects of solution pH, contact time, initial uranium concentration, and temperature on the sorption capacity of the sorbent with respect to U(VI) from wastewater were investigated by batch method, followed by optimizing the effect of influential parameters by experimental design using central composite design. The sorption of UO22+ ions on the sorbents follows the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models. Maximum sorption capacity for U(VI) was 192.31 mg g−1 of the modified sorbent at 35 °C. Thermodynamic data showed that sorption of U(VI) on the sorbent was through endothermic and spontaneous processes. The sorption studies on radioactive effluents of the nuclear industry demonstrated that the modified sorbent had a favorable selectivity for uranium removal in the presence of several other metal ions.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the policies of the nuclear fuel factory in Isfahan but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abutaleb A, Tayeb AM, Mahmoud MA, Daher AM, Desouky OA, Bakather OY, Farouq R (2020) Removal and recovery of U(VI) from aqueous effluents by flax fiber: adsorption, desorption and batch adsorber proposal. J Adv Res 22:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.011
Bandosz TJ, Jagiello J, Schwarz JA (1992) Comparison of methods to assess surface acidic groups on activated carbons. Anal Chem 64:891–895. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00032a012
Basile M, Unruh DK, Streicher L, Forbes TZ (2017) Spectral analysis of the uranyl squarate and croconate system: evaluating differences between the solution and solid-state phases. Cryst Growth Des 17:5330–5341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.7b00838
Boehm HP (2002) Surface oxides on carbon and their analysis: a critical assessment. Carbon 40:145–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00165-8
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Chaisit S, Chanlek N, Khajonrit J, Sichumsaeng T, Maensiri S (2020) Preparation, characterization, and electrochemical properties of KOH-activated carbon from cassava root Materials Research Express 7:105605. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abbf84
Cheng Y, He P, Dong F, Nie X, Ding C, Wang S, Zhang Y, Liu H, Zhou S (2019) Polyamine and amidoxime groups modified bifunctional polyacrylonitrile-based ion exchange fibers for highly efficient extraction of U(VI) from real uranium mine water. Chem Eng J 367:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.149
Chung Y, Yun Y-M, Kim Y-J, Hwang YS, Kang S (2018) Preparation of alumina-zirconia (Al-Zr) ceramic nanofiltration (NF) membrane for the removal of uranium in aquatic system. Water Supply 19:789–795. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.123
Côrtes LN et al. (2019) Biochars from animal wastes as alternative materials to treat colored effluents containing basic red 9 Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 7:103446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103446
Deng H, Z-j L, Wang L, L-y Y, J-h L, Z-y C, Z-f C, W-q S (2019) Nanolayered Ti3C2 and SrTiO3 composites for photocatalytic reduction and removal of uranium(VI). ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:2283–2294. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00205
Duan J, Ji H, Xu T, Pan F, Liu X, Liu W, Zhao D (2021) Simultaneous adsorption of uranium(VI) and 2-chlorophenol by activated carbon fiber supported/modified titanate nanotubes (TNTs/ACF): effectiveness and synergistic effects. Chem Eng J 406:126752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126752
Elsayed NH, Alatawi RAS, Monier M (2021) Amidoxime modified chitosan based ion-imprinted polymer for selective removal of uranyl ions. Carbohydr Polym 256:117509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117509
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2011) Utilization of rice husks as a feedstock for preparation of activated carbon by microwave induced KOH and K2CO3 activation Bioresource Technology 102:9814-9817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.102
Ganguly P, Sarkhel R, Das P (2020) Synthesis of pyrolyzed biochar and its application for dye removal: batch, kinetic and isotherm with linear and non-linear mathematical analysis. Surf Interfaces 20:100616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100616
Ghanim B, O’Dwyer TF, Leahy JJ, Willquist K, Courtney R, Pembroke JT, Murnane JG (2020) Application of KOH modified seaweed hydrochar as a biosorbent of vanadium from aqueous solution: characterisations, mechanisms and regeneration capacity. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104176
Ghasemi Torkabad M, Keshtkar AR, Safdari SJ (2017) Comparison of polyethersulfone and polyamide nanofiltration membranes for uranium removal from aqueous solution. Prog Nucl Energy 94:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2016.10.005
Guo X, Liu Q, Liu J, Zhang H, Yu J, Chen R, Song D, Li R, Wang J (2019) Magnetic metal-organic frameworks/carbon dots as a multifunctional platform for detection and removal of uranium. Appl Surf Sci 491:640–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.108
Hassani S, Shirani M, Semnani A, Hassani M, Firooz A (2017) Removal of Congo red by magnetic nano-alumina using response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Desalination Water Treat 62:241–251. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.0018
Huang Y, Zheng H, Li H, Zhao C, Zhao R, Li S (2020) Highly selective uranium adsorption on 2-phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid-decorated chitosan-coated magnetic silica nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 388:124349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124349
Ishag A, Li Y, Zhang N, Wang H, Guo H, Mei P, Sun Y (2020) Environmental application of emerging zero-valent iron-based materials on removal of radionuclides from the wastewater: a review. Environ Res 188:109855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109855
Leon CAL, Solar JM, Calemma V, Radovic LR (1992) Evidence for the protonation of basal plane sites on carbon. Carbon 30:797–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(92)90164-R
Li B, Hu J, Xiong H, Xiao Y (2020a) Application and properties of microporous carbons activated by ZnCl2: adsorption behavior and activation mechanism. ACS Omega 5:9398–9407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00461
Li F-F, Cui W-R, Jiang W, Zhang C-R, Liang R-P, Qiu J-D (2020b) Stable sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic framework for detection and efficient adsorption of uranium from radioactive wastewater. J Hazard Mater 392:122333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122333
Liew RK, Chong MY, Osazuwa OU, Nam WL, Phang XY, Su MH, Cheng CK, Chong CT, Lam SS (2018) Production of activated carbon as catalyst support by microwave pyrolysis of palm kernel shell: a comparative study of chemical versus physical activation. Res Chem Intermed 44:3849–3865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3388-y
Liu C, Dong Z, Yu C, Gong J, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Liu Y (2021a) Study on photocatalytic performance of hexagonal SnS2/g-C3N4 nanosheets and its application to reduce U(VI) in sunlight. Appl Surf Sci 537:147754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147754
Liu Y, Huo Y, Wang X, Yu S, Ai Y, Chen Z, Zhang P, Chen L, Song G, Alharbi NS (2021b) Impact of metal ions and organic ligands on uranium removal properties by zeolitic imidazolate framework materials. J Clean Prod 278:123216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123216
Lu X, Zhang D, Tesfay Reda A, Liu C, Yang Z, Guo S, Xiao S, Ouyang Y (2017) Synthesis of amidoxime-grafted activated carbon fibers for efficient recovery of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:11936–11947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b02690
Mahmoud ME, Khalifa MA, El Wakeel YM, Header MS, Abdel-Fattah TM (2017) Engineered nano-magnetic iron oxide-urea-activated carbon nanolayer sorbent for potential removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution. J Nucl Mater 487:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.01.046
Marciniak M, Goscianska J, Pietrzak R (2018) Physicochemical characterization of ordered mesoporous carbons functionalized by wet oxidation. J Mater Sci 53:5997–6007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1960-2
Marsh H, Reinoso FR (2006) Activated carbon. Elsevier
Marsh H, Yan DS, O'Grady TM, Wennerberg A (1984) Formation of active carbons from cokes using potassium hydroxide Carbon 22:603-611. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(84)90096-4
Mokhine ND, Mathuthu M, Stassen E (2020) Recovery of uranium from residue generated during Mo-99 production, using organic solvent extraction. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 115:102822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.102822
Mullick A, Moulik S, Bhattacharjee S (2018) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by low-cost rice husk-based activated carbon: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Indian Chem Eng 60:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/00194506.2017.1288173
Naderi P, Shirani M, Semnani A, Goli A (2018) Efficient removal of crystal violet from aqueous solutions with Centaurea stem as a novel biodegradable bioadsorbent using response surface methodology and simulated annealing: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.091
Nnadozie EC, Ajibade PA (2020) Data for experimental and calculated values of the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) on APTES functionalized magnetite biochar using Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin equations. Data Brief 32:106292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.106292
Om Prakash M, Raghavendra G, Ojha S, Panchal M (2021) Characterization of porous activated carbon prepared from arhar stalks by single step chemical activation method. Mater Today Proc 39:1476–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.370
Qu J, Liu Y, Cheng L, Jiang Z, Zhang G, Deng F, Wang L, Han W, Zhang Y (2021) Green synthesis of hydrophilic activated carbon supported sulfide nZVI for enhanced Pb(II) scavenging from water: characterization, kinetics, isotherms and mechanisms. J Hazard Mater 403:123607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123607
Ribeiro C, Scheufele FB, Espinoza-Quiñones FR, Módenes AN, Vieira MGA, Kroumov AD, Borba CE (2018) A comprehensive evaluation of heavy metals removal from battery industry wastewaters by applying bio-residue, mineral and commercial adsorbent materials. J Mater Sci 53:7976–7995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2150-6
Saleh TA, Naeemullah TM, Sarı A (2017) Polyethylenimine modified activated carbon as novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of uranium from aqueous solution. Chem Eng Res Des 117:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.10.030
Saputra A, Swantomo D, Ariyanto T, Sulistyo H (2019) Uranium removal from wastewater using Mg(OH)2-impregnated activated carbon. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4269-8
Song S, Wang K, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Zhang R, Chen J, Wen T, Wang X (2019) Self-assembly of graphene oxide/PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for uranium immobilization from wastewater. Environ Pollut 250:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.020
Suárez L, Centeno TA (2020) Unravelling the volumetric performance of activated carbons from biomass wastes in supercapacitors. J Power Sources 448:227413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227413
Taha MH, El-Maadawy MM, Hussein AEM, Youssef WM (2018) Uranium sorption from commercial phosphoric acid using kaolinite and metakaolinite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 317:685–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5951-9
Tan Y, Li L, Zhang H, Ding D, Dai Z, Xue J, Liu J, Hu N, Wang Y (2018) Adsorption and recovery of U(VI) from actual acid radioactive wastewater with low uranium concentration using thioacetamide modified activated carbon from liquorice residue. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 317:811–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5952-8
Tsai W-T, Bai Y-C, Lin Y-Q, Lai Y-C, Tsai C-H (2020) Porous and adsorption properties of activated carbon prepared from cocoa pod husk by chemical activation. Biomass Conv Bioref 10:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00403-7
Wang C, Huang D, He F, Jin T, Huang B, Xu J, Qian Y (2020) Efficient removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by triethylenetetramine-functionalized single-walled carbon nanohorns. ACS Omega 5:27789–27799. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02715
Wazir AH, Haq I, Manan A, Khan A (2020) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from coal by chemical activation with KOH. Int J Coal Prep Util:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/19392699.2020.1727896
Wu Q, Lv H, Zhao L (2020) Applications of carbon nanomaterials in chiral separation. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 129:115941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115941
Yagmur E, Gokce Y, Tekin S, Semerci NI, Aktas Z (2020) Characteristics and comparison of activated carbons prepared from oleaster (Elaeagnus angustifolia L.) fruit using KOH and ZnCl2. Fuel 267:117232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117232
Yi Z, Liu J, Zeng R, Liu X, Long J, Huang B (2020) Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution by Camellia oleifera shell-based activated carbon: adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Water Sci Technol 82:2592–2602. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.504
Yildirim A, Baran MF, Acay H (2020) Kinetic and isotherm investigation into the removal of heavy metals using a fungal-extract-based bio-nanosorbent. Environ Technol Innov 20:101076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101076
Zahran F, El-Maghrabi HH, Hussein G, Abdelmaged SM (2019) Fabrication of bentonite based nanocomposite as a novel low cost adsorbent for uranium ion removal. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 11:100205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.100205
Zhang C, Li X, Chen Z, Wen T, Huang S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Wang X (2018) Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbonaceous materials and their highly efficient capture of uranium from solutions. Sci China Chem 61:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-017-9132-7
Zhang J, Chen X, Zhou J, Luo X (2020a) Uranium biosorption mechanism model of protonated Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Hazard Mater 385:121588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121588
Zhang M, Yuan M, Zhang M, Wang M, Chen J, Li R, Qiu L, Feng X, Hu J, Wu G (2020b) Efficient removal of uranium from diluted aqueous solution with hydroxypyridone functionalized polyethylene nonwoven fabrics. Radiat Phys Chem 171:108742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108742
Zhong X, Liang W, Wang H, Xue C, Hu B (2021) Aluminum-based metal-organic frameworks (CAU-1) highly efficient UO22+ and TcO4− ions immobilization from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 407:124729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124729
Zhuang S, Wang J (2020) Poly amidoxime functionalized carbon nanotube as an efficient adsorbent for removal of uranium from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 319:114288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114288
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the supports provided by the Graduate Office of the University of Shahrekord.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Majid Mohammad Nezhad: investigation, writing-original draft, conceptualization and methodology. Abolfazl Semnani and Nahid Tavakkoli: conceptualization, editing, and supervision. Mahboube Shirani: data curation and software, writing of original draft.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nezhad, M.M., Semnani, A., Tavakkoli, N. et al. Efficient removal and recovery of uranium from industrial radioactive wastewaters using functionalized activated carbon powder derived from zirconium carbide process waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57073–57089 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14638-3