Abstract
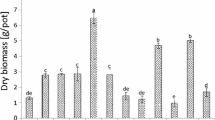
Contamination of soils by nickel (Ni) has become a serious environmental problem throughout the world, and this substance wields dangerous effects on the ecosystem and food chain. A pot experiment was conducted to examine the effect of rice straw (RS), rice straw biochar (BI), and calcite (CC) at 1% and 2% application rates in a Ni-contaminated soil. The objective was to potentially stabilize Ni and reduce its bioavailability to spinach (Spinacia Oleracea L.). Spinach plants were grown in a Ni-contaminated Ultisol (commonly known as a red clay soil). Plant growth parameter results indicated that a BI 2% application rate significantly increased the root and shoots dry biomass increased by 1.7- and 6.3-fold, respectively, while essential nutrients were enhanced in the spinach plant compared to those in the untreated soil (CK). Moreover, adding amendments significantly decreased CaCl2 extractable Ni by 62.5% 94.1%, and 87.2%, while the toxicity characteristics leaching procedure (TCLP) fell by 26.7%, 47.8%, and 41.7% when using RS, BI, and CC, respectively, at 2% compared to CK. The Ni concentrations in the spinach roots declined by 51.6%, 73.3%, and 68.9%, and in the shoots reduced by 54.1%, 76.7%, and 70.8% for RS, BI, and CC, at a 2% application rate, respectively. Bio-concentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF) dropped significantly by as much as 72.7% and 20%, respectively, for BI 2% application rate. Results of the present study clearly indicated that biochar potential soil amendments for Ni stabilization, thereby reducing its bioavailability in the Ni-contaminated soil. This process enhanced the safety of food to be consumed and mitigated security risks.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are included within the manuscript.
References
Ali U, Shaaban M, Bashir S, Fu Q, Zhu J, Shoffikul IM, Hu H (2020) Effect of rice straw, biochar and calcite on maize plant and Ni bio-availability in acidic Ni contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 259:109674
Ali U, Shaaban M, Bashir S, Gao R, Fu Q, Zhu J, Hu H (2019) Rice straw, biochar and calcite incorporation enhance nickel (Ni) immobilization in contaminated soil and Ni removal capacity. Chemosphere 244:125418
Azhar M, Zia Ur Rehman M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Naeem A, Ayub MA, Anwar UL, Haq M, Iqbal A, Rizwan M (2019) Comparative effectiveness of different biochars and conventional organic materials on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium accumulation in cereals. Chemosphere 227:72–81
Bashir S, Salam A, Chhajro MA, Fu Q, Khan MJ, Zhu J, Shaaban M, Kubar KA, Ali U, Hu H (2018a) Comparative efficiency of rice husk-derived biochar (RHB) and steel slag (SS) on cadmium (Cd) mobility and its uptake by Chinese cabbage in highly contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediation 20(12):1221–1228. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1448364
Bashir S, Hussain Q, Shaaban M, Hu H (2018b) Efficiency and surface characterization of different plant derived biochar for cadmium (Cd) mobility, bioaccessibility and bioavailability to Chinese cabbage in highly contaminated soil. Chemosphere 211:632–639
Bashir S, Ali U, Shaaban M, Gulshan AB, Iqbal J, Khan S, Husain A, Niaz A, Mehmood S, Kamran M, Hu H (2020) Role of sepiolite for cadmium (Cd) polluted soil restoration and spinach growth in wastewater irrigated agricultural soil. J Environ Manag 258:110020
Boostani HR, Najafi-Ghiri M, Mirsoleimani A (2019) The effect of biochars application on reducing the toxic effects of nickel and growth indices of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) in a calcareous soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:1751–1760
Ding Y, Liu YG, Liu SB, Li ZW, Tan XF, Huang XX, Zeng GM, Zhou L, Zheng BH (2016) Biochar to improve soil fertility. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 36(36):1–18
El-Naggar A, Raja PAU, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Ok YS (2018) Potential of biochar to immobilize nickel in contaminated soils. In: Nickel in Soils and Plants, pp 293–318
Feng YY, Hua HEX, Ren G, Liang MA, Sheng YY (2014) Effects of rice straw and its biochar addition on soil labile carbon and soil organic carbon. J Integr Agric 13(3):491–498
Gao R, Hu H, Fu Q, Li Z, Xing Z, Ali U, Zhu J, Liu Y (2020) Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu contaminated soil by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate: Speciation transformation, risk evaluation and mechanism inquiry. Sci Total Environ 730:139119
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size Analysis. Part 1. Physical Mineralogical Methods, pp. 383–411
Hafeez A, Ali S, Ma XL, Tung SA, Shah AN, Ahmad S, Chattha MS, Souliyanonh B, Zhang Z, Yang GZ (2019) Photosynthetic characteristics of boll subtending leaves are substantially influenced by applied K to N ratio under the new planting model for cotton in the Yangtze River Valley. Field Crop Res 237:43–52
Hamid Y, Tang L, Lu M, Hussain B, Zehra A, Khan MB, He Z, Gurajala HK, Yang X (2019) Assessing the immobilization efficiency of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium phytoavailability to wheat. J Soils Sediments 19:3708–3717
Herath I, Kumarathilaka P, Navaratne A, Rajakaruna N, Vithanage MJ (2015) Immobilization and phytotoxicity reduction of heavy metals in serpentine soil using biochar. J. Soils Sediments 15:126–138
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Biomass Bioenergy 57:196–204
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Huang L, Riaz M, Bashir S, Mustafa A, Abbasi GH, Xue B, Ali U (2020) Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J Plant Growth Regul 39:266–281
Khan MN, Lan Z, Sial TA, Zhao Y, Haseeb A, Jianguo Z, Zhang A, Hill RL (2019) Straw and biochar effects on soil properties and tomato seedling growth under different moisture levels. Arch Agron Soil Sci 65(12):1704–1719. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1575510
Khan WU, Ramzani PMA, Anjum S, Abbas F, Iqbal M, Yasar A, Ihsan MZ, Anwar MN, Baqar M, Tauqeer HM, Virk ZA, Khan SA (2017) Potential of miscanthus biochar to improve sandy soil health, in situ nickel immobilization in soil and nutritional quality of spinach. Chemosphere 185:1144–1156
Lahori AH, Zhang Z, Guo Z, Mahar A, Li R, Awasthi MK, Sial TA, Kumbhar F, Wang P, Shen F, Zhao J, Huang H (2017) Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:313–323
Li F, Cao X, Zhao L, Wang J, Ding Z (2014) Effects of mineral additives on biochar formation: carbon retention, stability, and properties. Environ Sci Technol 48:11211–11217
Lu RK (1999) Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry. Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House, Beijing (Chinese)
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Lahori AH, Awasthi MK, Wang Z, Guo Z, Wang Q, Feng S, Li R, Zhang Z (2017) (Im)mobilization of soil heavy metals using CaO, FA, sulfur, and Na2S: a 1-year incubation study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:607–620
MEEPRC (2018) (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China). Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. (GB 15618-2018) (in Chinese)
Mosa A, El-Banna MF, Gao B (2016) Biochar filters reduced the toxic effects of nickel on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) grown in nutrient film technique hydroponic system. Chemosphere 149:254–262
Naeem MA, Khalid M, Aon M, Abbas G, Tahir M, Amjad M, Murtaza B, Yang A, Akhtar SS (2017) Effect of wheat and rice straw biochar produced at different temperatures on maize growth and nutrient dynamics of a calcareous soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:2048–2061
Nawab J, Khan N, Ahmed R, Khan S, Ghani J, Rahman Z, Khan F, Wang XP, Muhammad J, Sher H (2019) Influence of different organic geo-sorbents on Spinacia oleracea grown in chromite mine-degraded soil: a greenhouse study. J. Soils Sediments 19:2417–2432
Pariona Ameber (2017) World leaders in spinach production." World atlas, Apr. 25, 2017, worldatlas.com/articles/world-leaders-in-spinach-production.html
Ramzani PMA, Iqbal M, Kausar S, Ali S, Rizwan M, Virk ZA (2016) Effect of different amendments on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth, yield, nutrient uptake and grain quality in Ni-contaminated soil Environ. Sci Pollut Res 23:18585–18595
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ali S, Fatima N, Yousaf B, Naeem A, Sabir M, Ahmad HR, Ok YS (2016) Contrasting effects of biochar, compost and farm manure on alleviation of nickel toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.) in relation to plant growth, photosynthesis and metal uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:218–225
Rehman MZU, Khalid H, Akmal F, Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Iqbal M, Khalid MU, Azhar M (2017) Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ Pollut 227:560–568
Rizwan M, Mostofa MG, Ahmad MZ, Imtiaz M, Mehmood S, Adeel M, Dai Z, Li Z, Aziz O, Zhang Y, Tu S (2018) Nitric oxide induces rice tolerance to excessive nickel by regulating nickel uptake, reactive oxygen species detoxification and defense-related gene expression. Chemosphere 19:23–35
Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Chhajro MA, Huang G, Fu Q, Zhu J, Aziz O, Hu H (2016) Influence of pyrolytic and non-pyrolytic rice and castor straws on the immobilization of Pb and Cu in contaminated soil. Environ Technol 37:2679–2686
Salam A, Bashir S, Khan I, Hu H (2019) Two years impacts of rapeseed residue and rice straw biochar on Pb and Cu immobilization and revegetation of naturally co-contaminated soil. Appl Geochem 105:97–104
Sehrish AK, Aziz R, Hussain MM, Rafiq MT, Rizwan M, Muhammad N, Rafiq MK, Sehar A, Din J, Al-Wabel MI, Ali S (2019) Effect of poultry litter biochar on chromium (Cr) bioavailability and accumulation in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) grown in Cr-polluted soil. Arab J Geosci 12:12–57
Shaaban M, Van Zwieten L, Bashir S, Younas A, Nunez-Delgado A, Chhajro MA, Kubar KA, Ali U, Rana MS, Mehmood MA, Hu R (2018) A concise review of biochar application to agricultural soils to improve soil conditions and fight pollution. J Environ Manag 228:429–440
Shahbaz AK, Iqbal M, Jabbar A, Hussain S, Ibrahim M (2018a) Assessment of nickel bioavailability through chemical extractants and red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) in an amended soil: Related changes in various parameters of red clover. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:116–127
Shahbaz AK, Lewińska K, Iqbal J, Ali Q, Iqbal M, Abbas F, Tauqeer HM, Ramzani PMA (2018b) Improvement in productivity, nutritional quality, and antioxidative defense mechanisms of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in nickel contaminated soil amended with different biochar and zeolite ratios. J Environ Manag 218:256–270
Shahbaz AK, Ramzani PM, Saeed R, Turan V, Iqbal M, Lewinska K, Abbas F, Saqib M, Tauqeer HM, Iqbal M, Fatima M, Rahman MU (2019) Effects of biochar and zeolite soil amendments with foliar proline spray on nickel immobilization, nutritional quality and nickel concentrations in wheat. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:182–191
Shaheen SM, Mladenovic S, Wang SL, Niazi NK, Tsadilas C, Ok YS, Rinklebe J (2019) Nickel mobilization/immobilization and phytoavailability in soils as affected by organic and inorganic amendments. Nickel Soils Plants:265–292
Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Rehman A, Cheema SA, Fahad S, Rehman S, Sharma A (2018) Nickel whether toxic or essential for plants and environment-A review. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:641–651
Shen Z, Som AM, Wang F, Jin F, McMillan O, Al-Tabbaa A (2016) Long-term impact of biochar on the immobilisation of nickel (II) and zinc (II) and the revegetation of a contaminated site. SciTotal Environ 542:771–776
Shen Z, Zhang Y, McMillan O, Jin F, Al-Tabbaa A (2017) Characteristics and mechanisms of nickel adsorption on biochars produced from wheat straw pellets and rice husk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12809–12819
Xu CY, Hosseini Bai S, Hao Y, Rachaputi RC, Wang H, Xu Z, Wallace H (2015) Effect of biochar amendment on yield and photosynthesis of peanut on two types of soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6112–6125
Younis U, Athar M, Malik A, Shah MHR, Mahmood S (2015) Biochar impact on physiological and biochemical attributes of spinach Spinacia oleracea (L.) in nickel contaminated soil. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 1(3):245–254
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from the National Sci-Tech Support Plan of China (2015BAD05B02).
Funding
The authors would like to thank National Science and Technology Support Program of China (2015BAD05B02) for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, UA and HH; formal analysis, SB and MS; investigation, UA and MSR; methodology, UA, LQ, QF, JZ; software, UA and SB; writing original draft, UA; writing—review and editing, UA, HH, and MAC; funding acquisition, resources, HH. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, U., Shaaban, M., Bashir, S. et al. Potential of organic and inorganic amendments for stabilizing nickel in acidic soil, and improving the nutritional quality of spinach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57769–57780 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14611-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14611-0