Abstract
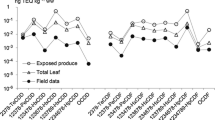
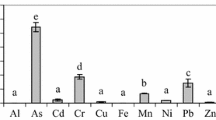
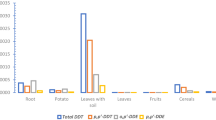
This study is the first research attempt to assess the environmental risks of an agricultural area contaminated with the p,p′-DDT and its metabolites (DDX) on human and terrestrial species through exposure to soil and agricultural products, simultaneously. The study was carried out for a DDX-contaminated agricultural area in Turkey. Soil samples obtained in two different harvest applications were analyzed in terms of DDX levels. Similarly, stem, leaf, and fruit samples of an agricultural product grown on the same soils were analyzed. Using the results of these analyses, DDX intake values were calculated for 5 different human receptor groups, 4 different bird species, and 4 different mammal species, and the risk values were calculated by using a stochastic approach based on a Monte Carlo simulation. Findings indicated a substantial level of carcinogenic risk in the human receptor groups. Furthermore, a significant risk of reproductive toxicity was determined for the birds and mammals. The findings prominently showed that these risks can develop not only through exposure to DDX-contaminated soils but also through the consumption of plants grown on these soils.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14449-6
References
Aksoy A, Dervisoglu M, Guvenc D, Gul O, Yazici F, Atmaca E (2013) Levels of organochlorine pesticide residues in butter samples collected from the Black Sea Region of Turkey. B Environ Contam Tox 90(1):110–115
Ali SN, Baqar M, Mumtaz M, Ashraf U, Anwar MN, Qadir A, Ahmad SR, Nizami AS, Jun H (2020) Organochlorine pesticides in the surrounding soils of POPs destruction facility: source fingerprinting, human health, and ecological risks assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7328–7340
Arikan K, Turan SL (2020) Organochlorine pesticide residues in feathers of four bird species from western part of Turkey. Turk J Zool 44(5):401–407
Bhandari G, Atreya K, Scheepers PT, Geissen V (2020) Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 253:126594
Bulut S, Akkaya L, Gok V, Konuk M (2010) Organochlorine pesticide residues in butter and kaymak in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. J Anim Vet Adv 9(22):2797–2801
Canadian Council for Ministers of the Environment (CCME) (1999) Canadian tissue residue guidelines for the protection of wildlife consumers of aquatic biota: DDT (total). In: Canadian environmental quality guidelines Winnipeg
Cok I, Durmaz TC, Durmaz E, Satiroglu MH, Kabukcu C (2010) Determination of organochlorine pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl levels in adipose tissue of infertile men. Environ Monit Assess 162(1–4):301–309
Daglioglu N, Gulmen MK, Akcan R, Efeoglu P, Yener F, Unal I (2010) Determination of organochlorine pesticides residues in human adipose tissue, data from Cukurova, Turkey. B Environ Contam Tox 85(1):97–102
Devi NL, Yadav IC, Raha P, Shihua Q, Dan Y (2015) Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of residual organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the Himalayas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(24):20154–20166
Djahed B, Taghavi M, Farzadkia M, Norzaee S, Miri M (2018) Stochastic exposure and health risk assessment of rice contamination to the heavy metals in the market of Iranshahr, Iran. Food Chem Toxicol 115:405–412
Ellison SLR, Williams A (2012) Quantifying uncertainty in analytical measurement. EURACHEM/CITAC Guide, third edition
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (1992) Guidelines for exposure assessment. EPA/600/Z-92/001. Washington (DC)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2007) Ecological soil screening levels for DDT and metabolites. OSWER Directive 9285.7–57. Washington (DC)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2019) Guidelines for human exposure assessment. EPA/100/B-19/001. Washington (DC)
Erdogrul O, Covaci A, Kurtul N, Schepens P (2004) Levels of organohalogenated persistent pollutants in human milk from Kahramanmaras region, Turkey. Environ Int 30(5):659–666
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2009) Risk assessment for birds and mammals. EFSA J 7(12):1438
Filiz N, Kucuksezgin F (2008) Composition and distribution of organochlorine pesticide residues in surface sediments from Gediz and Bakircay Rivers (Eastern Aegean). Fresenius Environ Bull 17(6):744–754
Gaw SK, Kim ND, Northcott GL, Wilkins AL, Robinson G (2008) Uptake of ΣDDT, arsenic, cadmium, copper, and lead by lettuce and radish grown in contaminated horticultural soils. J Agric Food Chem 56(15):6584–6593
Guo G, Zhang C, Wu G, Ding Q, Wang S, Li F (2013) Health and ecological risk-based characterization of soil and sediment contamination in shipyard with long-term use of DDT-containing antifouling paint. Sci Total Environ 450:223–229
Hussain A, Maqbool U, Asi M (1994) Studies on dissipation and degradation of C-14 DDT and C-14 DDE in Pakistani soils under field conditions. J Environ Sci Health Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 29(1):1–15
Isleyen M, Sevim P, White JC (2012) Accumulation of weathered p, p′-DDTs in hybridized Cucurbita pepo cultivars. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(8):1699–1704
Isleyen M, Sevim P (2012) Accumulation of weathered p, p′-DDE in xylem sap of grafted watermelon. Int J Phytoremediat 14(4):403–414
Isleyen M, Sevim P, Uslan M (2013) DDX profiles in agricultural fields used for cucurbit production in Sakarya, Turkey. Soil Sediment Contam 22(6):689–700
Jensen J, Pedersen MB (2006) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated soil. In: Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. New York, Springer, pp 73–105
Joseph L, Paulose SV, Cyril N, Santhosh SK, Varghese A, Nelson AB, Kunjankutty SV, Kasu S (2020) Organochlorine pesticides in the soils of Cardamom Hill Reserve (CHR), Kerala, India: geo spatial distribution, ecological and human health risk assessment. Environ Chem Ecotox 2:1–11
Karademir KM (2002) Modelling and risk assessment of the PCDD/Fs emissions of a hazardous waste incineration plant, PhD Thesis. Kocaeli University Applied Sciences Institute, Turkey
Kata M, Rao SS, Mohan KR (2015) Spatial distribution, ecological risk evaluation and potential sources of organochlorine pesticides from soils in India. Environ Earth Sci 74(5):4031–4038
Kurt PB, Ozkoc HB (2004) A survey to determine levels of chlorinated pesticides and PCBs in mussels and seawater from the Mid-Black Sea coast of Turkey. Mar Pollut Bull 48(11–12):1076–1083
Li QY, Wu JL, Zhao ZH, Sakiev K (2018) Organochlorine pesticides in soils from the Issyk-Kul region in the western Tian Shan Mountains, Kyrgyzstan: implication for spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment. J Mt Sci 15(7):1520–1531
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Wang C, Cui Y, Li J, Chen A, Liang G, Jiao B (2020) Occurrence, temporal variation, quality and safety assessment of pesticide residues on citrus fruits in China. Chemosphere 258:127381
Malusa E, Tartanus M, Danelski W, Miszczak A, Szustakowska E, Kicińska J, Furmanczyk EM (2020) Monitoring of DDT in agricultural soils under organic farming in Poland and the risk of crop contamination. Environ Manag 66(5):916–929
Ngweme GN, Al Salah DMM, Laffite A, Sivalingam P, Grandjean D, Konde JN, Mulaji JK, Breider F, Poté J (2020) Occurrence of organic micropollutants and human health risk assessment based on consumption of Amaranthus viridis, Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Sci Total Environ 754:142175
Nizamlioglu F, Aktumsek A, Kara H, Dinc I (2005) Monitoring of some organochlorine pesticide residues of butter in Konya, Turkey. J Environ Biol 26(2):375–378
Pivato A, Lavagnolo MC, Manachini B, Vanin S, Raga R, Beggio G (2017) Ecological risk assessment of agricultural soils for the definition of soil screening values: a comparison between substance-based and matrix-based approaches. Heliyon 3(4):e00284
Qu C, Qi S, Yang D, Huang H, Zhang J, Chen W, Yohannes HK, Sandy EH, Yang J, Xing X (2015) Risk assessment and influence factors of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in agricultural soils of the hill region: a case study from Ningde, southeast China. J Geochem Explor 149:43–51
Strause KD, Zwiernik MJ, Im SH, Bradley PW, Moseley PP, Kay DP, Park C, Jones PD, Blankenship AL, Newsted JL, Giesy JP (2007) Risk assessment of great horned owls (Bubo virginianus) exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls and DDT along the Kalamazoo River, Michigan, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(7):1386–1398
Turkish Statistical Institute (TURKSTAT) (2019) Vegetable and Fruit Production Report, Report No. 30685, Presidency of the Republic of Turkey, Ankara, Turkey
Turgut C (2003) The contamination with organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in surface water in Kucuk Menderes River in Turkey, 2000–2002. Environ Int 29(1):29–32
Turkish Environment and Forest Ministry (TEFM) (2010) The legislation on soil pollution control and contaminated sites by point resources. Report No: 27605, Ankara, Turkey
Turkish Agriculture and Forest Ministry (TAFM) (2016) The legislation of Turkish food codex on maximum residues levels for pesticides. Report No: 29899, Ankara, Turkey
Wang Z, Liu S, Lu K, Xu X, Zhang T (2020) Concentration, characterization and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in soils from the Corn Belt of northeast China. Eur J Soil Sci 71(4):654–666
White JC, Wang XP, Gent MPN, Iannucci-Berger W, Eitzer BD, Schultes NP, Arienzo M, Mattina MI (2003) Subspecies-level variation in the phytoextraction of weathered p,p′-DDE by Cucurbita pepo. Environ Sci Technol 37(19):4368–4373
White JC (2009) Optimizing planting density for p,p′-DDE phytoextraction by Cucurbita pepo. Environ Eng Sci 26(2):369–375
White JC (2010) Inheritance of p,p′-DDE phytoextraction ability in hybridized Cucurbita pepo cultivars. Environ Sci Technol 44(13):5165–5169
Yavuz H, Guler GO, Aktumsek A, Cakmak YS, Ozparlak H (2010) Determination of some organochlorine pesticide residues in honeys from Konya, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 168(1–4):277–283
Yu HY, Li FB, Yu WM, Li YT, Yang GY, Zhou SG, Zhang TB, Gao YZ, Wan HF (2013) Assessment of organochlorine pesticide contamination in relation to soil properties in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci Total Environ 447:160–168
Zayed SMAD, Mostafa IY, Elarab AE (1994) Chemical and biological release of C-14 bound residues from soil treated with C-14 p,p′-DDT. J Environ Sci Health Part B Pestic Food Contam Agric Wastes 29(1):169–175
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that (the/all other) data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article (and its supplementary information files).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PSE and MI performed the sampling and analysis for DDX levels. MKK performed the risk assessment methodology and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 65 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korucu, M.K., Elibol, P.S. & Isleyen, M. An environmental risk assessment for a DDX-contaminated agricultural area in Turkey: soil vs. plant or human vs. animal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 50127–50140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14154-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14154-4