Abstract
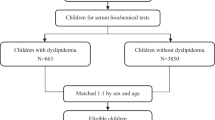
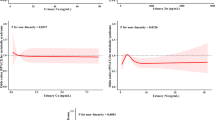
Hyperlipidemia, which is associated with certain environmental factors, is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Heavy metals are important pollutants from industrial emissions. However, the relationship between the exposure to heavy metals and the occurrence of hyperlipidemia is limited. This study aimed to investigate the association between serum metal levels and the risk of hyperlipidemia in adults living near a petrochemical complex. Our study subjects were 959 residents aged above 35 years in 11 townships near the largest petrochemical complex in central Taiwan. The serum levels of chromium, arsenic, and mercury in the study subjects were measured. The basic characteristics of the study subjects were collected via a questionnaire survey, and the levels of blood lipid biomarkers were analyzed by health examination. The definition of hyperlipidemia was defined in the provided guidelines. Adjusted generalized linear and logistic regression models were applied to evaluate the associations between petrochemical-related metal exposure and hyperlipidemia. The study subjects had chromium, arsenic, and mercury serum levels of 3.24±3.45, 3.45±4.66, and 1.24±1.08 (μg/L), respectively, and close proximity of the study subjects to the petrochemical complex was significantly associated with increased serum metal levels. The results showed that the total cholesterol levels were significantly associated with the increased serum chromium, arsenic, and mercury levels. And, the LDL-C levels were significantly associated with the increased serum mercury levels. In addition, the increased serum arsenic and mercury levels of the study subjects were significantly associated with higher odds ratios for abnormal total cholesterol levels and the risk of hyperlipidemia. Residing in close proximity to a petrochemical complex and high arsenic and mercury exposure were associated with elevated blood lipid levels and an increased risk of hyperlipidemia among the residential population in the vicinity of the petrochemical industry.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdullah MZ, Saat AB, Hamzah ZB (2012) Assessment of the impact of petroleum and petrochemical industries to the surrounding areas in Malaysia using mosses as bioindicator supported by multivariate analysis. Environ Monit Assess 184(6):3959–3969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2236-y
Afolabi OK, Wusu AD, Ogunrinola OO, Abam EO, Babayemi DO, Dosumu OA, Onunkwor OB, Balogun EA, Odukoya OO, Ademuyiwa O (2015) Arsenic-induced dyslipidemia in male albino rats: comparison between trivalent and pentavalent inorganic arsenic in drinking water. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 16:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40360-015-0015-z
Bell G, Mora S, Greenland P, Tsai M, Gill E, Kaufman JD (2017) Association of air pollution exposures with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and particle number: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37(5):976–982. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308193
Baraona E, Lieber CS (1998) Alcohol and lipids. Recent Dev Alcohol 14:97–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47148-5_5
Billimoria JD, Pozner H, Metselaar B, Best FW, James DC (1975) Effect of cigarette smoking on lipids, lipoproteins, blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and cellular components of human blood. Atherosclerosis 21(1):61–76
Bind MA, Peters A, Koutrakis P, Coull B, Vokonas P, Schwartz J (2016) Quantile regression analysis of the distributional effects of air pollution on blood pressure, heart rate variability, blood lipids, and biomarkers of inflammation in elderly American men: the Normative Aging Study. Environ Health Perspect 124(8):1189–1198. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1510044
Chan CC, Lee YL, Hung SH (2012) Air pollution and health among residents near a petrochemical complex in Yunlin County: a cohort study (2011–2012). Environmental Protection Bureau of Yunlin County, Taiwan
Chan CC, Wang CL, Chen YM, Chen CY, Tsai JS (2014) Environmental epidemiological cohort study in Yunlin County (2013–2014). Environmental Protection Bureau of Yunlin County, Taiwan
Chen LK, Lin MH, Hwang SJ, Wang P, Chwang LC (2007) Nutritional status and clinical outcomes among institutionalized elderly Chinese in Taiwan. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 44(3):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2006.07.002
Chio CP, Yuan TH, Shie RH, Chan CC (2014) Assessing vanadium and arsenic exposures for residents near a petrochemical complex by two-stage dispersion models. J Hazard Mater 271:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02.008
Chuang KJ, Yan YH, Chiu SY, Cheng TJ (2011) Long-term air pollution exposure and risk factors for cardiovascular diseases among the elderly in Taiwan. Occup Environ Med 68(1):64–68. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2009.052704
Cortis P, Vannini C, Cogoni A, De Mattia F, Bracale M, Mezzasalma V, Labra M (2016) Chemical, molecular, and proteomic analyses of moss bag biomonitoring in a petrochemical area of Sardinia (Italy). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(3):2288–2300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5393-7
Danaei G, Singh GM, Paciorek CJ, Lin JK, Cowan MJ, Finucane MM, Farzadfar F, Stevens GA, Riley LM, Lu Y, Rao M, Ezzati M (2013) The global cardiovascular risk transition: associations of four metabolic risk factors with national income, urbanization, and Western diet in 1980 and 2008. Circulation. 127(14):1493–1502. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001470
Dewailly E, Blanchet C, Gingras S, Lemieux S, Holub BJ (2003) Fish consumption and blood lipids in three ethnic groups of Québec (Canada). Lipids. 38(4):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-003-1070-4
Eom SY, Choi SH, Ahn SJ, Kim DK, Kim DW, Lim JA, Choi BS, Shin HJ, Yun SW, Yoon HJ, Kim YM, Hong YS, Yun YW, Sohn SJ, Kim H, Park KS, Pyo HS, Kim H, Oh SY, Kim J, Lee SA, Ha M, Kwon HJ, Park JD (2014) Reference levels of blood mercury and association with metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 87(5):501–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-013-0891-8
Fan Y, Zhang C, Bu J (2017) Relationship between selected serum metallic elements and obesity in children and adolescent in the U.S. Nutrients 9(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020104
Farzadfar F, Finucane MM, Danaei G, Pelizzari PM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Lin JK, Stevens GA, Riley LM, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in serum total cholesterol since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 321 country-years and 3.0 million participants. Lancet. 377(9765):578–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62038-7
Gonzalvo MC, Gil F, Hernandez AF, Villanueva E, Pla A (1997) Inhibition of paraoxonase activity in human liver microsomes by exposure to EDTA, metals and mercurials. Chem Biol Interact 105:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2797(97)00046-X
Harris WS (1997) N-3 fatty acids and serum lipoproteins, human studies. Am J Clin Nutr 65:1645–1654. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/65.5.1645S
Hsu HF, Tsou TC, Chao HR, Shy CG, Kuo YT, Tsai FY, Yeh SC, Ko YC (2010) Effects of arecoline on adipogenesis, lipolysis, and glucose uptake of adipocytes-a possible role of betel-quid chewing in metabolic syndrome. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 245(3):370–377
Illingworth DR, Connor WE, Hatcher LF, Harris WS (1989) Hypolipidemic effects of n-3 fatty acids in primary hyperlipoproteinemia. J Intern Med 225:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.1989.tb01441.x
Ip P, Wong V, Ho M, Lee J, Wong W (2004) Environmental mercury exposure in children: South China’s experience. Pediatr Int 46(6):715–721. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-200x.2004.01972.x
Jan FA, Ishaq M, Khan S, Shakirullah M, Asim SM, Ahmad I, Mabood F (2011) Bioaccumulation of metals in human blood in industrially contaminated area. J Environ Sci (China) 23(12):2069–2077. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60616-X
Kawakami T, Hanao N, Nishiyama K, Kadota Y, Inoue M, Sato M, Suzuki S (2012) Differential effects of cobalt and mercury on lipid metabolism in the white adipose tissue of high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258(1):32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.10.004
Kim YD, Eom SY, Yim DH, Kim IS, Won HK, Park CH, Kim GB, Yu SD, Choi BS, Park JD, Kim H (2016) Environmental exposure to arsenic, lead, and cadmium in people living near Janghang copper smelter in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 31(4):489–496. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.489
Li YH, Ueng KC, Jeng JS, Charng MJ, Lin TH, Chien KL, Wang CY, Chao TH, Liu PY, Su CH, Chien SC, Liou CW, Tang SC, Lee CC, Yu TY, Chen JW, Wu CC, Yeh HI (2017) 2017 Taiwan lipid guidelines for high risk patients. J Formos Med Assoc 116(4):217–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2016.11.013
Lin CC, Tsweng GJ, Lee CF, Chen BH, Huang YL (2015) Magnesium, zinc, and chromium levels in children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes. Clin Nutr 35(4):880–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.05.022
Lin CH, Hsu YT, Yen CC, Chen HH, Tseng CJ, Lo YK, Chan JYH (2018) Association between heavy metal levels and acute ischemic stroke. J Biomed Sci 25(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-018-0446-0
Mazumder DN, Haque R, Ghosh N, De BK, Santra A, Chakraborti D, Smith AH (2000) Arsenic in drinking water and the prevalence of respiratory effects in West Bengal, India. Int J Epidemiol 29(6):1047–1052. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/29.6.1047
Mendez MA, González-Horta C, Sánchez-Ramírez B, Ballinas-Casarrubias L, Cerón RH, Morales DV, Terrazas FA, Ishida MC, Gutiérrez-Torres DS, Saunders RJ, Drobná Z, Fry RC, Buse JB, Loomis D, García-Vargas GG, Del Razo LM, Stýblo M (2016) Chronic exposure to arsenic and markers of cardiometabolic risk: a cross-sectional study in Chihuahua, Mexico. Environ Health Perspect 124(1):104–111. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408742
Moradi A, Honarjoo N, Etemadifar M, Fallahzade J (2016) Bio-accumulation of some heavy metals in blood serum of residents in Isfahan and Shiraz, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 188(5):269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5217-3
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB (2016) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 133(4):e38-360. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350
Muthumani M, Miltonprabu S (2015) Ameliorative efficacy of tetrahydrocurcumin against arsenic induced oxidative damage, dyslipidemia and hepatic mitochondrial toxicity in rats. Chem Biol Interact 235:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.04.006
National Institutes of Health (2005) High blood cholesterol: what you need to know. NIH Publication No. 05–3290
Olfson M, Marcus SC, Corey-Lisle P, Tuomari AV, Hines P, L'Italien GJ (2006) Hyperlipidemia following treatment with antipsychotic medications. Am J Psychiatry 163(10):1821–1825. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.10.1821
Pirsch JD, D'Alessandro AM, Sollinger HW, Knechtle SJ, Reed A, Kalayoglu M, Belzer FO (1992) Hyperlipidemia and transplantation: etiologic factors and therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2(12 Suppl):S238–S242
Shie RH, Chan CC (2013) Tracking hazardous air pollutants from a refinery fire by applying on-line and off-line air monitoring and back trajectory modeling. J Hazard Mater 261:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.017
Song Y, Zhang J, Yu S, Wang T, Cui X, Du X, Jia G (2012) Effects of chronic chromium(vi) exposure on blood element homeostasis: an epidemiological study. Metallomics. 4(5):463–472. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mt20051a
Sun L, Yu Y, Huang T, An P, Yu D, Yu Z, Li H, Sheng H, Cai L, Xue J, Jing M, Li Y, Lin X, Wang F (2012) Associations between ionomic profile and metabolic abnormalities in human population. PLoS One 7(6):e38845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038845
Taiwan Society of Lipids and Atherosclerosis (2009) Taiwan dyslipidemia prevention consensus – dyslipidemia prevention and clinical treatment guidelines. http://www.tas.org.tw/index.php. Accessed 21 Jan 2020
Wang SL, Chang FH, Liou SH, Wang HJ, Li WF, Hsieh DP (2007) Inorganic arsenic exposure and its relation to metabolic syndrome in an industrial area of Taiwan. Environ Int 33(6):805–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.03.004
Wones RG, Deck CC, Stadler B, Roark S, Hogg E, Frohman LA (1993) Lack of effect of drinking water chlorine on lipid and thyroid metabolism in healthy humans. Environ Health Perspect 99:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1289/ehp.9399369
World Health Organization, 2017. Available on http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
Wu MM, Chiou HY, Wang TW, Hsueh YM, Wang IH, Chen CJ, Lee TC (2001) Association of blood arsenic levels with increased reactive oxidants and decreased antioxidant capacity in a human population of northeastern Taiwan. Environ Health Perspect 109(10):1011–1017. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.011091011
Ye J, Shi X (2001) Gene expression profile in response to chromium-induced cell stress in A549 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 222(1–2):189–197
You CH, Kim BG, Kim JM, Yu SD, Kim YM, Kim RB, Hong YS (2011) Relationship between blood mercury concentration and waist-to-hip ratio in elderly Korean individuals living in coastal areas. J Prev Med Public Health 44(5):218–225. https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.2011.44.5.218
Yuan TH, Chio CP, Shie RH, Pien WH, Chan CC (2016) The distance-to-source trend in vanadium and arsenic exposures for residents living near a petrochemical complex. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 26(3):270–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2015.2
Zhou Z, Lu YH, Pi HF, Gao P, Li M, Zhang L, Pei LP, Mei X, Liu L, Zhao Q, Qin QZ, Chen Y, Jiang YM, Zhang ZH, Yu ZP (2016) Cadmium exposure is associated with the prevalence of dyslipidemia. Cell Physiol Biochem 40(3–4):633–643. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452576
Acknowledgements
This study was funded with a grant obtained from the Public Health Bureau, Yunlin County, Taiwan (grant number YLPHB-10512). And, it is also funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (grant number MOST 107-3017-F-002-003, MOST 108-3017-F-002-001) and Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education in Taiwan (grant number NTU-107L9003 and NTU-108L9003).
Funding
I. The Public Health Bureau, Yunlin County, Taiwan (grant number YLPHB-10512)
II. The Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (grant number MOST 107-3017-F-002-003 and MOST 108-3017-F-002-001)
III. The Ministry of Education, Taiwan (grant number NTU-107L9003 and NTU-108L9003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-H. S. and C.-C. C.; methodology, C.-H. S. and T.-H. Y.; software, C.-H. S. and Y.-H. C.; validation, T.-H. Y. and Y.-H. C.; formal analysis, C.-H. S. and Y.-H. C.; investigation, T.-H. Y., S.-H. H., and Y.-P. Y.; resources, S.-H. H., Y.-P. Y., and C.-C. C.; data curation, S.-H. H. and Y.-P. Y.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-H. S.; writing—review and editing, T.-H. Y.; visualization, T.-H. Y. and Y.-H. C.; supervision, C.-C. C.; project administration, T.-H. Y. and C.-C. C.; funding acquisition, T.-H. Y. and C.-C. C. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the National Health Research Institutes in Taiwan, and written informed consent forms were signed by each subject.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shun, CH., Yuan, TH., Hung, SH. et al. Assessment of the hyperlipidemia risk for residents exposed to potential emitted metals in the vicinity of a petrochemical complex. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 27966–27975 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12642-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12642-1