Abstract
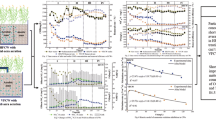
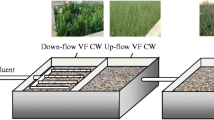
Two sets of hybrid constructed wetlands (HCWs) with the first-stage aeration were used to treat actual domestic sewage in this paper, where the effects of three important factors of aeration mode, hydraulic loading rates (HLR), and aeration volume on the removal of pollutants in both HCWs were studied in contrasts. In addition, the pollutant removal efficiency, the contribution of plants, and the characteristics of biofilm in both HCWs were explored. The results of 250-day experiment showed that the TN removal capacity of HCW combining vertical flow CW with horizontal flow CW (VF-HF) was better than HCW’s converse combination (HF-VF) in treatingsewage, while the removal efficiency of COD and NH4+-N were similar, and the concentrations of TN and COD in the effluent of VF-HF could successfully meet the National discharge requirements. Compared with the continuous aeration, the intermittent aeration only had a little effect on the removal of COD and NH4+-N, but could improve TN removal performance in both HCWs. Meanwhile, increasing the aeration volume was beneficial to remove NH4+-N but not TN in HCWs. In addition, although the pollutant removal performances in both HCWs were impacted, the removal capacity of TN in VF-HF was only affected a little, when HLR was increased by 50%. The contribution of plants’ uptake accounted for about 10% to nitrogen removal and 20% to phosphorus removal in both HCWs. The biomass at the filler surface near the plant rhizosphere was greater than that in the non-rhizosphere zones, and the impact of plant rhizosphere on the nitrification activity of biofilm was significantly greater than that on denitrification activity in both HCWs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ayaz SC, Aktas O, Akca L, Findik N (2015) Effluent quality and reuse potential of domestic wastewater treated in a pilot-scale hybrid constructed wetland system. J Environ Manag 156:115–120
Boog J, Nivala J, Aubron T, Wallace S, Van Afferden M, Müller RA (2014) Hydraulic characterization and optimization of total nitrogen removal in an aerated vertical subsurface flow treatment wetland. Bioresour Technol 162:166–174
Bugajski P, Kurek K, MdFNd C, Almeida MAA, Siwiec T, Borowski G, Czekała W, Dach J, Gajewska M (2018) The efficiency and technological reliability of biogenic compounds removal during long-term operation of a one-stage subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Sep Purif Technol
Cakir R, Gidirislioglu A, Cebi U (2015) A study on the effects of different hydraulic loading rates (HLR) on pollutant removal efficiency of subsurface horizontal-flow constructed wetlands used for treatment of domestic wastewaters. J Environ Manag 164:121–128
Cao L, Ji-Lai LU, Zhou J, Yong TU, Jiang YW (2015) Assessment of rural domestic sewage treatment technology in Taihu Basin. Environ Sci Technol
Chen J, Wei XD, Liu YS, Ying GG, Liu SS, He LY, Su HC, Hu LX, Chen FR, Yang YQ (2016) Removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic sewage by constructed wetlands: optimization of wetland substrates and hydraulic loading. Sci Total Environ 565:240–248
Dong QZ, Jinadasa KBSN, Gersberg RM, Yu L, Ng WJ, Tan SK (2014) Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in developing countries - a review of recent developments (2000-2013). J Environ Manag 141:116–131
Fan J, Zhang B, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Wu H (2013) Intermittent aeration strategy to enhance organics and nitrogen removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 141:117–122
Fu G, Huangshen L, Guo Z, Zhou Q, Wu Z (2016) Effect of plant-based carbon sources on denitrifying microorganisms in a vertical flow constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol:S0960852416315127
Gonzalo OG, Ruiz I, Soto M (2020) Effect of different bypass rates and unit area ratio in hybrid constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res:24
Hu YS, Zhao YQ, Zhao XH, Kumar JLG (2012a) Comprehensive analysis of step-feeding strategy to enhance biological nitrogen removal in alum sludge-based tidal flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 111:27–35
Hu Y, Zhao Y, Zhao X (2012b) High rate nitrogen removal in an alum sludge-based intermittent aeration constructed wetland. Environ Sci Technol
Hu Y, Zhao Y, Rymszewicz A (2014) Robust biological nitrogen removal by creating multiple tides in a single bed tidal flow constructed wetland. Sci Total Environ 470-471:1197–1204
Lam L, Kurisu K, Hanaki K (2015) Comparative environmental impacts of source-separation systems for domestic wastewater management in rural China. J Clean Prod 104:185–198
Leto C, Tuttolomondo T, Bella SL, Leone R, Licata M (2013) Effects of plant species in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland – phytoremediation of treated urban wastewater with Cyperus alternifolius L. and Typha latifolia L. in the West of Sicily (Italy). Ecol Eng 61:282–291
Li F, Lu L, Zheng X, Ngo HH, Liang S, Guo W, Zhang X (2014) Enhanced nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: effects of dissolved oxygen and step-feeding. Bioresour Technol 169:395–402
Li M, Wu H, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Kong Q (2017) Nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emission in surface flow constructed wetlands for treating sewage treatment plant effluent: effect of C/N ratios. Bioresour Technol:S0960852417301773
Liu L, Zhao X, Zhao N, Shen Z, Wang M, Guo Y, Xu Y (2013) Effect of aeration modes and influent COD/N ratios on the nitrogen removal performance of vertical flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 57:10–16
Pan J, Yuan F, Zhang Y, Huang L, Cheng F, Zheng F, Liu R (2016) Nitrogen removal in subsurface wastewater infiltration systems with and without intermittent aeration. Ecol Eng 94:471–477
Pelissari C, Dos Santos MO, Rousso BZ, Bento AP, De Armas RD, Sezerino PH (2016) Organic load and hydraulic regime influence over the bacterial community responsible for the nitrogen cycling in bed media of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 95:180–188
Pelissari C, Avila C, Trein CM, Garcia J, Armas RDD, Sezerino PH (2017) Nitrogen transforming bacteria within a full-scale partially saturated vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland treating urban wastewater. Sci Total Environ 574:390–399
Peng L, Hua Y, Cai J, Zhao J, Zhou W, Zhu D (2014) Effects of plants and temperature on nitrogen removal and microbiology in a pilot-scale integrated vertical-flow wetland treating primary domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 64:285–290
Redmond ED, Just CL, Parkin GF (2014) Nitrogen removal from wastewater by an aerated subsurface-flow constructed wetland in cold climates. Water Environ Res 86:305–313
Ruiz I, Díaz MA, Crujeiras B, García J, Soto M (2010) Solids hydrolysis and accumulation in a hybrid anaerobic digester-constructed wetlands system. Ecol Eng 36:1007–1016
Saeed T, Sun G (2012) A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media. J Environ Manag 112:429–448
Sepúlveda-Mardones M, López D, Vidal G (2017) Methanogenic activity in the biomass from horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 105:66–77
Sun H, Xu S, Wu S, Wang R, Zhuang G, Bai Z, Deng Y, Zhuang X (2019) Enhancement of facultative anaerobic denitrifying communities by oxygen release from roots of the macrophyte in constructed wetlands. J Environ Manag 246:157–163
Tatoulis T, Akratos CS, Tekerlekopoulou AG, Vayenas DV, Stefanakis AI (2017) A novel horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland: reducing area requirements and clogging risk. Chemosphere 186:257–268
Torrijos V, Gonzalo OG, Trueba-Santiso A, Ruiz I, Soto M (2016) Effect of by-pass and effluent recirculation on nitrogen removal in hybrid constructed wetlands for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment. Water Res 103:92–100
Torrijos V, Ruiz I, Soto M (2017) Effect of step-feeding on the performance of lab-scale columns simulating vertical flow-horizontal flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:22649–22662
Turon C, Comas J, Poch M (2009) Constructed wetland clogging: a proposal for the integration and reuse of existing knowledge. Ecol Eng 35:1710–1718
Vymazal J (2002): The use of sub-surface constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in the Czech Republic: 10 years experience. 18, 633-646
Vymazal J (2005) Horizontal sub-surface flow and hybrid constructed wetlands systems for wastewater treatment. Ecol Eng 25:478–490
Vymazal J (2013) The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: a review of a recent development. Water Res 47:4795–4811
Wang J, Tai Y, Man Y, Rui F, Xu Y (2018) Capacity of various single-stage constructed wetlands to treat domestic sewage under optimal temperature in Guangzhou City, South China. Ecol Eng J Ecotechnol
Wu H, Fan J, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W (2015a) Decentralized domestic wastewater treatment using intermittently aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands: impact of influent strengths. Bioresour Technol
Wu H, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Hu Z, Liang S, Fan J, Liu H (2015b) A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour Technol 175:594–601
Wu H, Fan J, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Liang S, Lv J, Lu S, Wu W, Wu S (2016) Intensified organics and nitrogen removal in the intermittent-aerated constructed wetland using a novel sludge-ceramsite as substrate. Bioresour Technol:S096085241630027X
Yadav A, Chazarenc F, Mutnuri S (2018) Development of the "French system" vertical flow constructed wetland to treat raw domestic wastewater in India. Ecol Eng 113:88–93
Yang Z, Yang L, Wei C, Wu W, Zhao X, Lu T (2017) Enhanced nitrogen removal using solid carbon source in constructed wetland with limited aeration. Bioresour Technol:S0960852417313044
Zhang CB, Liu WL, Wang J, Ge Y, Ge Y, Chang SX, Chang J (2011) Effects of monocot and dicot types and species richness in mesocosm constructed wetlands on removal of pollutants from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102:10260–10265
Zhang X, Hu Z, Zhang J, Fan J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Zeng C, Wu Y, Wang S (2018) A novel aerated surface flow constructed wetland using exhaust gas from biological wastewater treatment: performance and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 250:94–101
Zheng Y, Wang XC, Ge Y, Dzakpasu M, Xiong J (2015) Effects of annual harvesting on plants growth and nutrients removal in surface-flow constructed wetlands in northwestern China. Ecol Eng
Funding
This work was funded by the Science and Technology Innovation Demonstration project of social development of Xi’an Science and Technology Bureau (Grant number: 20SFSF0011), and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2021ZDLSF05-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FLY designed the experiment, analyzed the data, and wrote the original manuscript. YW guided the conduct of the experiment and the revision of the draft. WHW contributed significantly to the analysis and preparation of the manuscript. HZ helped perform the experiment. YCZ contributed to the conception of the experimental program. XMK, SZW, and TS provided the site for the experiment, as well as the early demonstration and investigation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Hybrid of VFCW followed by HFCW is conducive to treat domestic sewage.
• Intermittent aeration is the optimal mode for the efficient TN removal by HCW.
• P. australis uptake can contribute about 10% and 20% to the removal of TN and TP.
• Plant rhizosphere greatly affects nitrification activity of biofilm in CW system.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, FL., Wang, Y., Wang, WH. et al. Effect of first-stage aeration on treatment of domestic sewage in different hybrid constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 43402–43416 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12449-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12449-0