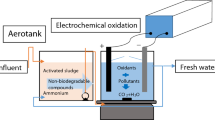
Abstract
The aim of this work was to evaluate the pollutant load from tannery effluents treated by chemical coagulation (CC) followed by electro-oxidation (EO), performed in two different experimental batch-recirculated setups, one with a BDD anode and the other with Ti/Pt/PbO2 and Ti/Pt/SnO2-Sb2O4 anodes (PS). Results were compared with those obtained from EO of the raw sample. CC was performed with a Fe3+ concentration of 0.25 g L−1, and the applied current densities for EO in each setup were 60 mA cm−2 for BDD and, in the PS setup, 20 and 40 mA cm−2 for Ti/Pt/SnO2-Sb2O4 and Ti/Pt/PbO2, respectively. During CC, removals of 27% in chemical oxygen demand (COD), 14% in total nitrogen, 100% in sulfide, and 73% in Cr(VI) were observed. COD removal in the EO of the raw sample was higher than that obtained for the combined CC + EO, for both setups, showing that the organic compounds removed by CC are mainly those that would be more easily removed by EO. For most of the other parameters related with carbon and nitrogen, the removals for CC + EO were higher than for EO alone. During EO, sulfide is converted to sulfate, especially with BDD. Concerning Cr(VI) concentration, it increases during EO, in particular for PS setup. Combined treatment, with both setups, proved to be an effective choice to treat tannery effluents.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Relevant data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Additional datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aboulhassan MA, Souabi S, Yaacoubi A, Baudu M (2006) Removal of surfactant from industrial wastewaters by coagulation flocculation process. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3(4):327–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325941
Achouri O, Panico AM, Bencheikh-Lehocine M, Derbal K, Pirozzi F (2017) Effect of chemical coagulation pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of tannery wastewater. J Environ Eng 143(9):04017039 https://ascelibrary.org/doi/10.1061/%28ASCE%29EE.1943-7870.0001235
Axelrad G, Gershfeld T, Feinerman E (2013) Reclamation of sewage sludge for use in Israeli agriculture: economic, environmental and organizational aspects. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management 56(10):1419–1448. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2012.732009
Azarian G, Miri M, Nematollahi D (2018) Combined electrocoagulation/electrooxidation process for the COD removal and recovery of tannery industry wastewater. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 37(2):637–644. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12711
Bengtsson M, Tillman AM (2004) Actors and interpretations in an environmental controversy: the Swedish debate on sewage sludge use in agriculture. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 42:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2004.02.004
Benhadji A, Ahmed MT, Maachi R (2011) Electrocoagulation and effect of cathode materials on the removal of pollutants from tannery wastewater of Rouïba. Desalination 277(1-3):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.014
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B-Environ 166-167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Brown LS, Holme TA (2011) Chemistry for engineering students, 2nd edn. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, CA
Caliari PC, Pacheco MJ, Ciriaco L, Lopes A (2017) Anodic oxidation of sulfide to sulfate: effect of the current density on the process kinetics. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 28(4):557–566 http://jbcs.sbq.org.br/imagebank/pdf/160274AR.pdf
Caliari PC, Pacheco MJ, Ciriaco L, Lopes A (2019) Tannery wastewater: organic load and sulfide removal dynamics by electrochemical oxidation at different anode materials. Environ Technol Innov 14:100345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100345
Candia-Onfray C, Espinoza N, Sabino da Silva EB, Toledo-Neira C, Espinoza LC, Santander R, García V, Salazar R (2018) Treatment of winery wastewater by anodic oxidation using BDD electrode. Chemosphere 206:709–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.175
Chaplin BP (2014) Critical review of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment applications. Environ. Sci: Processes and Impacts 16:1182–1203 https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2014/em/c3em00679d
Chowdhury M, Mostafa MG, Biswas TK, Saha AK (2013) Treatment of leather industrial effluents by filtration and coagulation processes. Water Resour Ind 3:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2013.05.002
Ciríaco L, Anjo C, Correia J, Pacheco MJ, Lopes A (2009) Electrochemical degradation of Ibuprofen on Ti/Pt/PbO2 and Si/BDD electrodes. Electrochim Acta 54:1464–1472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.09.022
Costa RC, Botta CMR, Espindola ELG, Olivi P (2008) Electrochemical treatment of tannery wastewater using DSA® electrodes. J Hazard Mat 153(1-2):616–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.005
Deghles A, Kurt U (2016) Treatment of tannery wastewater by a hybrid electrocoagulation/electrodialysis process. Chem Eng Process 104:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2016.02.009
Dogruel S, Genceli EA, Babuna FG, Orhon D (2006) An investigation on the optimal location of ozonation within biological treatment for a tannery wastewater. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1877–1885. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1620
Duan J, Gregory J (2003) Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 100-102:475–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-8686(02)00067-2
Eary LE, Rai D (1991) Chromate reduction by subsurface soils under acidic conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:676–683. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500030007x
Eaton A, Clesceri L, Rice E, Greenberg A, Franson MA (2005) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Fajardo AS, Martins RC, Silva DR, Quinta-Ferreira RM, Martínez-Huitle CA (2017) Electrochemical abatement of amaranth dye solutions using individual or an assembling of flow cells with Ti/Pt and Ti/Pt-SnSb anodes. Sep Purif Technol 179:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.01.029
Fernandes A, Santos D, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2014a) Nitrogen and organic load removal from sanitary landfill leachates by anodic oxidation at Ti/Pt/PbO2, Ti/Pt/SnO2-Sb2O4 and Si/BDD. Appl Catal B-Environ 148-149:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.060
Fernandes A, Spranger P, Fonseca AD, Pacheco MJ, Ciríaco L, Lopes A (2014b) Effect of electrochemical treatments on the biodegradability of sanitary landfill leachates. Appl. Catal B: Environ. 144:514–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.054
Fernández-Castro P, Vallejo M, San-Román MF, Ortiz I (2015) Insight on the fundamentals of advanced oxidation processes. Role and review of the determination methods of reactive oxygen species. J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 90:796–820
Green R, Waite TD, Melville MD, MacDonald BCT (2006) Characteristics of the acidity in acid sulfate soil drainage waters, McLeods Creek, Northeastern NSW, Australia. Environ Chem 3(3):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN05055
Guertin J, Jacobs JA, Avakian CP (2004) Chromium(VI) Handbook. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203487969
Haydar S, Aziz JA (2009) Coagulation–flocculation studies of tannery wastewater using combination of alum with cationic and anionic polymers. J Hazard Mater 168:1035–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.140
Houshyar Z, Ali Baradar Khoshfetrat AB, Fatehifar E (2012) Influence of ozonation process on characteristics of pre-alkalized tannery effluents. Chem Eng J 191:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.053
Isarain-Chávez E, de la Rosa C, Godínez LA, Brillas E, Peralta-Hernández JM (2014) Comparative study of electrochemical water treatment processes for a tannery wastewater effluent. J Electroanal Chem 713:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.11.016
Islam KMN, Misbahuzzaman K, Majumder AK, Chakrabarty M (2011) Efficiency of different coagulants combination for the treatment of tannery effluents: a case study of Bangladesh. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 5(6):409–419 https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajest/article/view/71957
Kimbrough DE, Cohen Y, Winer AM, Creelman L, Mabuni C (1999) A critical assessment of chromium in the environment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 29(1):1–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389991259164
Kuppusamy S, Jayaraman N, Jagannathan M, Kadarkarai M, Aruliah R (2017) Electrochemical decolorization and biodegradation of tannery effluent for reduction of chemical oxygen demand and hexavalent chromium. J Water Process Eng 20:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.09.008
Liu WH, Zhang CG, Gao PF, Liu H, Song YQ, Yang JF (2017) Advanced treatment of tannery wastewater using the combination of UASB, SBR, electrochemical oxidation and BAF. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 92:588–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5037
Lofrano G, Meriç S, Zengin GE, Orhon D (2013) Chemical and biological treatment technologies for leather tannery chemicals and wastewaters: a review. Sci Total Environ 461-462:265–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.004
Luján-Facundo MJ, Fernández-Navarro J, Alonso-Molina JL, Amorós-Muñoz I, Moreno Y, Mendoza-Roca JA, Pastor-Alcañiz L (2018) The role of salinity on the changes of the biomass characteristics and on the performance of an OMBR treating tannery wastewater. Water Res 142:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.046
Luu TL, Tien TT, Duong NB, Phuong NTT (2019) Study of the treatment of tannery wastewater after biological pretreatment by using electrochemical oxidation on BDD/Ti anode. Desalin Water Treat 137:194–201. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23352
Martínez-Huitle CA, dos Santos EV, de Araújo DM, Panizza M (2012) Applicability of diamond electrode/anode to the electrochemical treatment of a real textile effluent. J Electroanal Chem 674:103–107
Mendoza-Roca JA, Galiana-Aleixandre MV, Lora-García J, Bes-Piá A (2010) Purification of tannery effluents by ultrafiltration in view of permeate reuse. Sep Purif Technol 70:296–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.10.010
Mollah MYA, Schennach R, Parga JR, Cocke DL (2001) Electrocoagulation (EC)-science and applications. J Hazard Mater 84(1):29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00176-5
Moradi M, Moussavi G (2019) Enhanced treatment of tannery wastewater using the electrocoagulation process combined with UVC/VUV photoreactor: parametric and mechanistic evaluation. Chem Eng J 358:1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.069
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B-Environ 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Naumczyk JH, Kucharska MA (2017) Electrochemical treatment of tannery wastewater-Raw, coagulated, and pretreated by AOPs. J Environ Sci Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 52(7):649–664. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2017.1297140
Panizza M, Delucchi M, Sirés I (2010) Electrochemical process for the treatment of landfill leachate. J Appl Electrochem 40:1721–1727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-010-0109-7
Pletcher D, Tait SJD (1981) The electrolytic oxidation of chromic sulphate to chromic acid: the effects of lead anode preparation. J Appl Electrochem 11:493–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01132438
Rao NN, Somasekhar KM, Kaul SN, Szpyrkowicz L (2001) Electrochemical oxidation of tannery wastewater. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76:1124–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.493
Ryu HD, Lee SI, Chung KY (2007) Chemical oxygen demand removal efficiency of biological treatment process treating tannery wastewater following seawater flocculation. Environ Eng Sci 24(3):394–399. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2006.0095
Salazar R, Ureta-Zañartu MS, González-Vargas C, Brito CN, Martínez-Huitle CA (2018) Electrochemical degradation of industrial textile dye disperse yellow 3: Role of electrocatalytic material and experimental conditions on the catalytic production of oxidants and oxidation pathway. Chemosphere 198:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.092
Saleh FY, Parkerton TF, Lewis RV, Huang JH, Dickson KL (1989) Kinetics of chromium transformations in the environment. Sci Total Environ 86:25–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(89)90190-3
Santos D, Pacheco MJ, Gomes A, Lopes A, Ciríaco L (2013) Preparation of Ti/Pt/SnO2–Sb2O4 electrodes for anodic oxidation of pharmaceutical drugs. J Appl Electrochem 43:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-013-0527-4
Schroeder DC, Lee GF (1975) Potential transformations of chromium in natural waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 4:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280721
Sedlak DL, Chan PG (1997) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by ferrous iron. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(11):2185–2192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00077-X
Selvaraj H, Aravind P, George HS, Sundaram M (2020) Removal of sulfide and recycling of recovered product from tannery lime wastewater using photoassisted-electrochemical oxidation process. J Ind Eng Chem 83:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.11.024
Șengil IA, Kulaç S, Özacar M (2009) Treatment of tannery liming drum wastewater by electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 167:940–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.099
Senthilvelan T, Kanagaraj J, Mandal AB (2012) Application of enzymes for dehairing of skins: cleaner leather processing. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:889–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0458-5
Sirajuddin KL, Lutfullah G, Bhanger MI, Shah A, Niaz A (2007) Electrolytic recovery of chromium salts from tannery wastewater. J Hazard Mater 148:560–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.011
Song Z, Williams J, Edyvean RGJ (2001) Coagulation and anaerobic digestion of tannery wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 79:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758201531103
Song Z, Williams CJ, Edyvean RGJ (2004) Treatment of tannery wastewater by chemical coagulation. Desalination 164:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(04)00193-6
Souza CE, Machado SAS, Mazo LH, Avaca LA (1993) Oxidação eletroquímica do cromo (III) sobre Pb/PbO2. Quim Nova 16(5):426–430
Szpyrkowicz L, Kelsall GH, Kaul SN, Faveri M (2001) Performance of electrochemical reactor for treatment of tannery wastewaters. Chem Eng Sci 56:1579–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00385-7
Teixeira EC, Caliari PC (2005) Estimation of the concentration of suspended solids in rivers from turbidity measurement: error assessment. In: Walling DE, Horowitz AJ (ed) Sediment Budgets 1. IAHS Press 291, pp 151-160
Thiam A, Brillas E, Centellas F, Cabot L, Sirés I (2015a) Electrochemical reactivity of Ponceau 4R (food additive E124) in different electrolytes and batch cells. Electrochimica Acta 173:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.05.085
Thiam A, Sirés I, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E (2015b) Effect of anions on electrochemical degradation of azo dye Carmoisine (Acid Red 14) using a BDD anode and air-diffusion cathode. Separation and Purification Technology 140:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.11.012
Tien TT, Luu TL (2020) Electrooxidation of tannery wastewater with continuous flow system: Role of electrode materials. Environ Eng Res 25(3):324–334. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2018.349
Vannini C, Munz G, Mori G, Lubello C, Verni F, Petroni G (2008) Sulphide oxidation to elemental sulphur in a membrane bioreactor: performance and characterization of the selected microbial sulphur-oxidizing community. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:461–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2008.07.003
Vazifehkhoran AH, Shin SG, Triolo JM (2018) Use of tannery wastewater as an alternative substrate and a pre-treatment medium for biogas production. Bioresour Technol 258:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.116
Vlyssides AG, Israilides CJ (1997) Detoxification of tannery waste liquors with an electrolysis system. Environ Pollut 97:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00062-6
Funding
This work was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, FCT, through the funding of the UID Fiber Materials and Environmental Technologies (FibEnTech-UBI), projects PEst-OE/CTM/UI0195/2013 and UIDB/00195/2020. This work was also supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior, CAPES, for the financing of the Ph.D. Grant (Bolsista da CAPES – Proc. n° BEX 0714/13-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PCC: investigation, writing—original draft, visualization, project administration. MJP: methodology, validation, investigation, writing—review and editing. LC: resources, writing—review and editing, Visualization. AL: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Confict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caliari, P.C., Pacheco, M.J., Ciríaco, L. et al. Treatment of tannery effluent by chemical coagulation combined with batch-recirculated electro-oxidation at different anode materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 24138–24149 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12436-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12436-5