Abstract
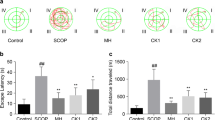
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by alterations in monoamines, oxidative stress, and metabolic dysfunctions. We aim to assess the therapeutic impacts of roots or leaf extract from Urtica dioica (UD; stinging nettle) against scopolamine (SCOP)-induced memory dysfunction, amnesia, and oxidative stress in rats. Spatial memory was assessed by Y maze test. Tissue analyses of norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin (5-HT), malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), glutathione (GSH, GSSG), AMP, ADP, and ATP were assessed by HPLC. mRNA levels of Tau and Hsp70 were estimated by PCR. UD extracts particularly nettle root (NR) significantly normalized the SCOP-induced memory deficits even more potent than sermion (SR) and donepezil (DON). Similarly, NR had potent therapeutic impacts on the levels of cortical and hippocampal monoamines e.g. DA, NE, and 5-HT. SCOP induced a dramatic oxidative stress as measured by MDA, NO, and GSSG levels; however, UD extracts showed significant anti-oxidative stress impacts. Additionally, UD extracts restored ATP levels and reduced the levels of AMP and ADP compared to SCOP-treated rats. Furthermore, cortical Tau and hippocampal Hsp70 were modulated by UD extracts particularly NR compared to the SCOP group. In conclusion, UD extracts particularly roots have potential therapeutic impacts against SCOP-induced neuroinflammatory and/or Alzheimer-like phenotype in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable
References
Abd-El-Fattah MA, Abdelakader NF, Zaki HF (2014) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects against scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 723:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.11.008
Arafa NM, Ali EH, Hassan MK (2017) Canagliflozin prevents scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats: comparison with galantamine hydrobromide action. Chem Biol Interact. 277:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.08.013
Bélanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 14(6):724–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Bihaqi SW, Singh AP, Tiwari M (2012) Supplementation of Convolvulus pluricaulis attenuates scopolamine-induced increased tau and amyloid precursor protein (AβPP) expression in rat brain. Indian J Pharmacol. 44(5):593–598. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.100383
Bolea I, Gella A, Unzeta M (2013) Propargylamine-derived multitarget-directed ligands: fighting Alzheimer’s disease with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 120(6):893–902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0948-y
Brown IR (2007) Heat shock proteins and neurodegenerative diseases. In: Cell stress proteins. Springer, New York, NY, pp 396–421
de Calignon A, Polydoro M, Suárez-Calvet M, William C, Adamowicz DH, Kopeikina KJ, Spires-Jones TL (2012) Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 73(4):685–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.033
de la Monte SM, Tong M (2014) Brain metabolic dysfunction at the core of Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 88(4):548–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.012
Delitheos B, Papamichael K, Tiligada E (2010) Histamine modulates the cellular stress response in yeast. Amino Acids. 38(4):1219–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0333-9
Francis PT, Ramírez MJ, Lai MK (2010) Neurochemical basis for symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 59(4-5):221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.010
Franklin TB, Krueger-Naug AM, Clarke DB, Arrigo AP, Currie RW (2005) The role of heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp27 in cellular protection of the central nervous system. Int J Hyperthermia. 21(5):379–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656730500069955
Giusi G, Alò R, Crudo M, Facciolo RM, Canonaco M (2008) Specific cerebral heat shock proteins and histamine receptor cross-talking mechanisms promote distinct lead-dependent neurotoxic responses in teleosts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 227(2):248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2007.10.018
Gülçin I, Küfrevioǧlu Öİ, Oktay M, Büyükokuroǧlu ME (2004) Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiulcer and analgesic activities of nettle (Urtica dioica L.). J Ethnopharmacol. 90(2-3):205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2003.09.028
Haider S, Perveen TS (2016) Scopolamine-induced greater alterations in neurochemical profile and increased oxidative stress demonstrated a better model of dementia: a comparative study. Brain Res Bull. 127:234–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.10.002
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Latz E (2014) Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 14(7):463–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3705
Jan KN, Singh S (2017) Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.): a reservoir of nutrition and bioactive components with great functional potential. J Food Measur Character 11(2):423–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9410-4
Jayatilleke E, Shaw S (1993) A high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for reduced and oxidized glutathione in biological samples. Anal Biochem. 214(2):452–457. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1993.1522
Karatepe M (2004) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and free malondialdehyde in human serum by HPLC-UV. LCGC Asia Pacific. 22(4):362–365
Khalifa AE (2004) Pro-oxidant activity of zuclopenthixol in vivo: differential effect of the drug on brain oxidative status of scopolamine-treated rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 23(9):439–445. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327104ht470oa
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2010) The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 34(8):1307–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.04.001
Lenth RV (1989) Quick and easy analysis of unreplicated factorials. Technometrics. 31:469–473. https://doi.org/10.2307/1269997
Liu H, Jiang Y, Luo Y, Jiang W (2006) A simple and rapid determination of ATP, ADP and AMP concentrations in pericarp tissue of litchi fruit by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Technol Biotechnol. 44(4):531–534
Lu RC, Tan MS, Wang H, Xie AM, Yu JT, Tan L (2014) Heat shock protein 70 in Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014:435203–435208. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/435203
Mather M, Harley CW (2016) The locus coeruleus: essential for maintaining cognitive function and the aging brain. Trends Cogn Sci. 20(3):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.01.001
Matsumori Y, Hong SM, Aoyama K, Fan Y, Kayama T, Sheldon RA, Vexler ZS, Ferriero DM, Weinstein PR, Liu J (2005) Hsp70 overexpression sequesters AIF and reduces neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 25(7):899–910. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600080
Muchowski PJ, Wacker JL (2005) Modulation of neurodegeneration by molecular chaperones. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1587
Pagel P, Schubert R, Wilhelm C, Wolf HU (2000) Development of an HPLC-method and synthesis of 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydroisoquinolines as reference compounds for the identification of possible neurotoxins in the blood of Parkinson’s disease patients. In Neurotoxic Factors in Parkinson’s disease and Related Disorders. (pp. 111-114). Springer, Boston, MA
Papadoyannis IN, Samanidou VF, Nitsos CC (1999) Simultaneous determination of nitrite and nitrate in drinking water and human serum by high performance anion-exchange chromatography and UV detection. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 22(13):2023–2041. https://doi.org/10.1081/JLC-100101783
Patel SS, Udayabanu M (2014) Urtica dioica extract attenuates depressive -like behavior and associative memory dysfunction in dexamethasone-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis. 29(1):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9480-0
Patel SS, Parashar A, Udayabanu M (2015) Urtica dioica leaves modulates muscarinic cholinergic system in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis. 30(3):803–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9646-9
Phillips C, Fahimi A, Mojabi FS, Salehi A (2015) Evolution of monoaminergic system degeneration in Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Recent Advances in Alzheimer Research: common pathogenic mechanisms between Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease Steps toward Therapy. pp 273–291., 1, 273
Puri A, Srivastava P, Pandey P, Yadav RS, Bhatt PC (2014) Scopolamine-induced behavioral and biochemical modifications and protective effect of Celastrus paniculatous and Angelica glauca in rats. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis. 4(3):158–169. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0738.132675
Reynolds A, Laurie C, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2007) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol. 82:297–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(07)82016-2
Roghani M, Joghataie MT, Jalili MR, Baluchnejadmojarad T (2006) Time course of changes in passive avoidance and Y-maze performance in male diabetic rats. Iranian Biomed J. 10(2):99–104 http://ibj.pasteur.ac.ir/article-1-355-en.html
Svensson TH, MathÉ JM, Andersson JL, Nomikos GG (1995) Mode of action of atypical neuroleptics in relation to the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia: Role of 5-HT receptor and! a-adrenoreceptor antagonism. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 15(1 Suppl 1):11S–18S. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004714199502001-00003
Tapia-Rojas C, Aranguiz F, Varela-Nallar L, Inestros NC (2016) Voluntary running attenuates memory loss, decreases neuropathological changes and induces neurogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 26(1):62–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12255
Tomitaka SI, Hashimoto K, Narita N, Minabe Y, Tamura A (1997) Regionally different effects of scopolamine on NMDA antagonist-induced heat shock protein HSP70. Brain Res. 763(2):255–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00497-6
Tota S, Nath C, Najmi AK, Shukla R, Hanif K (2012) Inhibition of central angiotensin-converting enzyme ameliorates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice: role of cholinergic neurotransmission, cerebral blood flow and brain energy metabolism. Behav Brain Res. 232(1):66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.03.015
Utkan T, Gocmez SS, Regunathan S, Aricioglu F (2012) Agmatine, a metabolite of L-arginine, reverses scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 102(4):578–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.07.003
Von Linstow CU, Severino M, Metaxas A, Waider J, Babcock AA, Lesch KP, Finsen B (2017) Effect of aging and Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology on brain monoamines in mice. Neurochem Int. 108:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.04.008
Winblad B, Carfagna N, Bonura L, Rossini BM, Wong EH, Battaglia A (2000) Nicergoline in dementia. CNS drugs. 14(4):267–287. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200014040-00003
Wu L, Xu M, Liu S, Chen G, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Yi J (2016) Donepezil delays photoreceptor apoptosis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in mice. Exp Ther Med. 11(6):2446–2454. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3254
Zaki HF, Abd-El-Fattah MA, Attia AS (2014) Naringenin protects against scopolamine-induced dementia in rats. Bull Facul Pharm. Cairo Uni. 52(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bfopcu.2013.11.001
Zhang J, Wang J, Zhou G, Tan Y, Tao H, Chen J, Pu Z, Ma J, She W, Kang A, Zhu Y, Liu P, Zhu Z, Shi X, Tang Y, Dua J (2019) Studies of the anti-amnesic effects and mechanisms of single and combined use of donepezil and ginkgo Ketoester tablet on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 18:8636835. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8636835
Zhou GS, Yuan YC, Yin Y, Tang YP, Xu RJ, Liu Y, Chen PD, Yin L, Duan JA (2020) Hydrophilic interaction chromatography combined with ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of underivatized neurotransmitters in dementia patients' urine samples. Anal Chim Acta. 1107:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.027
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/26), King Saud University, Riyadh, King of Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This work was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/26), King Saud University, Riyadh, King of Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHAA, RMM, MKH, EHAA, GAM, and HA conceived the study, designed the experiments, and acquired and analyzed the data. AHAA, HA, NEB, SA, MMAD, LA, and SH wrote the drafting and revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and study supervision. SH, LA, HA, and SD performed critical revision of the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All animal procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of Mansoura University (approval number: R/18.09.267).
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu Almaaty, A.H., Mosaad, R.M., Hassan, M.K. et al. Urtica dioica extracts abolish scopolamine-induced neuropathies in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 18134–18145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12025-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12025-y