Abstract
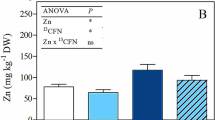
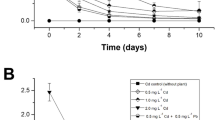
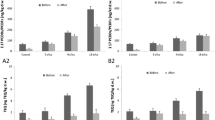
The plant association of Populus alba L. ‘Villafranca’, Brassica oleracea var. acephala sebellica (kale), and B. oleracea var. capitata ‘sonsma’ (cabbage) was exposed to Zn, Cd, and exogenous caffeine (13CFN)-contaminated water under growth chamber conditions. In the short term of treatment (15 days), poplar increased the root dry biomass (+ 25%) and decreased the chlorophyll content in new leaves (− 32%), compared to control. On the contrary, cabbage decreased the root dry biomass, enhancing the shoot dry biomass (+ 50%). Heavy metals were mainly concentrated in plant roots and in poplar reached the highest concentrations of 705 ± 232.6 and 338 ± 85.5 μg g−1 DW for Zn and Cd, respectively. The ability of poplar to accumulate more Zn and Cd than kale and cabbage in plant biomass was confirmed by heavy metal contents, following the order: poplar > kale = cabbage. However, poplar and Brassica sp. association was very useful for Zn and Cd decontaminations as reported by the bioconcentration factors (> 1). The concentration of 13CFN was below 2.4 ng g−1 FW in poplar and 7.4 ng g−1 FW in Brassica species, suggesting the caffeine uptake and degradation by plant association. Under our experimental conditions, the removal efficiency of the system was upper to 79%, indicating the capability of Populus-Brassica association to efficiently remove Zn, Cd, and 13CFN from mixed inorganic-organic–contaminated water in short term.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Acharya J, Kumar U, Rafi PM (2018) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent-a review. Int J Curr Eng Technol 8(3):526–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011
Ali H, Khan E (2018) Trophic transfer, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in food chains/webs - concepts and implications for wildlife and human health. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25:1353–1376. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1469398
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91(7):869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Alkhatib R, Alkhatib B, Al-Quraan N, Al-Eitan L, Abdo N, Muhaidat R (2016) Impact of exogenous caffeine on morphological, biochemical, and ultrastructural characteristics of Nicotiana tabacum. Biol Plant 60(4):706–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0600-z
Anju M (2017) Biotechnological strategies for remediation of toxic metal(loid)s from environment. In: Gahlawat SK, Salar RK, Siwach P, Duhan JS, Kumar S, Kaur P (eds) Plant biotechnology: recent advancements and developments. Springer, Singapore, pp 315–359
Arnon DI, Hoagland DR (1940) Crop production in artificial culture solutions and in soils with special reference to factors influencing yields and absorption of inorganic nutrients. Soil Sci 50:463–485
Ashihara H, Sano H, Crozier A (2008) Caffeine and related purine alkaloids: biosynthesis, catabolism, function and genetic engineering. Phytochemistry 69(4):841–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.029
Ashihara H, Mizuno K, Yokota T, Crozier A (2017) Xanthine alkaloids: occurrence, biosynthesis, and function in plants. In: Kinghorn A, Falk H, Gibbons S, Kobayashi J (eds) Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products 105. Springer, Cham, pp 2–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49712-9_1
Awad AM, Shaikh SHR, Jalab R, Gulied MH, Nasser MS, Benamor A, Adham S (2019) Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: a comprehensive review. Sep Purif Technol 228:115719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115719
Azimi A, Azari A, Rezakazemi M, Ansarpour M (2017) Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: a review. ChemBioEng Rev 4(1):37–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201600010
Batish DR, Singh HP, Kaur M, Kohli RK, Yadav SS (2008) Caffeine affects adventitious rooting and causes biochemical changes in the hypocotyl cuttings of mung bean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.). Acta Physiol Plant 30(3):401–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0132-4
Chandra R, Kang H (2016) Mixed heavy metal stress on photosynthesis, transpiration rate, and chlorophyll content in poplar hybrids. Forest Sci Technol 12(2):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2015.1044024
Chirakkara RA, Cameselle C, Reddy KR (2016) Assessing the applicability of phytoremediation of soils with mixed organic and heavy metal contaminants. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 15(2):299–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-016-9391-0
Cojocaru P, Gusiatin ZM, Cretescu I (2016) Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn as single or mixed pollutants from soil by rape (Brassica napus). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10693–10701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6176-5
David IG, Matache ML, Tudorache A, Chisamera G, Rozylowicz L, Radu GL (2012) Food chain biomagnification of heavy metals in samples from the lower Prut floodplain natural park. Environ Eng Manag J 11:69–73
Ding S, Ma CF, Shi WG, Liu WZ, Lu Y, Liu QF, Luo ZB (2017) Exogenous glutathione enhances cadmium accumulation and alleviates its toxicity in Populus × canescens. Tree Physiol 37:1697–1712. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpx132
Dos Santos Utmazian MN, Wieshammer G, Vega R, Wenzel WW (2007) Hydroponic screening for metal resistance and accumulation of cadmium and zinc in twenty clones of willows and poplars. Environ Pollut 148:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.045
Farago ME (2008) Plants and the chemical elements: biochemistry, uptake, tolerance and toxicity. John Wiley & Sons
Fischerová Z, Tlustoš P, Száková J, Šichorová K (2006) A comparison of phytoremediation capability of selected plant species for given trace elements. Environ Pollut 144(1):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.01.005
Franco JA, Bañón S, Vicente MJ, Miralles J, Martínez-Sánchez JJ (2011) Root development in horticultural plants grown under abiotic stress conditions–a review. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 86(6):543–556. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2011.11512802
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92(3):407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Fuksová Z, Száková J, Balík J, Tlustoš P (2010) Growth and metal uptake by plants grown in mono- and dual culture in metal-contaminated soils. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 19(2):188–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320380903548458
Giachetti G, Sebastiani L (2006) Metal accumulation in poplar plant grown with industrial wastes. Chemosphere 64(3):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.11.021
Haghighi M, Kafi M, Pessarakli M, Sheibanirad A, Sharifinia MR (2016) Using kale (Brassica oleracea var. acephala) as a phytoremediation plant species for lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) removal in saline soils. J Plant Nutr 39(10):1460–1471. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1161768
He JL, Li H, Luo J, Ma CF, Li SJ, Qu L, Gai Y, Jiang X, Janz D, Polle A, Tyree M, Luo ZB (2013a) A transcriptomic network underlies microstructural and physiological responses to cadmium in Populus x canescens. Plant Physiol 162:424–439. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.215681
He JL, Ma CF, Ma YL, Li H, Kang JQ, Liu TX, Polle A, Peng CH, Luo ZB (2013b) Cadmium tolerance in six poplar species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1008-8
Hu R, Zhang Z, Lin L, Liao M’, Tang Y, Liang D, Xia H, Wang J, Wang X, Lv X, Ren W (2019) Intercropping with hyperaccumulator plants decreases the cadmium accumulation in grape seedlings. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 69(4):304–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2018.1564786
Iori V, Pietrini F, Zacchini M (2012) Assessment of ibuprofen tolerance and removal capability in Populus nigra L. by in vitro culture. J Hazard Mater 229-230:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.097
Jakovljević T, Cvjetko Bubalo M, Orlović S, Sedak M, Bilandžić N, Brozinčević I, Redovniković IR (2014) Adaptive response of poplar (Populus nigra L.) after prolonged Cd exposure period. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3792–3802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2292-7
Kalaji HN, Jajoo A, Oukarroum A, Brestic N, Zivcak M, Samborska IA, Cetner MD, Łukasik I, Goltsev V, Ladle RJ (2016) Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 38:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2113-y
Karvelas M, Katsoyiannis A, Samara C (2003) Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process. Chemosphere 53(10):1201–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00591-5
Katanić M, Kovačević B, Dorđević B, Kebert M, Pilipović A, Klašnja B, Pekeč S (2015) Nickel phytoremediation potential of white poplar clones grown in vitro. Rom Biotech Lett 20(1):10085
Lee I, Baek K, Kim H, Kim S, Kim J, Kwon Y, Chang Y, Bae B (2007) Phytoremediation of soil co-contaminated with heavy metals and TNT using four plant species. J Environ Sci Health A 42(13):2039–2045. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520701629781
Li S, Wen J, He B, Wang J, Hu X, Liu J (2020a) Occurrence of caffeine in the freshwater environment: implications for ecopharmacovigilance. Environ Pollut 114371:114371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114371
Li S, He B, Wang J, Liu J, Hu X (2020b) Risks of caffeine residues in the environment: necessity for a targeted ecopharmacovigilance program. Chemosphere 243:125343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125343
Liu X, Jiang J, Yan Y, Dai YY, Deng B, Ding S, Su S, Sun W, Li Z, Gan Z (2018) Distribution and risk assessment of metals in water, sediments, and wild fish from Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 196:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.135
Lloyd G, McCown B (1981) Commercially - feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kolmialatifolia, by use of shoot tip culture. International Plant Propagators Society 30:421–427
Loos R, Carvalho R, António DC, Comero S, Locoro G, Tavazzi S, Paracchini B, Ghiani M, Lettieri T, Blaha L (2013) EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res 47:6475–6487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.024
Lv W, Yang L, Xu C, Shi Z, Shao J, Xian M, Chen J (2017) Cadmium disrupts the balance between hydrogen peroxide and superoxide radical by regulating endogenous hydrogen sulfide in the root tip of Brassica rapa. Front Plant Sci 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00232
Ma Q, Cao X, Tan X, Si L, Wu L (2017) Effects of cadmium stress on pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) growth and uptake of inorganic and organic nitrogenous compounds. Environ Exp Bot 137:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.02.001
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition in higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-473542-2.X5000-7
Mohanpuria P, Yadav SK (2009) Retardation in seedling growth and induction of early senescence in plants upon caffeine exposure is related to its negative effect on Rubisco. Photosynthetica 47(2):293–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-009-0045-0
Mourato MP, Moreira IN, Leitão I, Pinto FR, Sales JR, Martins LL (2015) Effect of heavy metals in plants of the genus Brassica. Int J Mol Sci 16(8):17975–17998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817975
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8(3):199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Pandey LK, Park J, Son DH, Kim W, Islam MS, Choi S, Lee H, Han T (2019) Assessment of metal contamination in water and sediments from major rivers in South Korea from 2008 to 2015. Sci Total Environ 651:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.057
Pierattini EC, Francini A, Raffaelli A, Sebastiani L (2016a) Degradation of exogenous caffeine by Populus alba and its effects on endogenous caffeine metabolism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7298–7307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5935-z
Pierattini EC, Francini A, Raffaelli A, Sebastiani L (2016b) Morpho-physiological response of Populus alba to erythromycin: a timeline of the health status of the plant. Sci Total Environ 569–570:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.152
Pierattini EC, Francini A, Huber C, Sebastiani L, Schröder P (2018) Poplar and diclofenac pollution: a focus on physiology, oxidative stress and uptake in plant organs. Sci Total Environ 636:944–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.355
Potters G, Pasternak TP, Guisez Y, Palme KJ, Jansen MA (2007) Stress-induced morphogenic responses: growing out of trouble? Trends Plant Sci 12(3):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.01.004
Pulford ID, Watson C (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees - a review. Environ Int 29(4):529–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00152-6
Quartacci MF, Micaelli F, Sgherri C (2014) Brassica carinata planting pattern influences phytoextraction of metals from a multiple contaminated soil. Agrochimica 58:77–89
Rai R, Agrawal M, Agrawal SB (2016) Impact of heavy metals on physiological processes of plants: with special reference to photosynthetic system. In: Singh A, Prasad S, Singh R (eds) Plant responses to Xenobiotics. Springer, Singapore, pp 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2860-1_6
Rascio N, Navari-Izzo F (2011) Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: how and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Sci 180(2):169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.08.016
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ et al (2018) Cadmium phytoremediation potential of Brassica crop species: a review. Sci Total Environ 631:1175–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.104
Romè C, Romeo S, Francini A, Andreucci A, Sebastiani L (2016) Leaves position in Populus alba Villafranca clone reveals a strategy towards cadmium uptake response. Plant Growth Regul 79(3):355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0139-6
Romeo S, Francini A, Ariani A, Sebastiani L (2014) Phytoremediation of Zn: identify the diverging resistance, uptake and biomass production behaviours of poplar clones under high zinc stress. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1813–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1813-9
Romeo S, Francini A, Sebastiani L, Morabito D (2017) High Zn concentration does not impair biomass, cutting radial growth, and photosynthetic activity traits in Populus alba L. J Soils Sediments 17(5):1394–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1251-y
Shi WG, Liu W, Yu W, Zhang Y, Ding S, Li H, Mrak T, Kraigher H, Luo ZB (2019) Abscisic acid enhances lead translocation from the roots to the leaves and alleviates its toxicity in Populus x canescens. J Hazard Mater 362:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.024
Shi WG, Liu W, Ma C, Zhang Y, Ding S, Yu W, Deng S, Zhou J, Li H, Luo Z (2020) Dissecting microRNAs-mRNAs regulatory networks underlying sulfur assimilation and cadmium accumulation in poplar leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 61:1614–1630. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa084
Sidhu GPS (2016) Physiological, biochemical and molecular mechanisms of zinc uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants. J Glob Biosci 5(9):4603–4633
Sridhar BM, Diehl SV, Han FX, Monts DL, Su Y (2005) Anatomical changes due to uptake and accumulation of Zn and Cd in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Environ Exp Bot 54(2):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.06.011
Sturikova H, Krystofova O, Huska D, Adam V (2018) Zinc, zinc nanoparticles and plants. J Hazard Mater 349:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.040
Sui Q, Cao X, Lu S, Zhao W, Qiu Z, Yu G (2015) Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater: a review. Emerg Contam 1(1):14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2015.07.001
Szczygłowska M, Piekarska A, Konieczka P, Namieśnik J (2011) Use of brassica plants in the phytoremediation and biofumigation processes. Int J Mol Sci 12(11):7760–7771. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12117760
Taghizadeh M, Solgi M, Karimi M, Sanati MH, Khoshbin S (2018) Heavy metals effects on Brassica oleracea and elements accumulation by salicylic acid. Arch Hyg Sci 7(1):1–11
Vannucchi F, Francini A, Pierattini EC, Raffaelli A, Sebastiani L (2019) Populus alba dioctyl phthalate uptake from contaminated water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25564–25572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05829-0
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq085
Wieshammer G, Unterbrunner R, García TB, Zivkovic MF, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW (2007) Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from agricultural soils by Salix ssp. and intercropping of Salix caprea and Arabidopsis halleri. Plant Soil 298(1–2):255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9363-9
Wu L, Li Z, Han C, Liu L, Teng Y, Sun X, Pan C, Huang Y, Luo Y, Christie P (2012) Phytoremediation of soil contaminated with cadmium, copper and polychlorinated biphenyls. Int J Phytoremediat 14(6):570–584. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.619227
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Feng W, Xin L, Xu Z (2019a) Phytoextraction potential of Pteris vittata L. co-planted with woody species for As, Cd, Pb and Zn in contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 650:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.055
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Huang B, Feng W (2019b) Complementarity of co-planting a hyperaccumulator with three metal (loid)-tolerant species for metal (loid)-contaminated soil remediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 169:306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.017
Zhang DQ, Hua T, Gersberg RM, Zhu J, Ng WJ, Tan SK (2013) Fate of caffeine in mesocosms wetland planted with Scirpus validus. Chemosphere 90:1568–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.059
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their thanks to the financial support provided by Agrobioscience PhD program at Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna of Pisa for granting FV scholarships and by PiAnta project granted by Regione Toscana, POR FESR 2014-2020 for part of the equipment used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FV, AF, and LS contributed to the planning of the experiment; FV and AR collected the biochemical and physiological data; FV, AF, and LS contributed to statistical elaboration and writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Consent to participate
All authors have contributed significantly to the paper, have read the manuscript, and agree to its submission.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vannucchi, F., Francini, A., Raffaelli, A. et al. Removal of multi-contaminants from water by association of poplar and Brassica plants in a short-term growth chamber experiment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 16323–16333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11804-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11804-x