Abstract
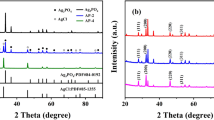
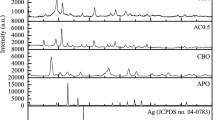
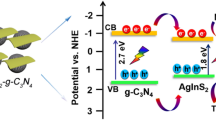
The design of stable and highly efficient photocatalysts had emerged as an economic and promising way for eliminating harmful pharmaceutical pollutants. In this study, a series of Ag2O-modified g-C3N4 composites with different Ag2O amounts (denoted as Ag2O-CNx) were fabricated via a facile reflux condensation methodology. Ofloxacin (OFL) was chosen as a model pollutant to evaluate the degradation efficiency of the photocatalytic system. The optimal photocatalytic activity was achieved with Ag2O-CN1.0, which reached up to 99.1% removal of OFL after 15-min reaction and the pseudo-first-order constant was 0.469 min−1, approximately 42 times higher than that of g-C3N4. Considering the complexity of the actual environment, the important influential factors such as catalyst dosage, initial OFL concentration, solution pH, and natural organic matter on the OFL degradation were systematically investigated. Additionally, Ag2O-CN1.0 showed good stability and recyclability in multiple cycle experiments. The feasible photodegradation mechanism of OFL was proposed with radical scavenger experiments, and the degradation products were determined. Furthermore, the enhanced photocatalytic activity could be ascribed to not only the high photogenerated charge separation efficiency and the surface plasmon resonance effect of metallic Ag, but also the p-n heterojunction formed between Ag2O and g-C3N4. Therefore, Ag2O-CN1.0 was a treatment material possessing great application prospects for eliminating OFL in wastewater.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Adhikari S, Lee HH, Kima DH (2020) Efficient visible-light induced electron-transfer in z-scheme MoO3/Ag/C3N4 for excellent photocatalytic removal of antibiotics of both ofloxacin and tetracycline. Chem Eng J 391:123504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123504
Akhundi A, Habibi-Yangjeh A (2016) Novel g-C3N4/Ag2SO4 nanocomposites: fast microwave-assisted preparation and enhanced photocatalytic performance towards degradation of organic pollutants under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 482:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.08.002
Bao YK, Chen KZ (2016) AgCl/Ag/g-C3N4 hybrid composites: preparation, visible light-driven photocatalytic activity and mechanism. Nano Lett 8(2):182–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0076-y
Cai C, Zhang ZY, Liu J, Shan N, Zhang H (2016) Visible light-assisted heterogeneous Fenton with ZnFe2O4 for the degradation of Orange II in water. Appl Catal B Environ 182:456–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.056
Chang XM, Yao XL, Ding N, Yin XF, Zheng QM, Lu SL, Shuai DM, Sun YX (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of trihalomethanes and haloacetonitriles on graphitic carbon nitride under visible light irradiation. Sci Total Environ 682:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.075
Chen L, Hua H, Yang Q, Hu CG (2015) Visible-light photocatalytic activity of Ag2O coated Bi2WO6 hierarchical microspheres assembled by nanosheets. Appl Surf Sci 327:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.117
Chen X, Kuo DH, Hou YX (2017a) Enhancing the photodegradation of charged pollutants under visible light in Ag2O/g-C3N4 catalyst by Coulombic interaction. J Mater Sci 52(9):5147–5154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0751-0
Chen F, Yang Q, Wang YL, Zhao JW, Wang DB, Li XM, Guo Z, Wang H, Deng YC, Niu CJ, Zen GG (2017b) Novel ternary heterojunction photcocatalyst of Ag nanoparticles and g-C3N4 nanosheets co-modified BiVO4 for wider spectrum visible-light photocatalytic degradation of refractory pollutant. Appl Catal B Environ 205:133–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.017
Chen P, Blaney L, Cagnetta G, Huang J, Wang B, Wang YJ, Deng SB, Yu G (2019) Degradation of ofloxacin by perylene diimide supramolecular nanofiber sunlight-driven photocatalysis. Environ Sci Technol 53:1564–1575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05827
Crespo-Alonso M, Nurchi VM, Biesuz R, Alberti G, Spano N, Pilo MI, Sanna G (2013) Biomass against emerging pollution in wastewater: ability of cork for the removal of ofloxacin from aqueous solutions at different pH. J Environ Chem Eng 1(4):1199–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.09.010
Feng Z, Zeng L, Zhang QL, Ge SF, Zhao XY, Lin HJ, He YM (2020) In situ preparation of g-C3N4/Bi4O5I2 complex and its elevated photoactivity in Methyl Orange degradation under visible light. J Environ Sci 87:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.032
Gou JF, Ma QL, Deng XY, Cui TQ, Zhang HX, Cheng XW, Li XL, Xie MZ, Cheng QF (2017) Fabrication of Ag2O/TiO2-Zeolite composite and its enhanced solar light photocatalytic performance and mechanism for degradation of norfloxacin. Chem Eng J 308:818–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.089
He J, Shao DW, Zheng LC, Zheng LJ, Feng DQ, Xu JP, Zhang XH, Wang WC, Wang WH, Lu F, Dong H, Cheng YH, Liu H, Zheng RK (2017) Construction of Z-scheme Cu2O/Cu/AgBr/Ag photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 203:917–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.086
Hu XX, Hu C, Wang R (2015) Enhanced solar photodegradation of toxic pollutants by long-lived electrons in Ag–Ag2O nanocomposites. Appl Catal B Environ 176-177:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.040
Ji HH, Zhang LL, Hu C (2017) Chemical-bond conjugated BiO(OH)xI1-x-AgI heterojunction with high visible light activity and stability in degradation of pollutants. Appl Catal B Environ 218:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.077
Kaur A, Gupta G, Ibhadon AO, Salunke DB, Sinha ASK, Kansal SK (2018a) A Facile synthesis of silver modified ZnO nanoplates for efficient removal of ofloxacin drug in aqueous phase under solar irradiation. J Environ Chem Eng 6(3):3621–3630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.032
Kaur M, Mehta SK, Kansal SK (2018b) Visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin and malachite green dye using cadmium sulphide nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 6(3):3631–3639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.04.006
Kumar A, Kumar A, Sharma G, Al-Muhtaseb AH, Naushad M, Ghfar AA, Stadler FJ (2018) Quaternary magnetic BiOCl/g-C3N4/Cu2O/Fe3O4 nano-junction for visible light and solar powered degradation of sulfamethoxazole from aqueous environment. Chem Eng J 334:462–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.049
Li H, Liu JY, Hou WG, Du N, Zhang RJ, Tao XT (2014) Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4/Bi2MoO6 heterojunctions with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 160-161:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.05.019
Li YJ, Xue JY, Tian J, Song XJ, Zhang XJ, Wang XZ, Cui HZ (2017) Silver oxide decorated graphitic carbon nitride for the realization of photocatalytic degradation over the full solar spectrum: from UV to NIR region. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 168:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.04.031
Liang SH, Zhang DF, Pu XP, Yao XT, Han RT, Yin J, Ren XZ (2019) A novel Ag2O/g-C3N4 p-n heterojunction photocatalysts with enhanced visible and near-infrared light activity. Sep Purif Technol 210:786–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.09.008
Liu CB, Cao C, Luo XB, Luo SL (2015) Ag-bridged Ag2O nanowire network/TiO2 nanotube array p-n heterojunction as a highly efficient and stable visible light photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 285:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.020
Liu L, Qi YH, Lu JR, Lin SL, An WJ, Liang YH, Cui WQ (2016) A stable Ag3PO4 @g-C3N4 hybrid core@shell composite with enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation. Appl Catal B Environ 183:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.10.035
Liu W, Li YY, Liu FY, Jiang W, Zhang DD, Liang JL (2019) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by carbon quantum dots modified porous g-C3N4: mechanisms, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Water Res 150:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.084
Lv SW, Liu JM, Zhao N, Li CY, Wang ZH, Wang S (2020) Benzothiadiazole functionalized Co-doped MIL-53-NH2 with electron deficient units for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A and ofloxacin under visible light. J Hazard Mater 387:122011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122011
Ma SL, Zhan SH, Jia YN, Shi Q, Zhou QX (2016) Enhanced disinfection application of Ag-modified g-C3N4 composite under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 186:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.051
Mageshwari K, Sathyamoorthy R, Park J (2015) Photocatalytic activity of hierarchical CuO microspheres synthesized by facile reflux condensation method. Powder Technol 278:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.03.004
Miao XL, Shen XP, Wu JJ, Jia ZY, Wang JH, Kong LR, Liu MM, Song CS (2017) Fabrication of an all solid Z-scheme photocatalyst g-C3N4/GO/AgBr with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal A Gen 539:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.04.009
Ou M, Wan SP, Zhong Q, Zhang SL, Song Y, Guo LN, Cai W, Xu YL (2018) Hierarchical Z-scheme photocatalyst of g-C3N4 @Ag/BiVO4 (040) with enhanced visible-light-induced photocatalytic oxidation performance. Appl Catal B Environ 221:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.005
Peng HB, Pan B, Wu M, Liu R, Zhang D, Wu D, Xing BS (2012) Adsorption of ofloxacin on carbon nanotubes: solubility, pH and cosolvent effects. J Hazard Mater 211-212:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.063
Prabavathia SL, Saravanakumara K, Mamba G, Muthuraj V (2019) 1D/2D MnWO4 nanorods anchored on g-C3N4 nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic degradation ofloxacin under visible light irradiation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 581:123845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123845
Ran R, Meng XC, Zhang ZS (2016) Facile preparation of novel graphene oxide-modified Ag2O/Ag3VO4/AgVO3 composites with high photocatalytic activities under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 196:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.012
Shabani M, Haghighi M, Kahforoushan D (2018) One-pot combustion fabrication of grain-like mesoporous intra-heterostructure Bi(x)O(y)Cl(z) nanophotocatalyst with substantial solar-light-driven degradation of antibiotic ofloxacin: influence of various fuels. Catal Sci Technol 8:4052–4069. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cy00547h
Shang YY, Chen X, Liu WW, Tan PF, Chen HY, Wu LD, Ma C, Xiong X, Pan J (2017) Photocorrosion inhibition and high-efficiency photoactivity of porous g-C3N4/Ag2CrO4 composites by simple microemulsion-assisted co-precipitation method. Appl Catal B Environ 204:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.11.025
Shi L, Liang L, Ma J, Wang FX, Sun JM (2014) Enhanced photocatalytic activity over the Ag2O–g-C3N4 composite under visible light. Catal Sci Technol 4(3):758. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cy00871a
Shi HL, He R, Sun L, Cao G, Yuan XJ, Xia DS (2019) Band gap tuning of g-C3N4 via decoration with AgCl to expedite the photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of oxalic acid. J Environ Sci 84:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.04.009
Song YL, Tian JY, Gao SS, Shao PH, Qi JY, Cui FY (2017) Photodegradation of sulfonamides by g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation: effectiveness, mechanism and pathways. Appl Catal B Environ 210:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.059
Sun M, Zeng Q, Zhao X, Shao Y, Ji PG, Wang CQ, Yan T, Du B (2017) Fabrication of novel g-C3N4 nanocrystals decorated Ag3PO4 hybrids: enhanced charge separation and excellent visible-light driven photocatalytic activity. J Hazard Mater 339:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.003
Tian L, Yang XF, Cui XK, Liu QQ, Tang H (2019) Fabrication of dual direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/MoS2/Ag3PO4 photocatalyst and its oxygen evolution performance. Appl Surf Sci 463:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.209
Wammer KH, Korte AR, Lundeen RA, Sundberg JE, McNeill K, Arnold WA (2013) Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacterials: norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water Res 47(1):439–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.025
Wang WG, Liu Y, Zhang HY, Qian YN, Guo ZC (2017) Re-investigation on reduced graphene oxide/Ag2CO3 composite photocatalyst: an insight into the double-edged sword role of RGO. Appl Surf Sci 396:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.030
Wei ZD, Wang R (2016) Hierarchical BiOBr microspheres with oxygen vacancies synthesized via reactable ionic liquids for dyes removal. Chin Chem Lett 27(5):769–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2016.03.013
Wei ZD, Liu JY, Fang WJ, Xu MQ, Qin Z, Jiang Z, Shangguan WF (2019) Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with simultaneous antibiotic wastewater degradation via the visible-light-responsive bismuth spheres-g-C3N4 nanohybrid: Waste to energy insight. Chem Eng J 358:944–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.096
Wen XJ, Niu CG, Zhang L, Liang C, Zeng GM (2018) A novel Ag2O/CeO2 heterojunction photocatalysts for photocatalytic degradation of enrofloxacin: possible degradation pathways, mineralization activity and an in depth mechanism insight. Appl Catal B Environ 221:701–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.060
Wu M, Yan JM, Zhang XW, Zhao M, Jiang Q (2015) Ag2O modified g-C3N4 for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under visible light irradiation. J Mater Chem A 3(30):15710–15714. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta03358f
Xiong T, Dong F, Zhou Y, Fu M, Ho WK (2015) New insights into how RGO influences the photocatalytic performance of BiOIO3/RGO nanocomposites under visible and UV irradiation. J Colloid Interface Sci 447:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.01.068
Xu J, Gao QZ, Bai XJ, Wang ZP, Zhu YF (2019) Enhanced visible-light-induced photocatalytic degradation and disinfection activities of oxidized porous g-C3N4 by loading Ag nanoparticles. Catal Today 332:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.024
Yu W, Liu XJ, Chu HP, Zhu G, Li JL, Liu JY, Niu LY, Sun Z, Pan LK (2015) Enhancement of visible light photocatalytic activity of Ag2O/F-TiO2 composites. J Mol Catal A Chem 407:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.06.015
Zhang C, Li Y, Shuai DM, Shen Y, Xiong W, Wang L (2019) Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for water disinfection and microbial control: a review. Chemosphere 214:462–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.137
Zhang DD, Qi JJ, Ji HD, Li S, Chen L, Huang TB, Xu CK, Chen XM, Liu W (2020a) Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin by perovskite-type NaNbO3 nanorods modified g-C3N4 heterojunction under simulated solar light: theoretical calculation, ofloxacin degradation pathways and toxicity evolution. Chem Eng J 400:125918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125918
Zhang SP, Wang YM, Cao Z, Xu J, Hua J, Huang Y, Cui CZ, Liu HL, Wang HL (2020b) Simultaneous enhancements of light-harvesting and charge transfer in UiO67/CdS/rGO composites toward ofloxacin photo-degradation. Chem Eng J 381:122771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122771
Zhao W, Guo Y, Wang SM, He H, Sun C, Yang SG (2015) A novel ternary plasmonic photocatalyst: ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheet hybrided by Ag/AgVO3 nanoribbons with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Appl Catal B Environ 165:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.016
Zhu BC, Xia PF, Ho WK, Yu JG (2015) Isoelectric point and adsorption activity of porous g-C3N4. Appl Surf Sci 344:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.086
Zhu Z, Lu ZY, Wang DD, Tang X, Yan YS, Shi WD, Wang WS, Gao NL, Yao X, Dong HJ (2016a) Construction of high-dispersed Ag/Fe3O4/g-C3N4 photocatalyst by selective photo-deposition and improved photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 182:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.029
Zhu LY, Santiago-Schubel B, Xiao HX, Hollert H, Kueppers S (2016b) Electrochemical oxidation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: mechanism, residual antibacterial activity and toxicity change. Water Res 102:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.005
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51808412) and the Central Government Guidance for Local Science and Technology Development Projects for Hubei province (Nos. 2018ZYYD024, 2019ZYYD068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huifen Yin: methodology, investigation, writing - original draft preparation; Hanlu Shi: investigation; Lei Sun: resources; Dongsheng Xia: funding acquisition, supervision; Xiangjuan Yuan: funding acquisition, writing - review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1170 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, H., Shi, H., Sun, L. et al. Construction of Ag2O-modified g-C3N4 photocatalyst for rapid visible light degradation of ofloxacin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 11650–11664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11390-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11390-y