Abstract
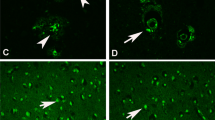
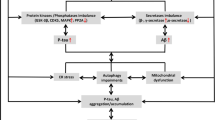
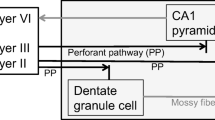
Zinc (Zn) is an essential trace element for most organisms, including human beings. It plays a crucial role in several physiological processes such as catalytic reaction of enzymes, cellular growth, differentiation and metabolism, intracellular signaling, and modulation of nucleic acid structure. Zn containing above 50 metalloenzymes is responsible for proteins, receptors, and hormones synthesis and has a critical role in neurodevelopment. Zn also regulates excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA and is found in high concentration in the synaptic terminals of hippocampal mossy fibers that maintains cognitive function. It regulates LTP and LTD by regulation of AMPA and NMDA receptors. But an excess or deficiency of Zn becomes neurotoxic or cause impairment in growth or sexual maturation. There is mounting evidence that supports this idea of Zn becoming neurotoxic and being involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Zn dyshomeostasis in AD is an area that needs attention as moderate concentration of Zn is involved in the memory regulation via regulation of amyloid plaque. Dyshomeostasis of Zn is involved in the pathogenesis of diseases like AD, ALS, depression, PD, and schizophrenia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaseth J, Dusek P, Roos PM (2018) Prevention of progression in Parkinson’s disease. Biometals 31:737–747
Adlard PA, Chung RS (2015) The molecular pathology of cognitive decline: focus on metals. Front Aging Neurosci 7:116
Agnihotri A, Aruoma OI (2020) Alzheimer’s disease and parkinson’s disease: a nutritional toxicology perspective of the impact of oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, nutrigenomics and environmental chemicals. J Am Coll Nutr 39(1):16–27
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, Gamst A, Holtzman DM, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Snyder PJ, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease:Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7:270–279
Al-Saleh I, Nester M, Abduljabbar M, Al-Rouqi R, Eltabache C, Al-Rajudi T, Elkhati R (2016) Mercury (Hg) exposure and its effects on Saudi breastfed infant’s neurodevelopment. Int J Hyg Environ Health 219:129–135
Andrade VM, Aschner M, Marreilha dos Santos AP (2017) Neurotoxicity of metal mixtures. Adv Neurobiol 18:227–265
Bagherani N, Smoller BR (2016) An overview of zinc and its importance in dermatology-part I: Importance and function of zinc in human beings. Glob Dermatol 3:330–336
Balachandran RC, Mukhopadhyay S, McBride D, Veevers J, Harrison FE, Aschner M, Haynes EN, Bowman AB (2020) Brain manganese and the balance between essential roles and neurotoxicity. J Biol Chem:1–31
Barnham KJ, Bush AI (2008) Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:222–228
Barroso I, Farinha R, Guimarães JT (2018) Proper zinc evaluation in clinical practice: Effect of sample type and its stability. Clin Biochem 59:93–95
Basha R, Wei W, Brydie M, Razmiafshari M, Zawia NH (2003) Lead-induced developmental perturbations in hippocampal Sp1 DNA-binding are prevented by zinc supplementation: in vivo evidence for Pb and Zn competition. Int J Dev Neurosci 21:1–12
Bates KA, Verdile G, Li Q-X, Ames D, Hudson P, Masters CL, Martins RN (2009) Clearance mechanisms of Alzheimer’s amyloid-b peptide: implications for therapeutic design and diagnostic tests. Mol Psychiatry 14:469–486
Beyer N, Coulson DT, Heggarty S, Ravid R, Hellemans J, Irvine GB, Johnston JA (2012) Zinc Transporter mRNA Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease Postmortem Brain. J Alzheimers Dis 29:863–873
Bonda DJ, Lee H, Blair JA, Zhu X, Perryab G, Smitha MA (2011) Role of metal dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Metallomics 3:267–270
Brown KH, Wuehler SE, Peerson JM (2001) The importance of zinc in human nutrition and estimation of the global prevalence of zinc deficiency. Foo J Alzheimers Dis d Nutr Bull 22:113–125
Bush AI (2013) The metal theory of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33:S277–S281
Bush A, Pettingell W, Multhaup G, Paradis M, Vonsattel J, Gusella J, Tanzi R (1994) Rapid induction of Alzheimer A beta amyloid formation by zinc. Science 265:1464–1467
Ceccatelli S, Daréb E, Moors M (2010) Methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity and apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 188:301–308
Chen T, Zhang Y, Shang Y, Gu X, Zhu Y, Zhu L (2018) NBD-BPEA regulates Zn2+- or Cu2+-induced Aβ40 aggregation and cytotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 30:260–267
Chiorcea-Paquim A, Enache TA, Oliveira-Brett AM (2018) Electrochemistry of Alzheimer disease amyloid beta peptides. Curr Med Chem 25:4066–4083
Corkins MR (2019) Aluminum effects in infants and children. Pediatrics 144 (6):e20193148
Costa LG (1998) Biochemical and molecular neurotoxicology: relevance to biomarker development, neurotoxicity testing and risk assessment. Toxicol Lett 103:417–421
Costa LG, Manzo L (1995) Biochemical markers of neurotoxicity: research epidemiological applications. Toxicol Lett 77:137–144
De-Paula VJ, Radanovic M, Diniz BS, Forlenza OV (2012) Alzheimer’s Disease. Subcell Biochem 65:329–352
DeTure MA, Dickson DW (2019) The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 14:32–36
Doneray H, Olcaysu E, Yildirim A, Ozden A (2017) The effect of the zinc concentration in breast milk on neonatal weight gain. J Trace Elem Med Biol 41:32–35
Dong S, Duan Y, Hu Y, Zhao Z (2012) Advances in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a re-evaluation of amyloid cascade hypothesis. Transl. Neurodegener12: 1-18
Dusek P, Roos PM, Litwin T, Schneider SA, Flaten TP, Aaseth J (2015) The neurotoxicity of iron, copper and manganese in Parkinson’s and Wilson’s diseases. J Trace Elem Med Biol 31:193–203
Ekino S, Susa M, Ninomiya T, Imamura K, Kitamura T (2007) Minamata disease revisited: an update on the acute and chronic manifestations of methyl mercury poisoning. J Neurol Sci 262:131–144
Fallah A, Mohammad-Hasani A, Colagar AH (2018) Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization. J Reprod Infertil 19:69–81
Forsleff L, Schauss AG, Bier ID, Stuart S (1999) Evidence of functional zinc deficiency in Parkinson's disease. J Altern Complement Med 5:57–64
Forte G, Alimonti A, Pino A, Stanzione P, Brescianini S, Brusa L, Sancesario G, Violante N, Bocca B (2005) Metals and oxidative stress in patients with Parkinson's disease. Ann I Super Sanita 41:189–195
Garzon-Rodriguez W, Yatsimirsky AK, Glabe CG (1999) Binding of Zn (II), Cu (II), and Fe (II) ions to alzheimer's Aß peptide studied by fluorescence. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9:2243–2248
Genoud S, Roberts BR, Gunn AP, Halliday GM, Lewis SJ, Ball HJ, Hare DJ, Double KL (2017) Subcellular compartmentalisation of copper, iron, manganese, and zinc in the Parkinson's disease brain. Metallomics 9:1447–1455
Gower-Winter SD, Levenson CW (2012) Zinc in the central nervous system: From molecules to behaviour. Biofactors 38:186–193
Greenough MA, Camakaris J, Bush AI (2013) Metal dyshomeostasis and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 62:540–555
Hancock SM, Finkelstein DI, Adlard PA (2014) Glia and zinc in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease: a mechanism for cognitive decline? Front Aging Neurosci 6:137–142
Hane F, Leonenko Z (2014) Effect of metals on kinetic pathways of amyloid-β aggregation. Biomolecules 4:101–116
Harilal S, Jose J, Parambi DG, Kumar R, Mathew GE, Uddin MS, Kim H, Mathew B (2019) Advancements in nanotherapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease: current perspectives. J. Pharm Pharmacol 71:1370–1383
Horgusluoglu E, Nudelman K, Nho K, Saykin AJ (2016) Adult neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases: a systems biology perspective. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 174:93–112
Huang Y, Wu Z, Cao Y, Lang M, Lu B, Zhou B (2014) Zinc binding directly regulates tau toxicity independent of tau hyperphosphorylation. Cell Rep 8:831–842
James SA, Churches QI, de Jonge MD, Birchall IE, Streltsov V, McColl G, Adlard PA, Hare DJ (2017) Iron, copper, and zinc concentration in Aβ plaques in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease correlates with metal levels in the surrounding neuropil. ACS Chem Neurosci 15:629–637
Jellinger KA (2013) The relevance of metals in the pathophysiology of neurodegeneration, pathological considerations. Int Rev Neurobiol 110:1–47
Johnson JW, Kotermanski SE (2006) Mechanism of action of memantine. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:61–67
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87
Jomova K, Vondrakova D, Lawson M, Valko M (2010) Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Cell Biochem 345:91–104
Kandiah N, Pai MC, Senanarong V, Looi I, Ampil E, Park KW, Karanam AK, Christopher S (2017) Rivastigmine: the advantages of dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase and its role in subcortical vascular dementia and Parkinson's disease dementia. Clin Interv Aging 12:697–707
Karri V, Schuhmacher M, Kumar V (2016) Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: a general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 48:203–213
Kausar S, Mustafa HG, Altaf AA, Mustafa G, Badshah A (2019) Galantamine. In: Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, Netherlands
Kim I, Park EJ, Seo J, Ko SJ, Lee J (2011) Zinc stimulates tau S214 phosphorylation by the activation of Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinasekinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Neuroreport 22:839–844
Kumar A, Singh A, Ekavali (2015) A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: an update. Pharmacol Rep 67:195–203
Lammich S, Kojro E, Postina R, Gilbert S, Pfeiffer R, Jasionowski M (1999) Constitutive and regulated α-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by a disintegrin metalloprotease. Proc NatlAcadSciUSA 96:3922–3927
Li X, Du X, Ni J (2019) Zn2+ Aggravates tau aggregation and neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 20:487–504
Liu Y, Nguyen M, Robert A, Meunier B (2019a) Metal Ions in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Key Role or Not? Acc Chem Res 52:2026–2035
Liu PP, Xie Y, Meng XY, Kang JS (2019b) History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct Tar 4:1–22
Lovell MA, Robertson JD, Teesdale WJ, Campbell JL, Markesbery WR (1998) Copper, iron and zinc in Alzheimer's disease senile plaques. J Neurol Sci 158:47–52
Mantyh P, Ghilardi J, Rogers S, DeMaster E, Allen C, Stimson E, Maggio J (1993) Aluminum, iron, and zinc ions promote aggregation of physiological concentrations of B-Amyloid peptide. J Neurochem 61:1171–1174
Méndez-Armenta M, Ríos C (2007) Cadmium neurotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23:350–358
Mezzaroba L, Alfieri DF, Simão ANC, Reiche EMV (2019) The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotoxicology 74:230–241
Morris DR, Levenson CW (2017) Neurotoxicity of Zinc. Adv Neurobiol 18:303–312
Myhre O, Utkilen H, Duale N, Brunborg G, Hofer T (2013) Metal dyshomeostasis and inflammation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: possible impact of environmental exposures. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 726954:1–19
Pan L, Patterson JC (2013) Molecular dynamics study of Zn (Aβ) And Zn(Aβ)2. PLoS One 8:70681
Peters DG, Connor JR, Meadowcroft MD (2015) The relationship between iron dyshomeostasis and amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer's disease: Two sides of the same coin. Neurobiol Dis 81:49–65
Petrilli MA, Kranz TM, Kleinhaus K, Joe P, Getz M, Johnson P, Chao MV, Malaspina D (2017) The emerging role for zinc in depression and psychosis. Front Pharmacol 8:414
Porlas RV, Lynn CL, de Castillo PCC, Dioquino (2018) Neurologic Wilson disease: case series on a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 20(4):341–345
Rachakonda V, Pan TH, Le WD (2004) Biomarkers of neurodegenerative disorders: how good are they? Cell Res 14:349–360
Roberts BR, Ryan TM, Bush AI, Masters CI, Duce JA (2012) The role of metallobiology and mmyloid-β meptides in alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 120:149–166
Sanabria-Castro A, Alvarado-Echeverría I, Monge-Bonilla C (2017) Molecular pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Ann Neurosci 24:46–54
Sensi SL, Paoletti P, Bush AI, Sekler I (2009) Zinc in the Physiology and Pathology of the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:780–791
Siblerud R, Mutter R, Moore E, Naumann J, Walach H (2019) A hypothesis and evidence that mercury may be an etiological factor in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health 24:5152–5161
Skrajnowska D, Bobrowska-Korczak B (2019) Role of zinc in immune system and anti-cancer defense mechanisms. Nutrients 22:2273–2281
Smith AP, Lee NM (2007) Role of zinc in ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Sc 8:131–143
Smith DG, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2007) The redox chemistry of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid β peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:1976–1990
Sun X, Wei Y, Xiong Y, Wang X, Xie A, Wang X, Yang Y, Wang Q, Lu Y, Liu R, Wang J (2012) Synaptic released zinc promotes tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). J Biol Chem 287:11174–11182
Sung P, Lin P, Liu C, Su H, Tsai K (2020) Neuroinflammation and neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease and potential therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 21:701
Swerdlow RH (2007) Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 2:347–359
Szewczyk B (2013) Zinc homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders. Front Aging Neurosci 5:33
Tarohda T, Ishida Y, Kawai K, Yamamoto M, Amano R (2005) Regional distributions of manganese, iron, copper, and zinc in the brains of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced parkinsonian rats. Anal Bioanal Chem 383:224–234
Tewari D, Stankiewicz AM, Mocan A, Sah AN, Tzvetkov NT, Huminiecki L, Horbańczuk JO, Atanasov AG (2018) Ethnopharmacological approaches for dementia therapy and significance of natural products and herbal drugs. Front Aging Neurosci 10:3
Thakur AK, Kamboj P, Goswami K, Ahuja K (2018) Pathophysiology and management of alzheimer’s disease: an overview. J anal pharm Res 9:226–235
Tyszka-Czochara M, Grzywacz A, Gdula-Argasi J, Librowski T, Wili-Ski B, Opoka W (2014) The role of zinc in the pathogenesis and treatment of central nervous system (CNS) diseases. Implications of zinc homeostasis for proper CNS function. Acta Pol Pharm 71:369–377
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MTD (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12:1161–1208
Wang C, Wang T, Zheng W, Zhao B, Danscher G, Chen Y, Wang Z (2010) Zinc overload enhances APP cleavage and Aβ deposition in the Alzheimer mouse brain. PLoS One 12:15349–15355
Wang L, Yin YL, Liu XZ, Shen P, Zheng YG, Lan XR, Lu CB, Wang JZ (2020) Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 9:1–13
Watt NT, Whitehouse IJ, Hooper NM (2011) The role of zinc in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:1–10
Wright RO, Baccarelli A (2007) Metals and neurotoxicology. J Nutr 137:2809–2813
Yamasaki T, Muranaka H, Kaseda Y, Mimori Y, Tobimatsu S (2012) Understanding the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a mini review on fMRI and ERP studies. Neurol Res Int 719056:1–10
Yokel RA (2006) Blood-brain barrier flux of aluminum, manganese, iron and other metals suspected to contribute to metal-induced neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 10:223–253
Zatta P, Drago D, Bolognin S, Sensi SL (2009) Alzheimer’s disease, metal ions and metal homeostatic therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:346–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, S.E., Rehuman, N.A., Harilal, S. et al. Molecular mechanism of zinc neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 43542–43552 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10477-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10477-w