Abstract
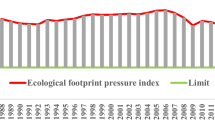
This article investigates the effects of real income, trade openness, and energy consumption on the ecological footprint using a panel data of 13 Asian countries over the 1973–2014 period. The empirical findings suggest that the panel variance-ratio test confirms the existence of a long-run equilibrium relationship among ecological footprint real income, trade openness, and energy consumption. Results from panel pooled mean group estimates confirm that the long-run elasticity of real income, trade openness, and energy consumption is 0.16, −0.07, and 0.51, respectively. The real income and energy consumption have a positive impact on the ecological footprint. There are three bidirectional causal relationships that were found between ecological footprint and real income; between energy consumption and ecological footprint; and between trade openness and ecological footprint. In addition, three unidirectional causalities can be found: a unidirectional causality running from real income to trade openness; from real income to energy consumption; and from trade openness to energy consumption. Those causal relationships show that economic indicators are highly related to ecological footprint. The findings recommend that various governments should fund more in renewable energy and efficiency upgrade and continue sustaining their growth without hurting the environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The data and description can be found at following address: https://www.footprintnetwork.org/our-work/ecological-footprint/
\( {\overline{y}}_{i,t}=\frac{1}{N}\sum \limits_{i=1}^N{y}_{i,t} \) and \( {\overline{x}}_{i,t}=\frac{1}{N}\sum \limits_{i=1}^N{x}_{i,t} \)
References
Acar S, Aşici AA (2017) Nature and economic growth in Turkey: what does ecological footprint imply? Middle East Dev J 9(1):101–115
Acaravci A, Ozturk I (2010) On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy Policy 35(12):5412–5420
Ahmed Z, Wang Z (2019) Investigating the impact of human capital on the ecological footprint in India: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26782–26796
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(18):18565–18582
Al-mulali U (2011) Oil consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in MENA countries. Energy 36(10):5412–5420
Al-mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015a) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energy Policy 76:123–131
Al-mulali U, Choong WW, Low ST, Mohammed AH (2015b) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and output in France. Energy Policy 30(10):4772–4778
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan NA (2020) Environmental Kuznets curve revisited: an analysis using ecological and material footprint. Ecol Indic 115:106416
Aşici AA, Acar S (2016) Does income growth relocate ecological footprint? Ecol Indic 61:707–714
Baležentis T, Streimikiene D, Zhang T, Liobikiene G (2019) The role of bioenergy in greenhouse gas emission reduction in EU countries: an environmental Kuznets curve modelling. Resour Conserv Recycl 142:225–231
Bello MO, Solarin SA, Yen YY (2018) The impact of electricity consumption on CO2 emission, carbon footprint, water footprint and ecological footprint: The role of hydropower in an emerging economy. J Environ Manag 219:218–230
Blackburne EF, Frank MW (2007) Estimation of nonstationary heterogeneous panels. Stata J 7(2):197–208
Boutaud A, Natacha G, Christian B (2006) Local environmental quality versus (global ecological carrying capacity: what might alternative aggregated indicators bring to the debates about environmental kunzites curves and sustainable development). Int J Sustain Dev 9(3):297–310
Bulut U (2017) The impacts of non-renewable and renewable energy on CO2 emissions in Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(18):15416–15426
Caviglia-Harris JL, Chambers D, Kahn JR (2009) Taking the “U” out of Kuznets: a comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation. Ecol Econ 68(4):1149–1159
Chandia KE, Gul I, Aziz S, Sarwar B, Zulfiqar S (2018) An analysis of the association among carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic performance: an econometric model. Carbon Manag 9(3):227–241
Chang CC (2009) A multivariate causality test of carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China. Appl Energy 87:3533–3537
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sust Energy Rev 76:138–154
Demetrescu M, Hanck C (2012) A simple nonstationary-volatility robust panel unit root test. Econ Lett 117:10–13
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450–1460
Halicioglu F (2012) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37:1156–1164
Hassan ST, Xia E, Khan NH, Ali Shah SM (2019) Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2929–2938
Herwartz H, Siedenburg F (2008) Homogeneous panel unit root tests under cross sectional dependence: finite sample modifications and the wild bootstrap. Comput Stat Data 53:137–150
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74
Jebli MB, Youssef SB, Ozturk I (2016) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Indic 60:824–831
Lean HH, Smyth R (2010) CO2 emissions, electricity consumption and output in ASEAN. Appl Energy 87(6):1858–1864
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Liu Y, Hao Y (2018) The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic development in the countries along “the Belt and Road”. Sci Total Environ 645:674–683
Liu H, Kim H, Liang S, Kwon O (2018) Export diversification and ecological footprint: a comparative study on EKC theory among Korea, Japan, and China. Sustainability 10:3657
Lu WC (2017) Greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: a panel cointegration analysis for 16 Asian countries. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(11):1436–1451
Lu WC (2018) The impact of information and communication technology, energy consumption, financial development, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 Asian countries. Mitig Adapt Strat GL 28(2):1–15
Magazzino C (2014) The relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Italy. Int J Sust Energy 35:1–14
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2017) Testing the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70(C):1366–1375
Ozcan B, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2019) Analysis long lasting effects of environmental policies: evidence from low, middle and high income economies. Sustain Cities Soc 44:130–143
Ozturk I, Al-mulali U, Saboori B (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1916–1928
Pedroni P (2001) Purchasing power parity tests in cointegrated panels. Rev Econ Stat 83:727–31
Pedroni P (2004) Panel Cointegration: Asymptotic and Finite Sample Properties of Pooled Time Series Tests with an Application to the PPP Hypothesis, Econometric Theory 20:597–625
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith R (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Sta Assoc 94:621–634
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and influence in large heterogenous panels with multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74:967–1012
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312
Sabir S, Gorus MS (2019) The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from the south Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33387–33398
Saboori B, Sulaiman J (2013) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries: a cointegration approach. Energy 55:813–822
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191
Saidi K, Hammami S (2015) The impact of CO2 emissions and economic growth on energy consumption in 58 countries. Energy Rep 1:62–70
Shabbir MS, Shahbaz M, Zeshan M (2014) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, real GDP and CO2 emissions nexus: a structural VAR approach in Pakistan. Bull Energy Econ 2:91–105
Shahbaz M, Sinha A (2019) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a literature survey. J Econ Stud 46(1):106–168
Shahbaz M, Kumar Tiwar A, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Solarin SA, Bello MO (2018) Persistence of policy shocks to an environmental degradation index: the case of ecological footprint in 128 developed and developing countries. Ecol Indic 89:35–44
Soytas U, Sari R (2009) Energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: challenges faced by a EU candidate member. Ecol Econ 68:1667–1675
Soytas U, Sari R, Ewing BT (2007) Energy consumption, income and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecol Econ 62:482–489
Stern DI (2014) The environmental Kuznets curve: a primer centre for climate economics and policy. Crawford School of Public Policy, ANU
Tsaurai K (2018) Greenhouse gas emissions and economic growth in Africa: does financial development play and moderating role? Int J Energy Econ Policy 8(6):267–274
Uddin GA, Salahuddin M, Alam K, Gow J (2017) Ecological footprint and real income: panel data evidence from the 27 highest emitting countries. Ecol Indic 77:166–175
Ulucak R, Bilgili F (2018) A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle, and low income countries. J Clean Prod 188:144–157
Ulucak R, Lin D (2017) Persistence of policy shocks to ecological footprint of the USA. Ecol Indic 80:337–343
Westerlund J (2005) New simple tests for panel cointegration. Econ Rev 24(3):297–316
Westerlund J, Edgerton DL (2008) A simple test for cointegration in dependent panels with structural breaks. Oxford B of Econ Stat 70(5):665–704
World Bank World Development Indicators Online (WDI) (2013) database (Accessed January 2015)
Yilanci V, Pata UK (2020) Investigating the EKC hypothesis for China: the role of economic complexity on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19251–19264
Zhu H, Duan L, Guo Y, Yu K (2016) The effects of FDI, economic growth and energy consumption on carbon emissions in ASEAN-5: evidence from panel quantile regression. Econ Model 58:237–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, WC. The interplay among ecological footprint, real income, energy consumption, and trade openness in 13 Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 45148–45160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10399-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10399-7