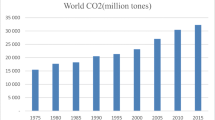
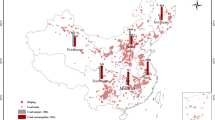
Abstract
As the largest carbon dioxide (CO2) emitter, China exists obvious regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions. However, such inequality and its dynamic change for recent years have not been systematically studied. In this paper, we evaluate China’s regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions during 1997–2016 using the Theil index and decompose it into within-region and between-region components based on eight regions. Furthermore, we apply the decomposition analysis to explore the contribution of different factors to such inequality, including the carbonization index, energy intensity, energy structure, labor productivity, and employment rate. The results show that China’s overall inequality in per capita CO2 emissions reduced first and increased thereafter during 1997–2016. Within-region inequality was the main source of overall inequality in 1997–2004, while between-region inequality contributed more during 2005–2016. Labor productivity and energy intensity were the two main drivers of overall inequality, but their contributions to the inequality between regions and within regions were quite different. Moreover, the impact of energy structure and carbonization index on regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions significantly increased during 2012–2016, which was related to the efforts made by local governments to improve the energy mix. Policy implications were given according to the above conclusions to improve regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai H, Qiao S, Liu T, Zhang Y, Xu H (2016) An inquiry into inter-provincial carbon emission difference in China: aiming to differentiated KPIs for provincial low carbon development. Ecol Indic 60:754–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.08.029
Bianco V, Cassetta F, Marino A et al (2019) Understanding energy consumption and carbon emissions in Europe: a focus on inequality issues. Energy 170:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.120
Chen L, Yang Z (2015) A spatio-temporal decomposition analysis of energy-related CO2 emission growth in China. J Clean Prod 103:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.025
Chen J, Cheng S, Song M, Wang J (2016) Interregional differences of coal carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energ Policy 96:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.05.015
Chen J, Cheng S, Song M (2017) Decomposing inequality in energy-related CO2 emissions by source and source increment: the roles of production and residential consumption. Energ Policy 107:698–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.05.003
Chen J, Xu C, Cui L, Huang S, Song M (2019) Driving factors of CO2 emissions and inequality characteristics in China: a combined decomposition approach. Energ Econ 78:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.12.011
China Electric Power Yearbook Editorial Board (CEPYEB) (1997-2016) China Electric Power Yearbook. China Electric Power Press, Beijing
Clarke-Sather A, Qu J, Wang Q, Zeng J, Li Y (2011) Carbon inequality at the sub-national scale: a case study of provincial-level inequality in CO2 emissions in China 1997-2007. Energy Policy 39:5420–5428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.05.021
Cui E, Ren L, Sun H (2017) Analysis on the regional difference and impact factors of CO2 emissions in China. Environ Prog Sustain 36:1282–1289. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12590
Du Q, Li J, Li Y et al (2019) Carbon inequality in the transportation industry: empirical evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut R. 27:6300–6311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07291-4
Duro JA, Padilla E (2006) International inequalities in per capita CO2 emissions: a decomposition methodology by Kaya factors. Energ Econ 28:170–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2005.12.004
Duro JA, Alcantara V, Padilla E (2010) International inequality in energy intensity levels and the role of production composition and energy efficiency: an analysis of OECD countries. Ecol Econ 69:2468–2474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.07.022
Duro JA, Teixido-Figueras J, Padilla E (2017) The causal factors of international inequality in CO2 emissions per capita: a regression-based inequality decomposition analysis. Enviro Resour Econ 67:683–700. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2471015
Fan M, Shao S, Yang L (2015) Combining global Malmquist–Luenberger index and generalized method of moments to investigate industrial total factor CO2 emission performance: a case of Shanghai (China). Energ Policy 79:189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.12.027
Grunewald N, Jakob M, Mouratiadou I (2014) Decomposing inequality in CO2 emissions: the role of primary energy carriers and economic sectors. Ecol Econ 100:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.02.007
Hao Y, Huang Y (2018) Exploring the nexus of energy consumption structure and CO2 emissions in China: empirical evidence based on the translog production function. J Environ Stud 27:2541–2551. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/81071
Heil MT, Wodon QT (1997) Inequality in CO2 emissions between poor and rich countries. J Environ Dev 6:426–452
Heil MT, Wodon QT (2000) Future inequality in CO2 emissions and the impact of abatement proposals. Environ Resour Econ 17:163–181
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2006) IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
International Energy Agency (IEA) (2018) CO2 emissions from fuel combustion--Highlights. OECD Publishing, Paris
Kaya Y (1989) Impact of carbon dioxide emissions control on GNP growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios. Paper Presented to the Energy and Industry Subgroup, Response Strategies Working Group, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Paris
Li Z, Pan L, Fu F, Liu P, Ma L, Amorelli A (2014) China’s regional disparities in energy consumption: an input-output analysis. Energy 78:426–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.10.030
Li H, Zhao Y, Qiao X, Liu Y, Cao Y, Li Y, Wang S, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Weng J (2017) Identifying the driving forces of national and regional CO2 emissions in China: based on temporal and spatial decomposition analysis models. Energ Eco 68:522–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.10.024
Lin B, Fei R (2015) Regional differences of CO2 emissions performance in China’s agricultural sector: a Malmquist index approach. Eur J Agron 70:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.06.009
Liu X, Wang X, Song J et al (2019) Indirect carbon emissions of urban households in China: patterns, determinants and inequality. J Clean Prod 241:118335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118335
Meng B, Wang J, Andrew R, Xiao H, Xue J, Peters GP (2016) Spatial spillover effects in determining China’s regional CO2 emissions growth: 2007-2010. Energ Econ 63:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.02.001
Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) (2013) Rules on implementing the action plan for prevention and control of atmospheric pollution in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province as well as their surrounding areas (in Chinese). Available from: http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2013/content_2541901.html
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC) (1997-2016a) China Energy Statistical Yearbooks, 1997-2016. China Statistical Press, Beijing
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC) (1997-2016b) China Statistical Yearbooks, 1997-2016. China Statistical Press, Beijing
Ouyang X, Lin B (2015) An analysis of the driving forces of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions in China’s industrial sector. Renew Sust Energ Rev 45:838–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.030
Padilla E, Duro JA (2013) Explanatory factors of CO2 per capita emission inequality in the European Union. Energ Policy 62:1320–1328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.07.018
Remuzgo L, Sarabia JM (2015) International inequality in CO2 emissions: a new factorial decomposition based on Kaya factors. Environ Sci Policy 54:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2015.05.020
Shan Y, Liu J, Liu Z, Xu X, Shao S, Wang P, Guan D (2016) New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors. Appl Energ 184:742–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.073
Shorrocks A (1980) The class of additively decomposable inequality measures. Econometrica. 48:613–625
State Council of the People’s Republic of China (SCPRC) (2006) Strategies and policies for regional coordinated development (in Chinese).
State Council of the People’s Republic of China (SCPRC) (2008) Guiding opinions of the state council on further pushing forward the reform, opening-up, and economic and social development of the Yangtze River Delta Areas (in Chinese). Available from: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2008-09/16/content_1715.html
Sun J, Shi J, Shen B, Li S, Wang Y (2018) Nexus among energy consumption, economic growth, urbanization and carbon emissions: heterogeneous panel evidence considering China’s regional differences. Sustainability 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072383
Theil H (1967) Economics and information theory. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Wang M, Feng C (2017) Decomposition of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: an empirical analysis based on provincial panel data of three sectors. Appl Energ 190:772–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.01.007
Wang H, Zhou P (2018) Assessing global CO2 emission inequality from consumption perspective: an index decomposition analysis. Ecol Econ 154:257–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2018.08.008
Wang Z, Zhang B, Liu T (2016) Empirical analysis on the factors influencing national and regional carbon intensity in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.077
Wang Y, Zhao T, Wang J, Guo F, Kan X, Yuan R (2019a) Spatial analysis on carbon emission abatement capacity at provincial level in China from 1997 to 2014: an empirical study based on SDM model. Atmos Pollut Res 10:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2018.06.003
Wang Y, Su X, Qi L, Shang P, Xu Y (2019b) Feasibility of peaking carbon emissions of the power sector in China’s eight regions: decomposition, decoupling, and prediction analysis. Environ Sci Pollut R. 26:29212–29233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05909-1
Wang Y, Yan Q, Li Z, Baležentis T, Zhang Y, Gang L, Streimikiene D (2020) Aggregate carbon intensity of China’s thermal electricity generation: the inequality analysis and nested spatial decomposition. J Clean Prod 247:119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119139
Wen L, Li Z (2020) Provincial-level industrial CO2 emission drivers and emission reduction strategies in China: combining two-layer LMDI method with spectral clustering. Sci Total Environ 700:134374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134374
Xi J (2019) Speech at a symposium on ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River. Qiushi Journal Online. 201920 (in Chinese). Available from: http://www.qstheory.cn
Xu B, Lin B (2016) A quantile regression analysis of China’s provincial CO2 emissions: where does the difference lie? Energ Policy 98:328–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.09.003
Xu X, Zhao T, Liu N, Kang J (2014a) Changes of energy-related GHG emissions in China: an empirical analysis from sectoral perspective. Appl Energ 132:298–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.07.025
Xu S, He Z, Long R (2014b) Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption in China: decomposition analysis using LMDI. Appl Energ 127:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.093
Xu X, Han L, Lv X (2016) Household carbon inequality in urban China, its sources and determinants. Ecol Econ 128:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.04.015
Yu A, Lin X, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Peng L (2019) Analysis of driving factors and allocation of carbon emission allowance in China. Sci Total Environ 673:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.047
Zhang Y, Da Y (2015) The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.021
Zhang C, Zhao W (2014) Panel estimation for income inequality and CO2 emissions: a regional analysis in China. Appl Energy 136:382–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.09.048
Zhang S, Zhao T (2019) Identifying major influencing factors of CO2 emissions in China: regional disparities analysis based on STIRPAT model from 1996 to 2015. Atmos Environ 207:136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.12.040
Zhao X, Fan L (2019) Spatial distribution characteristics and convergence of China’s regional energy intensity: an industrial transfer perspective. J Clean Prod 233:903–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.073
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science Research Fund Plan (15YJA790091), the Major Program of Social Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Education Commission (2016JWZD04), and the Independent Innovation Foundation of Tianjin University (2017XSZ-0055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, M., Zhao, T., Zhao, L. et al. Understanding regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions in China during 1997–2016: sources and driving factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 32100–32115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09524-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09524-3