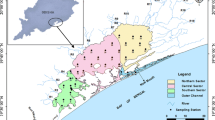
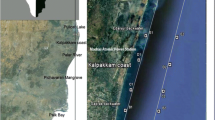
Abstract
Traditionally, the Bay of Bengal is considered as a less productive basin when compared with the neighbouring Arabian Sea. However, limited information is available for a comparative study between these two basins on plankton with relation to environmental properties of inshore waters. In order to understand the spatial variability in plankton biomass along tropical coastal waters, the analysis was carried out by collecting samples from 8 locations, covering both east and west coasts of India during dry and wet periods during 2011. Salinity showed considerable seasonal variability along west coast of India (WCI) and east coast of India (ECI); it has highly fluctuated during wet period along ECI. Suspended solids (SSC) and nitrate showed their concentrations along ECI than WCI. Phosphate and silicate exhibited significant seasonality along WCI, whereas insignificant along ECI. Inconsistency in the monsoonal runoff, physical processes and anthropogenic and terrestrial sources seems to be the major driving forces for these parameters. Nearly 3-fold higher phytoplankton biomass was noticed along WCI than ECI due to low SSC in the former region. Though the zooplankton population also followed the same pattern as phytoplankton, the difference between WCI and ECI is lesser than phytoplankton. Zooplankton abundance showed significant relation with phytoplankton and SSC along WCI and ECI, respectively. The present study reveals irrespective of nutrient concentrations; phytoplankton was dominantly constrained by light availability followed by grazers. Moreover, mesozooplankton was supported by not only phytoplankton but also alternative carbon sources; hence, variability in phytoplankton biomass and SSC leads to alterations in trophic interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Burkholder JM, Cochlan WP, Glibert PM, Gobler CJ, Heil CA, Kudela RM, Parsons ML, Rensel JEJ, Townsend DW, Trainer VL, Vargo GA (2008) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 8:39–53
Béthoux JP, Morin P, Ruiz-Pino DP (2002) Temporal trends in nutrient ratios: chemical evidence of Mediterranean ecosystem changes driven by human activity. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 49:2007–2016
Bharathi MD, Patra S, Sundaramoorthy S, Madeswaran P, Chandrasekar D, Sundaramanickam A (2018a) Seasonal variability in plankton food web composition in Tuticorin coastal waters, south east coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 137:408–417
Bharathi MD, Sundaramoorthy S, Patra S, et al. (2018b) Seasonal and spatial distribution of heterotrophic bacteria in relation to physico-chemical properties along Ennore coastal waters
Bharathi MD, Sarma VVSS, Ramaneswari K, Venkataramana V (2018c) Influence of river discharge on abundance and composition of phytoplankton in the western coastal Bay of Bengal during peak discharge period. Mar Pollut Bull 133:671–683
Bharathi MD, Patra S, Sundaramoorthy S et al (2017) Elucidation of seasonal variations of physicochemical and biological parameters with statistical analysis methods in Puducherry coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 122:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.05.048
Caraco NF, Cole JJ (1999) Human impact on nitrate export: an analysis using major world rivers. Ambio 28:167–170
Cetinić I, Viličić D, Burić Z, Olujć G (2006) Phytoplankton seasonality in a highly stratified karstic estuary (Krka, Adriatic Sea). Marine Biodiversity. Springer, In, pp 31–40
Choudhury AK, Pal R (2010) Phytoplankton and nutrient dynamics of shallow coastal stations at Bay of Bengal, Eastern Indian coast. Aquat Ecol 44:55–71
Cloern JE (1999) The relative importance of light and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth: a simple index of coastal ecosystem sensitivity to nutrient enrichment. Aquat Ecol 33:3–15
Cloern JE, Foster SQ, Kleckner AE (2014) Phytoplankton primary production in the world’s estuarine-coastal ecosystems. Biogeosciences 11:2477–2501
Das S, Chanda A, Dey S, Banerjee S, Mukhopadhyay A, Akhand A, Ghosh A, Ghosh S, Hazra S, Mitra D, Lotliker AA, Rao KH, Choudhury SB, Dadhwal VK (2016) Comparing the spatio-temporal variability of remotely sensed oceanographic parameters between the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal throughout a decade. Curr Sci 110:627–639
de Jonge VN, Elliott M, Orive E (2002) Causes, historical development, effects and future challenges of a common environmental problem: eutrophication. In: Nutrients and eutrophication in estuaries and coastal waters. Springer, pp 1–19
Dunne T (1978) Rates of chemical denudation of silicate rocks in tropical catchments. Nature 274:244–246
Goericke R (2002) Top-down control of phytoplankton biomass and community structure in the monsoonal Arabian Sea. Limnol Oceanogr 47:1307–1323
Gouda R, Panigrahy RC (1996) Ecology of phytoplankton in coastal waters off Gopalpur, east coast of India
Gowen RJ, Tett P, Bresnan E et al (2012) Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment and blooms of harmful phytoplankton. Oceanography and marine biology. CRC Press, In, pp 74–135
Grant GM, Gross E (1966) Oceanography—a view of the earth. Prentice-Hall, USA In: Grenz C, Cloern J, Hager SW, Cole BE (eds) Dyn Nutr Cycl Relat benthic Nutr Oxyg uxes Dur a spring Phytoplankt Bloom South San Fr Bay (USA). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 197:6780
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of seawater analysis, third completely revised and extended edition. Chemie, Verlag
Heisler J, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM, Anderson DM, Cochlan W, Dennison WC, Dortch Q, Gobler CJ, Heil CA, Humphries E, Lewitus A, Magnien R, Marshall HG, Sellner K, Stockwell DA, Stoecker DK, Suddleson M (2008) Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 8:3–13
Hughes HJ, Bouillon S, André L, Cardinal D (2012) The effects of weathering variability and anthropogenic pressures upon silicon cycling in an intertropical watershed (Tana River, Kenya). Chem Geol 308:18–25
Kennedy VS, Twilley RR, Kleypas JA, et al. (2002) Coastal and marine ecosystems & global climate change
Krishna MS, Prasad MHK, Rao DB, Viswanadham R, Sarma VVSS, Reddy NPC (2016) Export of dissolved inorganic nutrients to the northern Indian Ocean from the Indian monsoonal rivers during discharge period. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 172:430–443
Krishna MS, Viswanadham R, Prasad MHK, Kumari VR, Sarma VVSS (2019) Export fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon to the northern Indian Ocean from the Indian monsoonal rivers. Biogeosciences 16:505–519
Kumar J, Deshmukhe G, Dwivedi A, Surya S, Sreekanth GB, Singh SK (2015) Seasonal and spatial variation of microalgal abundance and chlorophyll a concentration in intertidal rocky pools along Mumbai Coast, India. Indian J Mar Sci 44: 421–427
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Law R, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol Lett 7:601–613
Mahapatro D, Panigrahy RC, Naik S et al (2011) Macrobenthos of shelf zone off Dhamara estuary, Bay of Bengal. J Oceanogr Mar Sci 2:32–42
Mohapatra RK, Panda CR (2017) Spatiotemporal variation of water quality and assessment of pollution potential in Paradip port due to port activities
Moharana P, Patra AK (2013) Spatial distribution and seasonal abundance of plankton population of Bay of Bengal at Digha sea-shore in West Bengal. Indian J Sci Res 4:93–97
Mukherjee J, Naidu SA, Sarma V, Ghosh T (2018) Influence of river discharge on zooplankton diet in the Godavari estuary (Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean). Adv Oceanogr Limnol 9
Nixon SW (1995) Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41:199–219
Paramasivam S, Kannan L (2005) Physico-chemical characteristics of Muthupettai mangrove environment, Southeast coast of India. Int J Ecol Environ Sci 31:273–278
Prasanna Kumar S, Muraleedharan PM, Prasad TG, et al. (2002) Why is the Bay of Bengal less productive during summer monsoon compared to the Arabian Sea? Geophys Res Lett 29:
Rai SV, Rajashekhar M (2014) Seasonal assessment of hydrographic variables and phytoplankton community in the Arabian Sea waters of Kerala, southwest coast of India. Braz J Oceanogr 62:279–289
Redfield AC (1963) The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. sea 2:26–77
Reid PC, Lancelot C, Gieskes WWC, Hagmeier E, Weichart G (1990) Phytoplankton of the North Sea and its dynamics: a review. Neth J Sea Res 26:295–331
Rippeth TP (2005) Mixing in seasonally stratified shelf seas: a shifting paradigm. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 363:2837–2854
Sahu G, Satpathy KK, Mohanty AK, Sarkar SK (2012) Variations in community structure of phytoplankton in relation to physicochemical properties of coastal waters, southeast coast of India
Sarma V, Krishna MS, Prasad VR et al (2014) Distribution and sources of particulate organic matter in the Indian monsoonal estuaries during monsoon. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 119:2095–2111
Sarma V, Patil JS, Shankar D, Anil AC (2019) Shallow convective mixing promotes massive Noctiluca scintillans bloom in the northeastern Arabian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 138:428–436
Sarma V, Sridevi B, Maneesha K et al (2013) Impact of atmospheric and physical forcings on biogeochemical cycling of dissolved oxygen and nutrients in the coastal Bay of Bengal. J Oceanogr 69:229–243
Satpathy KK, Mohanty AK, Sahu G, Sarguru S, Sarkar SK, Natesan U (2011) Spatio-temporal variation in physicochemical properties of coastal waters off Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India, during summer, pre-monsoon and post-monsoon period. Environ Monit Assess 180:41–62
Shetye SR, Gouveia AD, Shenoi SSC, Michael GS, Sundar D, Almeida AM, Santanam K (1991) The coastal current off western India during the northeast monsoon. Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Pap 38:1517–1529
Smayda TJ (1990) Novel and nuisance phytoplankton blooms in the sea: evidence for a global epidemic. RWS-North Sea Directorate
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis
Sukumaran M, Muthukumaravel K, Sivakami R (2013) Seasonal variation in physico-chemical characteristics of Agniar Estuary, Southeast Coast of India. Asia Pac J Res 2:108–120
Swaney DP, Hong B, Selvam AP et al (2015) Net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs and nitrogen fluxes from Indian watersheds: an initial assessment. J Mar Syst 141:45–58
Tiwari LR, Nair VR (1991) Contribution of zooplankton to the fishery of Dharamtar creek, adjoining Bombay harbour. J Indian Fish Assoc 21:15–19
Valiela I (2009) Global coastal change. John Wiley & Sons
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Debán L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3592
VishnuRadhan R, Sagayadoss J, Seelan E, Vethamony P, Shirodkar P, Zainudin Z, Shirodkar S (2015) Southwest monsoon influences the water quality and waste assimilative capacity in the Mandovi estuary (Goa state, India). Chem Ecol 31:217–234
Wunderlin Daniel Alberto, Dı́az Marı́a del Pilar, Amé Marı́a Valeria, Pesce Silvia Fabiana, Hued Andrea Cecilia, Bistoni Marı́a de los Ángeles (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study. Water Research 35(12):2881–2894
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Secretary to the Government of India, Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for giving us an opportunity to coordinate the R & D programme on Seawater Quality Monitoring (SWQM). Furthermore, we also express our sincere gratitude to the respective Principal Investigators at Regional Centre (RC) - National Institute of Oceanography (NIO), Mumbai; NIO, Goa; National Centre for Earth Science Studies, Thiruvananthapuram; Centre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology, Parangipettai; RC – NIO, Visakhapatnam; and Institute for Minerals and Materials Technology, Bhubaneswar for the implementation of the programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vedula VSS Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 63 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manuri, D.B., Chandrasekaran, M., Perumal, M. et al. Environmental gradients along the tropical coast drive plankton biomass and alter food web interactions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 36186–36202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09488-4