Abstract
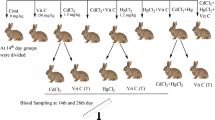
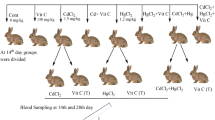
Mercury and cadmium are highly dangerous metals that can lead to disastrous effects in animals and humans. The aim of the current research was to elucidate the poisonous effects of mercuric chloride and cadmium chloride individually and in combination on biochemical profiles of plasma and their accumulation in heart. The therapeutic effect of vitamin C against these metals in rabbits was also studied. Mercuric chloride (1.2 μg/g), cadmium chloride (1.5 μg/g), and vitamin C (150 μg/g of body weight) were orally given to treatment groups of the rabbits (1—control; 2—vitamin; 3—CdCl2; 4—HgCl2; 5—vitamin + CdCl2; 6—vitamin + HgCl2; 7—CdCl2 + HgCl2, and 8—vitamin + CdCl2 + HgCl2. After the biometric determination of all intoxicated rabbits, biochemical parameters, viz low-density lipoproteins (LDL), high-density lipoproteins (HDL), cholesterol, creatine kinase, and troponin T (TnT) were analyzed using available kits. Levels of cholesterol (0.7 ± 0.1 mmol/l), creatine kinase (2985.2 ± 11 IU/L), LDL (20.35 ± 1.31 mg/dl), and troponin T (1.22 ± 0.03 μg/l) were significantly (P < 0.05) increased. HDL (84.78 ± 4.30 mg/dl) was significantly (P < 0.05) decreased, while supplementation of vitamin C decreased the adverse effects of CdCl2 and HgCl2 on biochemical parameters in all metal-exposed groups. A similar trend was also seen in rabbits treated with CdCl2 + vitamin and vitamin + CdCl2 + HgCl2. Accumulation of Cd and Hg was higher in heart tissues. This study, therefore, provides awareness on the cardiac toxicity of mercury and cadmium chlorides in the rabbits and the possible protective role of vitamin C against the perturbations induced by metals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz I, Elhabiby MI, Ashour AA (2013) Toxicity of cadmium and protective effect of bee honey, vitamins C and B complex. Hum ExpToxicol 32(4):362–370
Adam KR (1951) The effects of dithiols on the distribution of mercury in rabbits. Br J Pharmacol 6(3):483–491
Adams WJ, Blust R, Borgmann U, Brix KV, DeForest DK (2011) Utility of tissue residues for predicting effects of metals on aquatic organisms. Integr Environ Assess Manage 7:75–98
Ali S, Hussain S, Khan R, Mumtaz S, Ashraf N, Andleeb S, Shakir HA, Tahir HM, Khan MKA, Ulhaq M (2019) Renal toxicity of heavy metals (cadmium and mercury) and their amelioration with ascorbic acid in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(4):3909–3920
Ali S, Ejaz M, Dar KK, Nasreen S, Ashraf N, Gillani SF, Shafi N, Safeer S, Khan MA, Andleeb S, Mughal TA (2020) Evaluation of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effect of Artemisia vulgaris against diethylnitrosamine induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis in Balb C mice. Braz J Biol. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.185979
Alissa EM, Ferns GA (2011) Heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular disease. J Toxicol 2:870–925
Ashe WF, Largent EJ, Dutra FR, Hubbard DM, Blackstone M (1953) Behaviour of mercury in the animal organism following inhalation. Arch IndustHyg Occupational Med 7(1):19–43
Bashandy S (2006) Beneficial effect of combined administration of vitamin C and vitamin E in amelioration of chronic lead hepatotoxicity. Egyp J Hosp Med 23:371–384
Babaev VR, Whitesell RR, Li L, Linton MF, Fazio S, May JM (2011) Selective macrophage ascorbate deficiency suppresses early atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med 50(1):27–36
Bersényi A, Fekete SG, Szőcs Z, Berta E (2003) Effect of ingested heavy metals (cd, Pb and hg) on haematology and serum biochemistry in rabbits. Acta Vet Hung 51(3):297–304
Boscolo P, Carmignani M (1986) Mechanisms of cardiovascular regulation in male rabbits chronically exposed to cadmium. Br J Ind Med 43(9):605–610
Bridges CC, Zalups RK (2005) Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204(3):274–308
Bucolo G, David H (1973) Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clini Chem 19(5):476–482
Buha A, Matovic V, Antonijevic B, Bulat Z, Curcic M, Renieri EA, Tsatsakis AM, Schweitzer A, Wallace D (2018) Overview of cadmium thyroid disrupting effects and mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci 19(5):1501
Chan DY, Fry N, Waisberg M, Black WD, Hale BA (2004) Accumulation of dietary cadmium (cd) in rabbit tissues and excretions: a comparison of lettuce amended with soluble cd salt and lettuce with plant-incorporated cd. J Toxicol Environ Health 67:397–411
Dar KK, Ali S, Ejaz M, Nasreen S, Ashraf N, Gillani SF, Shafi N, Safeer S, Khan MA, Andleeb S, Mughal TA (2019) In vivo induction of hepatocellular carcinoma by diethylnitrosoamine and pharmacological intervention in balb c mice using Bergenia ciliata extracts. Braz J Biol, 79(4):629–638
Du Preez HH, Steyn GJ (1992) A preliminary investigation of the concentration of selected metals in the tissues and organs of the tigerfish (Hydrocynusvittatus) from the Olifants River, Kruger national Park. South Africa Water S A 18(2):131–136
Duruibe JO, Ogwuegbu MOC, Egwurugwu JN (2007) Heavy metal pollution and human bio toxic effects. Int J PhysSci 2(5):112–118
Edwards JR, Prozialeck WC (2009) Cadmium, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):289–293
El Okle OS, Lebda MA (2014) Could alpha-Lipoic acid protect against sub-chronic toxicity of heavy metals mixture in japanese quails? Life Sci J 11(12):907–917
Falandysz J (1991) Manganese, copper, zinc, iron, cadmium, mercury and lead in muscle meat, liver and kidneys of poultry, rabbit and sheep slaughtered in the northern part of Poland, 1987. Food Addit Contam 8(1):71–83
Farina M, Brandão R, Lara FS, Soares FAA, Souza DO, Rocha JBT (2003) Mechanisms of the inhibitory effects of selenium and mercury on the activity of d-Aminolevulinatedehydratase from mouse liver, kidney and brain. Toxicol Lett 139(1):55–66
Farina M, Aschner M, Rocha JBT (2011) Oxidative stress in MeHg-induced neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 256(2):405–417
Gallagher CM, Meliker JR (2010) Blood and urine cadmium, blood pressure, and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspec. 118(12):1676–1684
Ghosh N, Bhattacharya S (1992) Thyrotoxicity of the chlorides of cadmium and mercury in rabbit. Biomed Environ Sci 5(3):236–240
Glueck CJ, Bornovali S, Pranikoff J, Goldenberg N, Dharashivkar S, Wang P (2004) Metformin, preeclampsia, and pregnancy outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetic Med 21(8):829–836
Griffiths K, Aggarwal BB, Singh RB, Buttar HS, Wilson D, De Meester F (2016) Food antioxidants and their anti-inflammatory properties: a potential role in cardiovascular diseases and cancer prevention. Diseases 3(28):1–15
Horiguchi H, Oguma E, Kayama F (2011) Cadmium induces anemia through interdependent progress of hemolysis, body iron accumulation, and insufficient erythropoietin production in rats. Toxicol Sci 122(1):198–210
Massányi P, Toman R, Uhrín V, Renon P (1995) Distribution of cadmium in selected organs of rabbits after an acute and chronic administration. Ital J Food Sci 7:311–316
Mughal TA, Saleem MZ, Ali S, Anwar KK, Bashir MM, Babar M, Khan MA (2019) Evaluation of hepatotoxicity of carbon tetrachloride and pharmacological intervention by vitamin E in balb c mice. Pak J Zool 51(2):755–761
Grosicki A (2004) Influence of vitamin C on cadmium absorption and distribution in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:183–187
Gupta AD, Das SN, Dhundasi SA, Das KK (2008) Effect of garlic (Allium sativum) on heavy metal (nickel II and chromium VI) induced alteration of serum lipid profile in male albino rats. Inter J Environ Res Public Health 5(3):147–151
Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Sevanian A (2005) Antioxidant vitamin supplementation and cardiovascular disease. In Preventive Nutrition: Humana Press 4(2): 245–277
Houston MC (2014) The role of mercury in cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Dis Diagn 2:1–8
Hussain SA, Kareem MA, Rasool SN, Al Omar SY, Saleh A, Al-Fwuaires MA, Daddam JR, Devi KL (2018) Trace element determination and cardioprotection of terminalia pallida fruit ethanolic extract in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats by ICP-MS. Biol Trace Elem Res 181(1):112–221
Hussain S, Ali S, Mumtaz S, Shakir HA, Ahmad F, Tahir HM, Ulhaq M, Khan MA, Zahid MT (2020) Dose and duration-dependent toxicological evaluation of lead acetate in chicks. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08016-8
Imed M, Fatima H, Hamid K (2008) Protective effects of selenium (se) and zinc (Zn) on cadmium (cd) toxicity in the liver and kidney of the rat: histology and cd accumulation. Food and ChemToxicol 46(11):3522–3527
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72
Josthna P, Geetharathan T, Sujatha P, Deepika G (2012) Accumulation of lead and cadmium in the organs and tissues of rabbits. Int J Pharm Life Sci 3(12):2186–2189
Kaur S, Sharma S (2015) Assessment of biochemical alterations induced by acute and chronic doses of cadmium in albino mice. Asian J Pharmacol Toxicol 03(07):1–4
Khan R, Ali S, Mumtaz S, Andleeb S, Ulhaq M, Tahir HM, Khan MKA, Khan MA, Shakir HA (2019) Toxicological effects of toxic metals (cadmium and mercury) on blood and the thyroid gland and pharmacological intervention by vitamin C in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollu Res 26:16727–16741
Kukongviriyapan U, Pannangpetch P, Kukongviriyapan V, Donpunha W, Sompamit K et al (2014) Curcumin protects against cadmium-induced vascular dysfunction, hypertension and tissue cadmium accumulation in mice. Nutr 6:1194–1208
Kulka M (2016) A review of paraoxonase 1 properties and diagnostic applications. Pol J Vet Sci 19:225–232
Kuliczkowski W, Jołda-Mydłowska B, Kobusiak-Prokopowicz M, Antonowicz-Juchniewicz J, Kosmala W (2004) Effect of heavy metal ions on function of vascular endothelium in patients with ischemic heart disease. Pol Arch Med Wewn 111(6):679–685
Lamas GA, Goertz C, Boineau R, Mark DB, Rozema T, Nahin RL, Drisko JA, Lee KL (2012) Design of the trial to assess chelation therapy (TACT). Amer Heart J 163(1):7–12
Lass A, Sohal RS (2000) Effect of Coezyme Q1o and alpha-tocopherol content of mitochondria on production of superoxide anion radicals. FASEB J 14:87–94
Lim KM, Kim S, Noh JY, Kim K, Jang WH, Bae ON, Chung SM, Chung JH (2010) Low-level mercury can enhance procoagulant activity of erythrocytes: a new contributing factor for mercury-related thrombotic disease. Environ Health Perspect 118(7):928–935
Lin YS, Ginsberg G, Lin JW, Sonawane B (2014) Mercury exposure and omega-3 fatty acid intake in relation to renal function in the US population. Int J Hyg Environ Health 217(4–5):465–472
Lin TJ, Huang YL, Chang JS, Liu KT, Yen MC, Chen FW, Shih YL, Jao JC, Huang PC, Yeh IJ (2018) Optimal dosage and early intervention of L-ascorbic acid inhibiting K2Cr2O7-induced renal tubular cell damage. J Trace Elem Med Biol 48:1–7
Mackness M, Mackness B (2004) Paraoxonase 1 and atherosclerosis: is the gene or the protein more important? Free Radic Biol Med 37(9):1317–1323
Magos L, Clarkson TW (2006) Overview of the clinical toxicity of mercury. Ann ClinBiochem 43(4):257–268
Massanyi PN, Lukac J, Slivkova J, Kovacik AV, Makarevich P, Chrenek R, Toman Z, Forgacs Z, Somosy R, Stawarz GF (2007) Mercury induced alterations in rat kidneys and testes in vivo. J Environ Sci Health 42(7):865–870
Mazerik JN, Mikkilineni H, Kuppusamy VA, Steinhour E, Peltz A, Marsh CB, Kuppusamy P, Parinandi NL (2007) Mercury activates phospholipase A2 and induces formation of arachidonic acid metabolites in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Mechan Methods 17(9):541–557
Messner B, Bernhard D (2010) Cadmium and cardiovascular diseases: cell biology, pathophysiology, and epidemiological relevance. Biometals 23(5):811–822
Mumtaz S, Ali S, Khan R, Andleeb S, Ulhaq M, Khan MAKhan MA, Shakir HA (2019) The protective role of ascorbic acid in the hepatotoxicity of cadmium and mercury in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14087–14096
Mumtaz S, Ali S, Khan R, Shakir HA, Tahir HM, Mumtaz S, Saiqa Andleeb S (2020) Therapeutic role of garlic and vitamins C and E against toxicity induced by lead on various organs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 27(9):8953–8964
Murugavel P, Pari (2007) Diallyl tetrasulfide protects cadmium-induced alterations in lipids and plasma lipoproteins in rats. Nutr Res 27:356–361
Neathery MW, Miller WJ (1975) Metabolism and toxicity of cadmium, mercury, and lead in animals: a review. J Dairy Sci 58(12):1767–1781
Okubo N, Hombrouck C, Fornes P, Cosson C, Samii K, Mazoit JX, Edouard A (2000) Cardiac troponin I and myocardial contusion in the rabbit. Anesthesiology: J Amr Soc of Anesthesiol 93(3):811–817
Oriquat GA, Saleem TH, Naik RR, Moussa SZ, Al-Gindy RM (2012) A sub-chronic toxicity study of mercuric chloride in the rat. Jordan J Biol Sci 5(2):141–146
Park KC, Gaze DC, Collinson PO, Marber MS (2017) Cardiac troponins: from myocardial infarction to chronic disease. Cardiovasc Res 113(14):1708–1718
Payliss BJ, Hassanin M, Prenner EJ (2015) The structural and functional effects of hg (II) and cd (II) on lipid model systems and human erythrocytes: a review. Chem Physic Lipd 193:36–51
Pogwizd SM, Bers DM (2008) Rabbit models of heart disease. Drug Discov Today Dis Model 5(3):185–193
Prabu SM, Renugadevi J, Shagirtha K (2013) In vivo and in vitro antioxidative efficacy of naringenin on cadmium -induced toxicity in rats. Research & Reviews: J Toxicol 3(3):112–117
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Woods JM (2006) The vascular endothelium as a target of cadmium toxicity. Life Sci 79(16):1493–1506
Priscilla DH, Prince PS (2009) Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Chem Int 179(2–3):118–124
Quinn DL, Zarrow MX (1964) Inhibition of pregnant mare’s serum-induced ovulation in the immature rat. Endocrinol 74(3):309–313
Rana MN, Tangpong J, Rahman MM (2018) Theoxicodynamics of Lead, cadmium. Mercury and Arsenic-induced kidney toxicity and treatment strategy: A mini review Toxicology Reports 5:704–713
Rehman H, Aziz AT, Saggu S, Vanwert A, Zidan LN, Saggu S (2017) Additive toxic effect of deltamethrin and cadmium on hepatic, hematological and immunological parameters in mice. ToxicolInd Health 2:1–8
Sangartit W, Kukongviriyapan U, Donpunha W, Pakdeechote P, Kukongviriyapan V, Surawattanawan P, Greenwald SE (2014) Tetrahydrocurcumin protects against cadmiuminduced hypertension, raised arterial stiffness and vascular remodeling in mice. PLoS One 9:114–908
Sato H, Preisler H, Raza A, Larson RB (1990) MDR1 transcript levels as an indication of resistant disease in acute myelogenous leukaemia. Brit J Haem 75(3):340–345
Schlattner U, Tokarska-Schlattner M, Wallimann T (2006) Mitochondrial creatine kinase in human health and disease. Biochimica et BiophysicaActa Molecular Basis of Disease 1762(2):164–180
Sellers RS, Pardo I, Hu G, Khan KN, Perry R, Markiewicz V, Rohde C, Colangelo J, Reagan W, Clarke D (2017) Inflammatory cell findings in the female rabbit heart and stress-associated exacerbation with handling and procedures used in nonclinical studies. Toxicol Pathol 45(3):416–426
Sharifi AM, Darabi R, Akbarloo N, Larijani B, Khoshbaten A (2004) Investigation of circulatory and tissue ACE activity during development of lead-induced hypertension. Toxicol Lett 153(2):233–238
Šimůnek T, Klimtová I, Kaplanová J, Mazurová Y, Adamcová M, Štěrba M, Hrdina R, Geršl V (2004) Rabbit model for in vivo study of anthracycline-induced heart failure and for the evaluation of protective agents. Eur J Heart Fail 6(4):377–387
Talavera J, Giraldo A, Fernández-Del-Palacio MJ, García-Nicolás O, Seva J, Brooks G, & Moraleda JM (2015). An upgrade on the rabbit model of Anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy: shorter protocol, reduced mortality, and higher incidence of overt dilated cardiomyopathy. Biomed res Intl, 465342
Taşdemir M, Çelikezen FÇ, Oto G, Özbey F (2019) The effects of pretreatment with lithium metaborate dihydrate on lipid peroxidation and Ca, Fe, mg, and K levels in serum of Wistar albino male rats exposed to cd. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:1–0
Terasawa Y, Ladha Z, Leonard SW, Morrow JD, Newland D, Sanan D (2000) Increased atherosclerosis in hyper lipidemic mice deficient in alphatocopherol transfer protein and vitamin E. Proc. Natl Acad Sci U S A 28:830–834
Varoni MV, Palomba D, Gianorso S, Anania V (2003) Cadmium as an environmental factor of hypertension in animals: new perspectives on mechanisms. Vet Res Commun 27:807–810
Washington B, Williams S, Armstrong P, Mtshali C, Robinson JT, Myles EL (2006) Cadmium toxicity on arterioles vascular smooth muscle cells of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health 3:323–328
Watts SW, Chai S, Webb RC (1995) Lead acetate-induced contraction in rabbit mesenteric artery: interaction with calcium and protein kinase C. Toxicol 99(1–2):55–65
Wiggers GA, Pecanha FM, Briones AM, Perez-Giron JV, Miguel M, Vassallo DV, Cachofeiro V, Alonso MJ Salaices M (2008) Low mercury concentrations cause oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in conductance and resistance arteries. Am J Physiol heart circulatory Physiol(3)2: 122-131
Yildirim S, Celikezen FC, Oto G, Sengul E, Bulduk M, Tasdemir M, Cinar DA (2018) An investigation of protective effects of litium borate on blood and histopathological parameters in acute cadmium-induced rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 182(2):287–294
Wilson RJ, Willis R, Gearry P, Skidmore E, Fleming C, Frampton A (2017) Inadequate vitamin C status in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: associations with glycaemic control, obesity, and smoking. Nutr 9(9):997–102
Winiarska-Mieczan A (2018) Protective effect of tea against lead and cadmium-induced oxidative stress—a review. Biometals 31:909–926
Wojciechowski J, Kowalski W (1975) Cardiac and aortic lesions in chronic experimental poisoning with mercury vapors in rabbits. Pol Med Sci Hist Bull 15(2):255–260
Yousef MI (2004) Aluminium-induced changes in hemato-biochemical parameters, lipid peroxidation and enzyme activities of male rabbits: protective role of ascorbic acid. Toxicol 199(1):47–57
Zalups RK, Barfuss D (1990) Accumulation of inorganic mercury along the renal proximal tubule of the rabbit. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 106(2):245–253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Awan, Z., Mumtaz, S. et al. Cardiac toxicity of heavy metals (cadmium and mercury) and pharmacological intervention by vitamin C in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 29266–29279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09011-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09011-9