Abstract
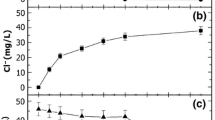
Radiation-induced degradation of chlorobenzene was conducted at 0.1, 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, and 1.0 mmol/dm3 concentrations in aerated environment and at 1.0 mmol/dm3 in oxygen-free and N2O-saturated solutions. The results demonstrated that the elimination of chloride is important when the solution is oxygen free, because the \( {\mathrm{e}}_{\mathrm{aq}}^{-} \) attacks at the ipso position of the chloro group produces hydrochloric acid. The degradation was affected to a large extent by the concentration and to a lesser extent by the presence or absence of oxygen in the solutions which were irradiated. Thereby, the degradation occurred faster in the solutions with air and without oxygen and more slowly in the saturated solution with N2O. Some by-products were identified using an HPLC-UV-mass system. In addition, it was found that there is a linear correlation between the ln C/C0 and the dose, indicating that the radiolytic degradation followed pseudo-first-order reaction kinetics. The radiolytic oxidation was followed by the chemical oxygen demand (COD) test. The COD decreases when the solute concentration increases. The COD results were for a 0.47 mmol/dm3 of 5.94 mg O2 dm−3 kGy−1 and for 0.09 mmol/dm3 of 7.45 mg O2 dm−3 kGy−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarrán G, Mendoza E (2019) Radiolytic oxidation and degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17055–17065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04845-4
Albarrán G, Schuler RH (2003) Concerted effects in the reaction of OH radicals with aromatics: Radiolytic oxidation of salicylic acid. Radiat Phys Chem 67:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(03)00052-5
Albarrán G, Schuler RH (2005) Concerted effects of substituents in the reaction of OH radicals with aromatics: the cresols. J Phys Chem A 109:9363–9370. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0539876
Albarrán G, Schuler RH (2007) Hydroxyl radical as a probe of the charge distribution in aromatics: phenol. J Phys Chem A 111:2507–2510. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp068736r
Bhatia K, Schuler RH (1974) Oxidation of hydroxycyclohexadienyl radical by metal ions. J Phys Chem 78:2335–2338. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150671a007
Bielski BJ, Cabelli DE, Arudi RL, Ross AB (1985) Reactivity of HO2/O̅2 radicals in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Data 14:1041–1110. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.555739
Bobrowski K (2017) Radiation chemistry of liquid systems. In: Sun Y. Chmielewski AG (ed) Applications of ionizing radiation in materials processing. Institute of Nuclear Chemistry and Technology. Warszawa, pp 81–116
Byrnea C, Subramanianc G, Pillaia SC (2018) Recent advances in photocatalysis for environmental applications. J Environ Chem Eng 6:3531–3555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.080
Chamam M, Földváry CM, Hosseini AM, Tungler A, Takács E, Wojnárovits L (2012) Mineralization of aqueous phenolate solutions: a combination of irradiation treatment and wet oxidation. Radiat Phys Chem 81:1484–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2011.11.013
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44:2997–3027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039
Collivignarelli C, Sorlini S (2004) AOPs with ozone and UV radiation in drinking water: contaminants removal and effects on disinfection byproducts formation. Water Sci Technol 49:51–56. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2004.0218
Czaplicka M (2006) Photo-degradation of chlorophenols in the aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 134:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.039
Deng Y, Zhao R (2015) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment. Curr Pollut Rep 1:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0015-z
Eberhardt M, Martínez MI (1975) Radiation-induced homolytic aromatic substitution. V Effect of metal ions on the hydroxylation of toluene. J Phys Chem 79:1917–1920. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100585a006
Eberhardt M, Yoshida M (1973) Radiation-induced homolytic aromatic substitution. I. Hydroxylation of nitrobenzene, chlorobenzene, and toluene. J Phys Chem 77:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100624a005
Fang X, Pan X, Rahmann A, Schuchmann H-P, von Sonntag C (1995) Reversibility in the reaction of cyclohexadienyl radicals with oxygen in aqueous solution. Chem Eur J 1:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.19950010706
Fang X, Mark G, von Sonntag C (1996) OH radical formation by ultrasound in aqueous solutions. Part I: the chemistry underlying the terephthalate dosimeter. Ultrason Sonochem 3:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4177(95)00032-1
Garcia-Segura S, Ocon JD, Chong MN (2018) Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents - a review. Saf Environ Prot 113:48–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.014
Ge F, Zhu L, Wang J (2008) Distribution of chlorination products of phenols under various pHs in water disinfection. Desalination 225:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.03.016
Getoff N, Solar S (1988) Radiation induced decomposition of chlorinated phenols in water. Radiat Phys Chem 31:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-0197(88)90115-4
Homlok R, Takács E, Wojnárovits L (2013) Degradation of organic molecules in advanced oxidation processes: relation between chemical structure and degradability. Chemosphere 91:383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.073
Hu J, Wang J (2007) Degradation of chlorophenols in aqueous solution by γ-radiation. Radiat Phys Chem 76:1489–1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2007.02.058
Janata E, Schuler RH (1982) Rate constant for scavenging \( {\mathbf{e}}_{\mathbf{aq}}^{-} \) in nitrous oxide-saturated solutions. J Phys Chem 86:2078–2084. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100208a035
Jovanovic SV, Hara Y, Steenken S, Simic MG (1995) Antioxidant potential of gallocatechins. A pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis study. J Am Chem Soc 117:9881–9888. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00144a014
Kurt Z, Spain JC (2013) Biodegradation of Chlorobenzene, 1,2-Dichlorobenzene, and 1,4-Dichlorobenzene in the Vadose Zone. Environ Sci Technol 47:6846–6854. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3049465
Lee B, Lee M (2005) Decomposition of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) by gamma irradiation. Environ Sci Technol 39:9278–9285. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0489590
Madavan V, Schuler RH (1980) A radiation chemical study of the oxidation of hydroxycyclohexadienyl radical by ferricyanide. Radiat Phys Chem 16:139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-5724(80)90220-4
Merga G, Schuchmann HP, Rao BSM, von Sonntag C (1996) •OH radical-induced oxidation of chlorobenzene in aqueous solution in the absence and presence of oxygen. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:1097–1103. https://doi.org/10.1039/P29960001097
Mincher BJ, Curry RD (2000) Considerations for choice of a kinetic fig of merit in process radiation chemistry for waste treatment. Appl Radiat Isot 52:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(99)00161-X
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilara VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Naresh N, Mahamuni NN, Adewuyi Y (2010) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) involving ultrasound for wastewater treatment: a review with emphasis on cost estimation. Ultrason Sonochem 17:990–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.09.005
Nuñez-Gaytan AM, Vera-Avila LE, García de Llasera M, Covarrubias-Herrera R (2010) Speciation and transformation pathways of chlorophenols formed from chlorination of phenol at trace level concentration. J Environm Sci Health Part A 45:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2010.493785
OrigenPro (2015) Microcal software Inc. Origin Lab Corporation, Northampton
Raghavan NV, Steenken S (1980) Electrophilic reaction of the OH radical with phenol. Determination of the distribution of isomeric dihydrocyclohexadienyl radicals. J Am Chem Soc 102:3495–3499. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00530a031
Schuler RH, Albarrán G (2002) The rate constants for reaction of •OH radicals with benzene and toluene. Radiat Phys Chem 64:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(01)00497-2
Schuler RH, Hartzell AL, Behar B (1981) Track effect in radiation chemistry. Concentration dependence for the scavenging of OH by ferrocyanide in N2O-saturated aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 85:192–199. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150602a017
Skoczko I, Piekutin J (2014) Photo-Fenton method usage to organic compounds degradation. Desalin Water Treat 52:3837–3842. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.887497
Spinks JWT, Woods RJ (1990) An introduction to radiation chemistry, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 314–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.887497
Sycz M (2013) Photochemical degradation of chlorobenzene. Dissertation University of Waterloo, Canada
Szabó L, Tóth T, Homlok R, Rácz G, Takács E, Wojnárovits L (2014) Hydroxyl radical induced degradation of salicylates in aerated aqueous solution. Radiat Phys Chem 97:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.11.039
Torun M, Solpan D, Güven O (2014) Removal of dissolved organic pollutants from water by gamma-irradiation based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) Hacettepe. J Biol Chem 42:115–127
Trojanowicz M, Chudziak A, Bryl-Sandelewska T (1998) Radiolytic degradation of chlorophenols for their removal from polluted waters. Technol Conserv Environ Proc Symp 255-262 IAEA-SM-350/17. XA9847716
US Environmental Protection Agency (1975) Preliminary assessment of suspected carcinogens in drinking water. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office Substances, Washington, D. C. 33. EPA
von Sonntag C (2006) Free-radical-induced DNA damage and its repair. A Chemical Perspective. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. Peroxyl radicals. pp 159–194. ISBN 978–3–540-30592-7 (online) 978–3–540-26120-9, (print) https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-30592-0_8
von Sonntag C, Dowideit P, Fang X, Mertens R, Pan X, Schuchmann MN, Schuchmann H-P (1997) The fate of peroxyl radicals in aqueous solution. Water Sci Technol 35:9–15. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1997.0074
Wojnárovits L, Takács E (2017) Wastewater treatment with ionizing radiation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 311:973–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-4869-3
Woods RJ, Pikaev AK (1994) Applied radiation chemistry, radiation processing. Wiley, New York ISBN-0-471-54452-3
Yalkowsky SH, He Y, Jain P (2003) Handbook of aqueous solubility data. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yu S, Lee B, Lee M, Cho I-H, Chang S-W (2008) Decomposition and mineralization of cefaclor by ionizing radiation: kinetics and effects of the radical scavengers. Chemosphere 71:2106–2112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.020
Zehavi D, Rabani J (1971) Pulse Radiolytic investigation of \( {\mathrm{O}}_{\mathrm{aq}}^{-} \) radical ions. J Phys Chem 75:1738–1744. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100906a017
Zona R, Solar S (2003) Oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by ionizing radiation: degradation detoxification and mineralization. Radiat Phys Chem 66:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(02)00330-4
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Fis. Francisco García Flores from ICN-UNAM for carrying out sample irradiation.
Funding
The work described here was supported by the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (Grant PAPIIT- IN200419).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albarrán, G., Mendoza, E. Radiolytic degradation of chlorobenzene in aerated and deoxygenated aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 22855–22864 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08227-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08227-z