Abstract
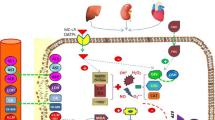
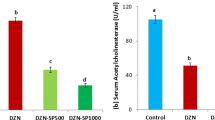
Fucoidans (FUC) are organic sulfated polysaccharides from natural seaweeds with multiple biological actions. The current study was performed to assess the chemoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects of FUC from Laminaria japonicum against diazinon (DZN)-induced injuries to rat cardiac, hepatic, and renal tissues. Forty male Wistar rats were assigned into five groups, receiving saline, oral FUC 200 mg/kg/day, subcutaneous DZN 20 mg/kg/day, DZN plus FUC 100 mg/kg/day, or DZN plus FUC 200 mg/kg/day (each treatment was given daily for 4 weeks). Data analysis showed that DZN-intoxicated rats exhibited significantly higher (p < 0.05) serum levels of alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, urea, creatine, creatine kinase, creatine kinase-MB, lactate dehydrogenase, cholesterol, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α, as well as lower levels of acetylcholinesterase, compared to control rats. In addition, DZN intoxication was associated with significantly higher (p < 0.05) cardiac, hepatic, and renal tissue concentrations of malondialdehyde and nitric oxide, as well as lower glutathione concentrations, and activities of glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase enzymes in comparison to control rats. Treatment with FUC (at 100 or 200 mg/kg/day) ameliorated all the aforementioned alterations in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, FUC from Laminaria japonicum ameliorated DZN-induced oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory effects, and injuries to the cardiac, hepatic, and renal tissues. These effects may be related to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of FUC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AChE:
-
acetylcholinesterase
- ALP:
-
alkaline phosphatase
- ALT:
-
alanine transaminase
- AST:
-
aspartate transaminase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- CK:
-
creatine kinase
- DZN:
-
diazinon
- FUC:
-
fucoidan
- GSH-Px:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- IL:
-
interleukin
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
Abdel-Daim MM (2016) Synergistic protective role of ceftriaxone and ascorbic acid against subacute diazinon-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Cytotechnology 68:279–289
Abdel-Daim MM, Abushouk AI, Alkhalf MI, Toraih EA, Fawzy MS, Ijaz H, Aleya L, Bungau SG (2018) Antagonistic effects of Spirulina platensis on diazinon-induced hemato-biochemical alterations and oxidative stress in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:27463–27470
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ahmadabadi A, Akbari Z, Ahmadimoghaddam D, Larki-Harchegani A (2019) The role of ghrelin and tumor necrosis factor alpha in diazinon-induced dyslipidemia: insights into energy balance regulation. Pestic Biochem Physiol 157:138–142
Ahmadi A, Heidarian E, Ghatreh-Samani K (2019) Modulatory effects of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) leaf extract against oxidative stress and hepatic TNF-alpha gene expression in acute diazinon-induced liver injury in rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 30:20180180. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2018-0180
Ajibade TO, Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Asenuga ER, Afolabi JM, Adedapo AA (2016) Mitigation of diazinon-induced cardiovascular and renal dysfunction by gallic acid. Interdiscip Toxicol 9:66–77
AlKahtane AA, Abushouk AI, Mohammed ET, AlNasser M, Alarifi S, Ali D, Alessia MS, Almeer RS, AlBasher G, Alkahtani S, Aleya L, Abdel-Daim MM (2019) Fucoidan alleviates microcystin-LR-induced hepatic, renal, and cardiac oxidative stress and inflammatory injuries in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06931-z
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CS, Richmond W, Fu PC (1974) Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem 20:470–475
Babson AL, Babson SR (1973) Kinetic colorimetric measurement of serum lactate dehydrogenase activity. Clin Chem 19:766–769
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Cakici O, Akat E (2013) Effects of oral exposure to diazinon on mice liver and kidney tissues: biometric analyses of histopathologic changes. Anal Quant Cytopathol Histopathol 35:7–16
Carvalho AC, Sousa RB, Franco ÁX, Costa JVG, Neves LM, Ribeiro RA, Sutton R, Criddle DN, Soares PM, de Souza MH (2014) Protective effects of fucoidan, a P-and L-selectin inhibitor, in murine acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 43:82–87
Chen J, Wang W, Zhang Q, Li F, Lei T, Luo D, Zhou H, Yang B (2013) Low molecular weight fucoidan against renal ischemia–reperfusion injury via inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. PLoS One 8:e56224
Čolović MB, Vasić VM, Avramović NS, Gajić MM, Djurić DM, Krstić DZ (2015) In vitro evaluation of neurotoxicity potential and oxidative stress responses of diazinon and its degradation products in rat brain synaptosomes. Toxicol Lett 233:29–37
Coulombe J, Favreau L (1963) A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin Chem 9:102–108
Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, D’Incecco A, Piccoli A, Totani L, Tinari N, Morozevich GE, Berman AE, Bilan MI (2007) A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 17:541–552
Danaei GH, Memar B, Ataee R, Karami M (2019) Protective effect of thymoquinone, the main component of Nigella sativa, against diazinon cardio-toxicity in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 42:585–591
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Ezzi L, Haouas Z, Salah IB, Sakly A, Grissa I, Chakroun S, Kerkeni E, Hassine M, Mehdi M, Cheikh HB (2016) Toxicopathic changes and genotoxic effects in liver of rat following exposure to diazinon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11163–11170
Fischer R, Maier O (2015) Interrelation of oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease: role of TNF. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:610813. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/610813
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Hong SW, Lee HS, Jung KH, Lee H, Hong SS (2012) Protective effect of fucoidan against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Arch Pharm Res 35:1099–1105
Jia Y, Sun Y, Weng L, Li Y, Zhang Q, Zhou H, Yang B (2016) Low molecular weight fucoidan protects renal tubular cells from injury induced by albumin overload. Sci Rep 6:31759
Jo M, Kim T-H, Seol D-W, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Billiar TR, Strom SC (2000) Apoptosis induced in normal human hepatocytes by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Nat Med 6:564–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/75045
Kalimuthu S, Kim SK (2015) Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharides from brown algae as therapeutic target for cancer. In: Kim SK (eds) Handbook of anticancer drugs from marine origin. Springer, Cham
Kang KS, Kim ID, Kwon RH, Lee JY, Kang JS, Ha BJ (2008) The effects of fucoidan extracts on CCl(4)-induced liver injury. Arch Pharm Res 31:622–627
Larkin DJ, Tjeerdema RS (2000) Fate and effects of diazinon. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 166:49–82
Larsen K (1972) Creatinine assay by a reaction-kinetic principle. Clin Chim Acta 41:209–217
Li B, Lu F, Wei X, Zhao R (2008) Fucoidan: structure and bioactivity. Molecules 13:1671–1695
Li J, Zhang Q, Li S, Dai W, Feng J, Wu L, Liu T, Chen K, Xia Y, Lu J (2017) The natural product fucoidan ameliorates hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 94:687–696
Lim JD, Lee SR, Kim T, Jang SA, Kang SC, Koo HJ, Sohn E, Bak JP, Namkoong S, Kim HK, Song IS, Kim N, Sohn EH, Han J (2015) Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus protects against alcohol-induced liver damage by modulating inflammatory mediators in mice and HepG2 cells. Mar Drugs 13:1051–1067
Mihara M, Uchiyama M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Navarro JJ, Milena FF, Mora C, León C, Claverie F, Flores C, García J (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in diabetic nephropathy: relationship with urinary albumin excretion and effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Kidney Int 68:S98–S102
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Mora-Fernandez C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:433–442
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Ogasawara N, Matsushima M, Kawamura N, Atsumi K, Yamaguchi T, Ochi H, Kusatsugu Y, Oyabu S, Hashimoto N, Hasegawa Y (2017) Modulation of immunological activity on macrophages induced by diazinon. Toxicology 379:22–30
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Pakzad M, Fouladdel S, Nili-Ahmadabadi A, Pourkhalili N, Baeeri M, Azizi E, Sabzevari O, Ostad SN, Abdollahi M (2013) Sublethal exposures of diazinon alters glucose homostasis in Wistar rats: biochemical and molecular evidences of oxidative stress in adipose tissues. Pestic Biochem Physiol 105:57–61
Pozharitskaya ON, Shikov AN, Faustova NM, Obluchinskaya ED, Kosman VM, Vuorela H, Makarov VG (2018) Pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after oral administration to rats. Mar Drugs 16:132
Proskocil BJ, Grodzki ACG, Jacoby DB, Lein PJ, Fryer AD (2019) Organophosphorus pesticides induce cytokine release from differentiated human THP1 cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 61:620–630
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63
Shah MD, Iqbal M (2010) Diazinon-induced oxidative stress and renal dysfunction in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3345–3353
Slotkin TA, Skavicus S, Ko A, Levin ED, Seidler FJ (2019) Perinatal diazinon exposure compromises the development of acetylcholine and serotonin systems. Toxicology 424:152240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2019.152240
Szasz G, Gruber W, Bernt E (1976) Creatine kinase in serum: 1 Determination of optimum reaction conditions. Clin Chem 22:650–656
Thomes P, Rajendran M, Pasanban B, Rengasamy R (2010) Cardioprotective activity of Cladosiphon okamuranus fucoidan against isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats. Phytomedicine 18:52–57
Tietz N, Burtis C, Duncan P, Ervin K, Petitclerc C, Rinker A, Shuey D, Zygowicz E (1983) A reference method for measurement of alkaline phosphatase activity in human serum. Clin Chem 29:751–761
Toledo-Ibarra G, Resendiz KD, Ventura-Ramón G, González-Jaime F, Vega-López A, Becerril-Villanueva E, Pavón L, Girón-Pérez M (2016) Oxidative damage in gills and liver in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to diazinon. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 200:3–8
Vahidirad M, Arab-Nozari M, Mohammadi H, Zamani E, Shaki F (2018) Protective effect of captopril against diazinon induced nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity via inhibition of ROS-NO pathway. Drug Chem Toxicol 41:287–293
Voltan R, Secchiero P, Casciano F, Milani D, Zauli G, Tisato V (2016) Redox signaling and oxidative stress: cross talk with TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 81:364–374
Wang D, Singhasemanon N, Goh KS (2017) A review of diazinon use, contamination in surface waters, and regulatory actions in California across water years 1992–2014. Environ Monit Assess 189:310
Wang Y, Xing M, Cao Q, Ji A, Liang H, Song S (2019) Biological activities of fucoidan and the factors mediating its therapeutic effects: a review of recent studies. Mar Drugs 17:183
Würzburg U, Hennrich N, Lang H, Prellwitz W, Neumeier D, Knedel M (1976) Determination of creatine kinase-MB in serum using inhibiting antibodies (author’s transl). Klin Wochenschr 54:357–360
Yang JW, Yoon SY, Oh SJ, Kim SK, Kang KW (2006) Bifunctional effects of fucoidan on the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:345–350
Yu X, Zhang Q, Cui W, Zeng Z, Yang W, Zhang C, Zhao H, Gao W, Wang X, Luo D (2014) Low molecular weight fucoidan alleviates cardiac dysfunction in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats by reducing oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Diabetes Res 2014:420929. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/420929
Zhang Q, Li Z, Xu Z, Niu X, Zhang H (2003) Effects of fucoidan on chronic renal failure in rats. Planta Med 69:537–541
Acknowledgements
The project was funded by Researchers Supporting Porject number (RSP-2019/121), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi.
Funding
This project was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2019/121), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The Ethical Committee at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Suez Canal University (Ismailia, Egypt) reviewed our experimental design and animal handling procedures (approval no. 201617).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Daim, M.M., Abushouk, A.I., Bahbah, E.I. et al. Fucoidan protects against subacute diazinon-induced oxidative damage in cardiac, hepatic, and renal tissues. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 11554–11564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07711-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07711-w