Abstract
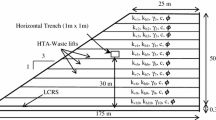
Vertical wells are commonly used for recirculating leachate into a landfill which can offer significant environmental and economic benefits. However, in some cases, the leachate collection and removal system (LCRS) at the bottom is overloaded and clogged due to biological and chemical processes. This results in a relatively high leachate level which could pose a threat to landfill slope stability. This study develops a three-dimensional landfill slope model with vertical recirculation wells and then investigates the effect of LCRS clogging on leachate recirculation and slope stability in terms of leachate saturation, pore water pressure, and factor of safety (FS) of a landfill slope. The results show that with an increase in clogging level that is characterized by an increased leachate level, the pore water pressure below the well injection screen is significantly increased by leachate recirculation, giving rise to a decreased slope FS value. In such conditions, the landfill slope formed by highly anisotropic waste is more likely to suffer instability. To prevent this kind of slope failure, a safe injection pressure of vertical recirculation wells is proposed for a wide range of parameter combinations involving waste anisotropy, clogging level, and the setback distance from the slope surface. This design guideline can be used to control the injection pressure in leachate recirculation applications and contributes to a better understanding of the slope stability of a bioreactor landfill.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
COMSOL Inc (2017) COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3: User’s Guide
Del Moro G, Barca E, Cassano D, Di Iaconi C, Mascolo G, Brunetti G (2014) Landfill wall revegetation combined with leachate recirculation: a convenient procedure for management of closed landfills. ENVIRON SCI POLLUT R 21(15):9366–9375
Dixon N, Jones DRV (2005) Engineering properties of municipal solid waste. GEOTEXT GEOMEMBRANES 23(3):205–233
Durmusoglu E, Sanchez IM, Corapcioglu MY (2006) Permeability and compression characteristics of municipal solid waste samples. Environ Geol 50(6):773–786
Feng SJ, Chen ZW, Cao BY (2016) Three-dimensional modelling of leachate recirculation using vertical wells in bioreactor landfills. WASTE MANAGE RES 34(12):1307–1315
Feng SJ, Zheng QT, Chen HX (2017) Unsaturated flow parameters of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag 63:107–121
Feng SJ, Chen ZW, Chen HX, Zheng QT, Liu R (2018) Slope stability of landfills considering leachate recirculation using vertical wells. Eng Geol 241:76–85
Feng SJ, Fu WD, Zhou AN, Lyu F (2019a) A coupled hydro - mechanical - biodegradation model for municipal solid waste in leachate recirculation. Waste Manag 98:81–91
Feng SJ, Chang JY, Chen HX, Zhang DM (2019b) Numerical analysis of earthquake-induced deformation of liner system of typical canyon landfill. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 116:96–106
Fleming IR, Rowe RK (2004) Laboratory studies of clogging of landfill leachate collection and drainage systems. Can Geotech J 41(1):134–153
Giri RK, Reddy KR (2014) Slope stability of bioreactor landfills during leachate injection: effects of heterogeneous and anisotropic municipal solid waste conditions. WASTE MANAGE RES 32(3):186–197
Haydar MM, Khire MV (2005) Leachate recirculation using horizontal trenches in bioreactor landfills. J Geotech Geoenviron 131(7):837–847
Jain P, Townsend TG, Tolaymat TM (2010) Steady-state design of vertical wells for liquids addition at bioreactor landfills. Waste Manag 30(11):2022–2029
Kamaruddin MA, Yusoff MS, Rui LM, Isa AM, Zawawi MH, Alrozi R (2017) An overview of municipal solid waste management and landfill leachate treatment: Malaysia and Asian perspectives. ENVIRON SCI POLLUT R 24(35):26988–27020
Khire MV, Mukherjee M (2007) Leachate injection using vertical wells in bioreactor landfills. Waste Manag 27(9):1233–1247
Lu SF, Xiong JH, Feng SJ, Chen HX, Bai ZB, Fu WD, Lü F (2019) A finite-volume numerical model for bio-hydro-mechanical behaviors of municipal solid waste in landfills. Comput Geotech 109:204–219
Merry SM, Jr EK, Fritz WU (2005) Reconnaissance of the July 10, 2000, Payatas landfill failure. J PERFORM CONSTR FAC 19(2):100–107
Morris JWF, Vasuki NC, Baker JA, Pendleton CH (2003) Findings from long-term monitoring studies at MSW landfill facilities with leachate recirculation. Waste Manag 23(7):653–666
Reddy KR, Hettiarachchi H, Parakalla N, Gangathulasi J, Bogner J, Lagier T (2009) Hydraulic conductivity of MSW in landfills. J Environ Eng 135(8):677–683
Reddy KR, Kulkarni HS, Khire MV, Khire MV (2015) Two-phase modeling of leachate recirculation using vertical wells in bioreactor landfills. Environ Model Assess 20(5):475–490
Tchobanoglous G, Theisen H, Vigil S (1993) Integrated solid waste management: engineering principles and management issues. McGraw-Hill, New York
Thiel R, Christie M (2005) Leachate recirculation and potential concerns on landfill stability. In proceedings of the 19th annual GRI conference, Las Vegas, USA, 14-16 December
Tinet AJ, Oxarango L, Bayard R, Benbelkacem H, Stoltz G, Staub MJ, Gourc JP (2011) Experimental and theoretical assessment of the multi-domain flow behaviour in a waste body during leachate infiltration. Waste Manag 31(8):1797–1806
Townsend TG, Miller WL (1998) Leachate recycle using horizontal injection. Adv Environ Res 2(2):129–138
Townsend TG, Powell J, Jain P, Xu QY, Tolaymat T, Reinhart D (2015) Sustainable practices for landfill design and operation. Springer, Berlin
Warith M (2002) Bioreactor landfills: experimental and field results. Waste Manag 22(1):7–17
Xu QY, Tolaymat T, Townsend TG (2012) Impact of pressurized liquids addition on landfill slope stability. J Geotech Geoenviron 138(4):472–480
Zekkos D, Bray JD, Kavazanjian E, Matasovic N, Rathje EM, Riemer MF, Stokoe KH (2006) Unit weight of municipal solid waste. J Geotech Geoenviron 132(10):1250–1261
Zhan TL, Ng CW (2004) Analytical analysis of rainfall infiltration mechanism in unsaturated soils. INT J GEOMECH 4(4):273–284
Zhang WJ, Zhang GG, Chen YM (2013) Analyses on a high leachate mound in a landfill of municipal solid waste in China. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1747–1752
Zheng QT, Rowe RK, Feng SJ (2019) Recovery response of vertical gas wells in non-homogeneous landfills. Waste Manag 83:33–45
Funding
Much of the work described in this paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 41725012, 41572265, and 41931289, the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (0200219152), the Shuguang Scheme under Grant No. 16SG19, and the Newton Advanced Fellowship of the Royal Society under Grant No. NA150466. The writers would like to greatly acknowledge all these financial supports and express their sincerest gratitude.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, SJ., Chen, ZW. & Zheng, QT. Effect of LCRS clogging on leachate recirculation and landfill slope stability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 6649–6658 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07383-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07383-1