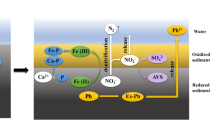
Abstract
Sediment is an endogenous pollution source, which often leads water systems to eutrophication due to the release of nutrients, especially phosphorus (P). Calcium nitrate (CN) was dosed to the water systems under different modes to control P release from the sediments in this study. A 63-day static laboratory test was conducted to explore the effects of intermittent dosing and one-time dosing modes of CN on P locking in the sediment and the concentrations of nitrogen (N) and P in waters. Results showed that 89% total phosphorus (TP) in the overlying water and 91% TP in the interstitial water of sediment were reduced in the intermittent dosing reactor, which were 4% and 13% higher than those in the one-time dosing reactor, respectively. Thus, the concentration of TP in the overlying water of the dosing reactors was both below 0.1 mg/L during the whole experiment. Meanwhile, the mean values of oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) in the sediment increased to − 110.7 ± 42.02 mV when CN was added intermittently, which were significantly higher than those of the one-time dosing reactor (− 158.3 ± 44.61 mV) and control reactor (− 320.7 ± 0.05 mV). Compared with one-time dosing mode, the intermittent dosing not only reduced the maximum concentrations of NO2−-N from 9.21 to 1.79 mg/L and NO3−-N from 92.42 to 27.58 mg/L but also shorten their retention time in the overlying water, which might depress the toxic threats to aquatic animals in water environments. Therefore, the intermittent dosing of CN could not only improve the P locking effect but also minimize the risks to aquatic animals in water environments under the premise of reasonable dosage selected. In a word, this research provided an effective operation mode for locking P with CN in the heavily polluted water bodies, which is also advantageous to avoid toxic threats to aquatic animals in water environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burley KL, Prepas EE, Chambers PA (2001) Phosphorus release from sediments in hardwater eutrophic lakes: the effects of redox-sensitive and -insensitive chemical treatments. Freshw Biol 46(8):1061–1074
Camargo JA, Alonso A (2006) Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: a global assessment. Environ Int 32:831–849
Camargo JA, Alonso A, Salamanca A (2005) Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: a review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere 58:1255–1267
Chen L, Wang Y, Shi L, Zhao J, Wang W (2019) Identification of allelochemicals from pomegranate peel and their effects on Microcystis aeruginosa growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:22389–22399
Cooke GD, Welch EB, Martin AB, Fulmer DG, Hyde JB, Schrieve GD (1993) Effectiveness of Al, Ca, and Fe salts for control of internal phosphorus loading in shallow and deep lakes. Hydrobiologia 253:323–335
Costa DD, Gomes AA, Fernandes M, Lopes da Costa Bortoluzzi R, Magalhaes MLB, Skoronski E (2018) Using natural biomass microorganisms for drinking water denitrification. J Environ Manag 217:520–530
Du H, Chen Z, Mao G, Chen L, Crittenden J, Li RYM, Chai L (2019) Evaluation of eutrophication in freshwater lakes: a new non-equilibrium statistical approach. Ecol Indic 102:686–692
Fan P, Wang Y, Wang WH, Chai BH, Lu XX, Zhao JC (2019) Release characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments formed under different supplemental water sources in Xi’an moat, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:10746–10755
Hansen J, Reitzel K, Jensen HS, Andersen FØ (2003) Effects of aluminum, iron, oxygen and nitrate additions on phosphorus release from the sediment of a Danish softwater lake. Hydrobiologia 492:139–149
Huang L, Li Z, Bai X, Li R, Wu H, Wei D, Yu L (2016) Laboratory study of phosphorus retention and release by eutrophic lake sediments: modeling and implications for P release assessments. Ecol Eng 95:438–446
Jensen FB (2003) Nitrite disrupts multiple physiological functions in aquatic animals. Comp Biochem Phys A 135:9–24
Lewis WM, Wurtsbaugh WA, Paerl HW (2011) Rationale for control of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus to reduce eutrophication of inland waters. Environ Sci Technol 45:10300–10305
Li X, Xie Q, Chen S, Xing M, Guan T, Wu D (2019) Inactivation of phosphorus in the sediment of the Lake Taihu by lanthanum modified zeolite using laboratory studies. Environ Pollut 247:9–17
Lin J, Qiu P, Yan X, Xiong X, Jing L, Wu C (2015) Effectiveness and mode of action of calcium nitrate and Phoslock® in phosphorus control in contaminated sediment, a microcosm study. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:1–12
Liu T, Yuan J, Dong W, Wu H, Wang H (2015) Effects on inorganic nitrogen compounds release of contaminated sediment treatment with in situ calcium nitrate injection. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:1250–1260
Liu X, Tao Y, Zhou K, Zhang Q, Chen G, Zhang X (2017) Effect of water quality improvement on the remediation of river sediment due to the addition of calcium nitrate. Sci Total Environ 575:887–894
McAndrew B, Ahn C (2017) Developing an ecosystem model of a floating wetland for water quality improvement on a stormwater pond. J Environ Manag 202:198–207
Meis S, Spears BM, Maberly SC, Perkins RG (2013) Assessing the mode of action of Phoslock(R) in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (Loch Flemington, UK). Water Res 47:4460–4473
Muri G, Čermelj B, Jaćimović R, Ravnikar T, Šmuc A, Turšič J, Vreča P (2017) Factors that contributed to recent eutrophication of two Slovenian mountain lakes. J Paleolimnol 59:411–426
Ni Z, Wang S, Wang Y (2016) Characteristics of bioavailable organic phosphorus in sediment and its contribution to lake eutrophication in China. Environ Pollut 219:537–544
Pessot CA, Åtland Å, Liltved H, Lobos MG, Kristensen T (2014) Water treatment with crushed marble or sodium silicate mitigates combined copper and aluminium toxicity for the early life stages of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac Eng 60:77–83
Russo RC, Thurston RV, Emerson K (1981) Acute toxicity of nitrite to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri): effects of pH, nitrite species, and anion species. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 38:387–393
Schindler DW, Hecky RE, Findlay DL, Stainton MP, Parker BR, Paterson MJ, Beaty KG, Lyng M, Kasian SE (2008) Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:11254–11258
Scott G, Crunkilton RL (2010) Acute and chronic toxicity of nitrate to fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas), ceriodaphnia dubia, and Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2918–2922
Sueitt AP, Yamada-Ferraz TM, Oliveira AF, Botta CM, Fadini PS, Nascimento MR, Faria BM, Mozeto AA (2015) Ecotoxicological risks of calcium nitrate exposure to freshwater tropical organisms: laboratory and field experiments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 117:155–163
Wang H, Wang H (2009) Mitigation of lake eutrophication: loosen nitrogen control and focus on phosphorus abatement. Prog Nat Sci 19:1445–1451
Wang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Liu H, Yan S (2012) Large-scale utilization of water hyacinth for nutrient removal in Lake Dianchi in China: the effects on the water quality, macrozoobenthos and zooplankton. Chemosphere 89:1255–1261
Wang L, Long X, Chong Y, Yu G (2016) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments during the denitrification process enhanced by calcium nitrate addition: effect of AVS residual. Ecol Eng 87:333–339
Wang G, Wang Y, Guo Y, Peng D (2017) Effects of four different phosphorus-locking materials on sediment and water quality in Xi’an moat. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:264–274
Wang GB, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2018) Combination effect of sponge iron and calcium nitrate on severely eutrophic urban landscape water: an integrated study from laboratory to fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:8350–8363
Wang WH, Wang Y, Fan P, Chen LF, Chai BH, Zhao JC, Sun LQ (2019a) Effect of calcium peroxide on the water quality and bacterium community of sediment in black-odor water. Environ Pollut 248:18–27
Wang Y, Wang WH, Yan FL, Ding Z, Feng LL, Zhao JC (2019b) Effects and mechanisms of calcium peroxide on purification of severely eutrophic water. Sci Total Environ 650:2796–2806
Wauer G, Gonsiorczyk T, Kretschmer K, Casper P, Koschel R (2005) Sediment treatment with a nitrate-storing compound to reduce phosphorus release. Water Res 39:494–500
Willenbring PR, Miller MS, Weidenbacher WD (2009) Reducing sediment phosphorus release rates in Long Lake through the use of calcium nitrate. Lake and Reservoir Management 1:118–121
Winquist E, Björklöf K, Schultz E, Räsänen M, Salonen K, Anasonye F, Cajthaml T, Steffen KT, Jørgensen KS, Tuomela M (2014) Bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil with fungi– from laboratory to field scale. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 86:238–247
Xiang F, Geng L, Lü K, Zhang J, Minter EJA, Yang Z (2012) Effect of long-term nitrite exposure on the cladoceran Daphnia obtusa: survival, moults, and reproduction. Biochem Syst Ecol 41:98–103
Yamada TM, Sueitt AP, Beraldo DA, Botta CM, Fadini PS, Nascimento MR, Faria BM, Mozeto AA (2012) Calcium nitrate addition to control the internal load of phosphorus from sediments of a tropical eutrophic reservoir: microcosm experiments. Water Res 46:6463–6475
Yin H, Kong M, Fan C (2013) Batch investigations on P immobilization from wastewaters and sediment using natural calcium rich sepiolite as a reactive material. Water Res 47:4247–4258
Yu P, Wang J, Chen J, Guo J, Yang H, Chen Q (2019) Successful control of phosphorus release from sediments using oxygen nano-bubble-modified minerals. Sci Total Environ 663:654–661
Zhang SX, Peng R, Jiang R, Chai XS, Barnes DG (2018a) A high-throughput headspace gas chromatographic technique for the determination of nitrite content in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1538:104–107
Zhang Y, Song C, Ji L, Liu Y, Xiao J, Cao X, Zhou Y (2018b) Cause and effect of N/P ratio decline with eutrophication aggravation in shallow lakes. Sci Total Environ 627:1294–1302
Funding
This study was funded by Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Research Key Project (grant no. 2016JZ019) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21677115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lu, X., Fan, P. et al. Effects of different dosing modes of calcium nitrate on P locking in sediment and nutrient concentrations in waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 7504–7514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07382-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07382-2