Abstract
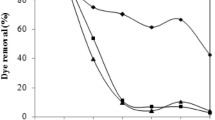
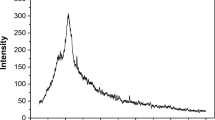
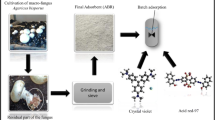
The adsorption of acid red 97 dye (RED 97) by the waste of the filamentous fungus Beauveria bassiana was analyzed. The adsorbent was obtained as a waste of a fermentative process, and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT–IR), X–ray powder diffractometry (XRD), and specific surface area (BET). After the characterization, adsorption tests were carried out to determine the ideal conditions of pH, adsorbent mass, and contact time for the process. Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamic studies, and the treatment of textile effluent were also investigated. The adsorbent characterization allowed the visualization of its amorphous structure, with irregular and heterogeneous particles. The pore diameter was 51.9 nm and the surface area was 0.247 m2 g−1. 1.2 g L−1 of the adsorbent and pH of 2.0 were the ideal conditions for RED 97 adsorption. The pseudo–second–order kinetic model was the most appropriate to represent the experimental data, being the equilibrium reached in about 110 min. The Langmuir model was the most suitable to represent the equilibrium data, with maximum adsorption capacity of 194.1 mg g−1 at 45 °C. The adsorption processes was thermodynamically spontaneous, favorable, and exothermic. In the treatment of a real textile effluent, 5 g L−1 of the spores was capable to decolorize 70% of the solution. Therefore, spore wastes of Beauveria bassiana were promising for RED 97 adsorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhassani HA, Rauf MA, Ashraf SS (2007) Efficient microbial degradation of Toluidine Blue dye by Brevibacillus sp. Dyes Pigments 75:395–400
Balarak D, Mostafapour FK (2016) Adsorption behavior of acid red 97 dye on canola stalks. J Sci Eng Res 3:148–154
Banat IN, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile dye–containing effluents: a review. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227
Bankole PO, Adekunle AA, Govindwar SP (2018) Enhanced decolorization and biodegradation of acid red 88 dye by newly isolated fungus, Achaetomium strumarium. J Environ Chem Eng 6:1589–1600
Bellatin L, Herrera O, Navarro A, Sun-Kou R, Llanos B (2014) Estudio de la biosorción de Rojo ácido 18, Azul básico 99 y Amarillo básico 57, presentes en los tintes de cabellos, con residuos de hojas de té verde. Rev Soc Quím Perú 80:9–23
Benchekor H, Iddou A, Hentit H, Aziz A, Piccin JS (2018) Multilayer adsorption of purple NR5 industrial dye by Aristeus antennautus shell in aqueous solution. Key Eng Mater 762:109–114
Brindley GW, Brown G (1980) Crystal structures of clay minerals and their X–ray identification. Mineralogical Society, London. https://doi.org/10.1180/mono-5
Bumpus JA (1995) Microbial degradation of azo dyes. In: Singh VP (ed) Biotransformation: microbial degradation of health–risk compounds. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 157–175
Chen JJ, Ahmad AL, Ooi BS (2013) Poly(N–isopropylacrylamide–co–acrylic acid) hydrogels for copper ion adsorption: equilibrium isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 1(2013):339–348
Da Silva CG, Faria JL (2003) Photochemical and photocatalytic degradation of an azo dye in aqueous solution by UV irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 155:133–143
Demarchi CA, Campos M, Rodrigues CA (2013) Adsorption of textile dye reactive red 120 by the chitosan–Fe(III)–crosslinked: batch and fixed–bed studies. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1350–1358
Dotto GL, Costa JAV, Pinto LAA (2013) Kinetic studies on the biosorption of phenol by nanoparticles from Spirulina sp. LEB 18. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1137–1143
El-bindary AA, Diab MA, Hussien MA, El-Sonbati AZ, Eessa AM (2014) Adsorption of Acid Red 57 from aqueous solutions onto polyacrylonitrile/activated carbon composite. Spectrochim Acta – Part A: Molec Biomolec Spectroscopy 124:70–77
Errais E, Duplay J, Elhabiri M, Khodja M, Ocampo R, Baltenweck-Guyot R, Darragi F (2012) Anionic RR120 dye adsorption onto raw clay: surface properties and adsorption mechanism. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 403:69–78
Escudero LB, Quintas PY, Wuilloud RG, Dotto GL (2019) Recent advances on elemental biosorption. Environ Chem Lett 17:409–427
Freundlich H (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. Z Phys Chem 57:358–471
Fu F, Xiong Y, Xie B, Chen R (2007) Adsorption of Acid Red 73 on copper dithiocarbamate precipitate–type solid wastes. Chemosphere 66:1–7
Georgin J, Silva Marques B, Peres EC, Allasia D, Dotto GL (2018) Biosorption of cationic dyes by Pará chestnut husk (Bertholletia excelsa). Water Sci Technol 77:1612–1621
Ghazi Mokri HS, Modirshahla N, Behnajady MA, Vahid B (2015) Adsorption of C.I. Acid Red 97 dye from aqueous solution onto walnut shell: kinetics, thermodynamics parameters, isotherms. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1401–1408
Gola D, Dey P, Bhattacharya A, Mishra A, Malik A, Namburath M, Ahammad SZ (2016) Multiple heavy metal removal using an entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana. Bioresour Technol 218:388–396
Gola D, Malik A, Namburath M, Ahammad SZ (2018) Removal of industrial dyes and heavy metals by Beauveria bassiana: FTIR, SEM, TEM and AFM investigations with Pb(II). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20486–20496
Goldstein JI, Newbury DE, Echil P, Joy DC, Romig AD Jr, Lyman CE, Fiori C, Lifshin E (1992) Scanning electron microscopy and X–ray microanalysis. Plenum Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0491-3
Graba Z, Hamoudi S, Bekka D, Bezzi N, Boukherroub R (2015) Influence of adsorption parameters of basic red dye 46 by the rough and treated Algerian natural phosphates. J Ind Eng Chem 25:229–238
Heibati B, Couto SR, Al-Ghouti MA, Asif M, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Kinetics and thermodynamics of enhanced adsorption of the dye AR 18 using activated carbons prepared from walnut and poplar woods. J Mol Liq 208:99–105
Hessel C, Allegre C, Maisseu M, Charbit F, Moulin P (2007) Guidelines and legislation for dye house effluents. J Environ Manag 83:171–180
Hussein KA, Hassan SHA, Joo JH (2011) Potential capacity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae in the biosorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+. J Gen Appl Microbiol 57:347–355
Khodam F, Rezvani Z, Amani-Ghadim AR (2015) Enhanced adsorption of Acid Red 14 by co–assembled LDH / MWCNTs nanohybrid: optimization, kinetic and isotherm. J Ind Eng Chem 21:1286–1294
Lang W, Sirisansaneeyakul S, Ngiwsara L, Mendes S, Martins LO, Okuyama M, Kimura A (2013) Characterization of a new oxygen insensitive azo reductase from Brevibacillus laterosporus TISTR1911: toward dye decolorization using a packed bed metal affinity reactor. Bioresour Technol 150:298–306
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Li X, Zhang D, Sheng F, Qing H (2018) Adsorption characteristics of copper (II), zinc (II) and mercury (II) by four kinds of immobilized fungi residues. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:357–366
Lima EC, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong Use of Equilibrium Constant in the Van’t Hoof Equation for Calculation of Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434
Liu Y, Shen L (2008) A general rate law equation for biosorption. Biochem Eng J 38:390–394
Mishra A, Malik A (2013) Recent advances in microbial metal bioaccumulation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:1162–1222
Myslak ZW, Bolt HM (1998) Occupational exposure to azo dyes risk of bladder cancer. Zbl Arbeitsmed 38:310–321
Piccin JS, Cadaval TRS, Pinto LAA, Dotto GL (2017) Adsorption isotherms in liquid phase: experimental, modeling, and interpretations. Chapter 2. In: Bonilla–Petriciolet A, Mendoza–Castillo DI, Reynel–Ávila E. (ed) Adsorption processes for water treatment and purification. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 31–52.
Przystaś W, Zabłocka-Godlewska E, Grabińska-Sota E (2015) Efficacy of fungal decolorization of a mixture of dyes belonging to different classes. Braz J Microbiol 46:415–424
Qu B, Zhou J, Xiang X, Zheng C, Zhao H, Zhou X (2008) Adsorption behavior of azo dye C. I. acid red 14 in aqueous solution on surface soils. J Environ Sci 20:704–709
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1026
Saratale RG, Gandhi SS, Purankar MV, Kurade MB, Govindwar SP, Oh SE, Saratale GD (2013) Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye C.I. Remazol Red and textile effluent by isolated Lysinibacillus sp. RGS. J Biosci Bioeng 115:658–667
Silverstein RM, Webster FX, Kiemle DJ (2007) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. Wiley, New York
Solis M, Solis A, Perez HI, Mnjarrez N (2012) Microbial decolouration of azo dyes: a review. Process Biochem 47:1723–1748
Sonai GG, Souza SMAGU, Oliveira D, Souza AAU (2016) The application of textile sludge adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 2 dye. J Environ Manag 168:149–156
Souza ARC, Baldoni DB, Lima J, Porto V, Marcuz C, Ferraz RC, Kuhn RC, Jacques RJS, Guedes JVC, Mazutti MA (2015) Bioherbicide production by Diaporthe sp. isolated from the Brazilian Pampa biome. Biocat Agric Biotec 4:575–578
Srikantan C, Suraishkumar GK, Srivastava S (2018) Effect of light on the kinetics and equilibrium of the textile dye (Reactive Red 120) adsorption by Helianthus annuus hairy roots. Bioresour Technol 257:84–91
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Oliver JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069
Thue PS, Sophia AC, Lima EC, Wamba AG, de Alencar WS, dos Reis GS, Dias SLP (2018) Synthesis and characterization of a novel organic–inorganic hybrid clay adsorbent for the removal of acid red 1 and acid green 25 from aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 171:30–44
Wang L, Li J (2013) Adsorption of C.I. Reactive Red 228 dye from aqueous solution by modified cellulose from flax shive: kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics. Ind Crop Prod 42:153–158
Wang L, Chen Z, Wen H, Cai Z, He C, Wang Z, Yan W (2018a) Microwave assisted modification of activated carbons by organic acid ammoniums activation for enhanced adsorption of acid red 18. Powder Technol 323:230–237
Wang L, Yan W, He C, Wen H, Cai Z, Wang Z, Chen Z, Liu W (2018b) Microwave–assisted preparation of nitrogen–doped biochars by ammonium acetate activation for adsorption of acid red 18. Appl Surf Sci 433:222–231
Xu D, Gu C, Chen X (2013) Adsorption and removal of acid red 3R from aqueous solution using flocculent humic acid isolated from lignite. Procedia Environ Sci 18:127–134
Zazycki MA, Godinho M, Perondi D, Foletto EL, Collazzo GC, Dotto GL (2018) New biochar from pecan nutshells as an alternative adsorbent for removing reactive red 141 from aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 171:57–65
Zulfiqar Ahmed MN, Chandrasekhar KB, Nagabhushana BM (2018) Adsorption of Acid Red 97 by α–Fe2O3 nanopowder: isotherm and kinetic studies. Int J Sci Eng Manage 3:34–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgin, J., Alves, E., Drumm, F. et al. Application of Beauveria bassiana spore waste as adsorbent to uptake acid red 97 dye from aqueous medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 36967–36977 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06792-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06792-6