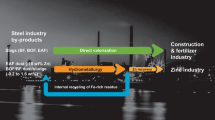
Abstract
Due to the increasing demand of metals by industry and the limited availability of natural resources, the secondary supply of these elements from discarded products, such as waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), is an important strategy for pursuing a sustainable development. Nevertheless, the complex and heterogeneous composition of this waste stream stands as one of the main drawbacks in the definition of innovative recovery processes. This study investigated the recovery potential of a multi-step leaching process to extract the strategic metals, namely precious metals and rare earth elements (REEs), from the dust produced during the industrial shredding treatment of WEEE. Using a first double-oxidative step with sulfuric acid, most rare earth elements contained in the dust were dissolved at high percentages. Moreover, around 50% of gold was extracted in a second leaching step using 0.25 M thiourea, in a solid to liquid ratio of 0.2 g/70 mL, at 600 rpm. In this regard, the optimum operating conditions were studied by a 23 full factorial design. Experimental results address the definition of a novel approach, pursuing the recovery of resources of great industrial interest from the residues originating from WEEE mechanical treatments typically performed at large scale. As this dust fraction is not sent for recovery but currently disposed, the proposed recycling strategy promotes the diversion of waste from landfill while reducing the need for virgin materials via lower-impact metallurgical processes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil A, Erust C, Gahan CS, Ozgun M, Sahin M, Tuncuk A (2015) Precious metal recovery from waste printed circuit boards using cyanide and non-cyanide lixiviants – a review. Waste Manag 45:258–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.017
Bachér J, Kaartinen T (2017) Liberation of printed circuit assembly (PCA) and dust generation in relation to mobile phone design in a size reduction process. Waste Manag 60:609–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.09.037
Bachér J, Mrotzek A, Wahlström M (2015) Mechanical pre-treatment of mobile phones and its effect on the printed circuit assemblies (PCAs). Waste Manag 45:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.009
Bakas I, Fischer C, Haselsteiner S et al (2014) Present and potential future recycling of critical metals in WEEE. Copenaghen Resource Institute (ED), Copenaghen, Denmark
Bas AD, Deveci H, Yazici EY (2014) Treatment of manufacturing scrap TV boards by nitric acid leaching. Sep Purif Technol 130:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.04.008
Behnamfard A, Salarirad MM, Vegliò F (2013) Process development for recovery of copper and precious metals from waste printed circuit boards with emphasize on palladium and gold leaching and precipitation. Waste Manag 33:2354–2363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.07.017
Binnemans K, Jones PT, Blanpain B, van Gerven T, Yang Y, Walton A, Buchert M (2013) Recycling of rare earths: a critical review. J Clean Prod 51:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.12.037
Birloaga I, De Michelis I, Ferella F et al (2013) Study on the influence of various factors in the hydrometallurgical processing of waste printed circuit boards for copper and gold recovery. Waste Manag 33:935–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.01.003
Birloaga I, Coman V, Kopacek B, Vegliò F (2014) An advanced study on the hydrometallurgical processing of waste computer printed circuit boards to extract their valuable content of metals. Waste Manag 34:2581–2586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.08.028
Brandl H, Bosshard R, Wegmann M (2001) Computer-munching microbes: metal leaching from electronic scrap by bacteria and fungi. Hydrometallurgy 59:319–326
Cesaro A, Marra A, Belgiorno V, Guida M (2017) Effectiveness of WEEE mechanical treatment: separation yields and recovered material toxicity. J Clean Prod 142:2656–2662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.011
Chancerel P, Meskers CEM, Hagelüken C, Rotter VS (2009) Assessment of precious metal flows during preprocessing of waste electrical and electronic equipment. J Ind Ecol 13:791–810. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2009.00171.x
Cui J, Zhang L (2008) Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: a review. J Hazard Mater 158:228–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.001
De Michelis I, Kopacek B (2018) HydroWEEE project: design and construction of a mobile demonstration plant. In: Vegliò F, Birloaga I (eds) Waste electrical and electronic equipment Recycling. Aqueous recovery methods. Woodhead Publishin, pp 357–383
De Michelis I, Ferella F, Varelli EF, Vegliò F (2011) Treatment of exhaust fluorescent lamps to recover yttrium: experimental and process analyses. Waste Manag 31:2559–2568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.07.004
Deveci H, Yazici E, Aydin U, Akcil A (2010) Extraction of copper from scrap TV boards by Sulphuric acid leaching under Oxidising conditions
Diaz F, Florez S, Friedrich B (2015) Mass flow analysis and metal losses by the degradation process of organic-containing WEEE scraps. Chem Ing Tech 87:1599–1608. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.201500064
European Commission (2017) Study on the review of the list of critical raw materials. Crit Assess. ISBN 978-92-79-47937-3. https://doi.org/10.2873/876644
Ficeriová J, Baláz P, Dutková E, Gock E (2008) Leaching of gold and silver from crushed au-ag wastes. Open Chem J 2:6–9
Graedel TE, Allwood J, Birat J-P, Buchert M, Hagelüken C, Reck BK, Sibley SF, Sonnemann G (2011) What do we know about metal Recycling rates? J Ind Ecol 15:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00342.x
Gurung M, Adhikari BB, Kawakita H, Ohto K, Inoue K, Alam S (2013) Recovery of gold and silver from spent mobile phones by means of acidothiourea leaching followed by adsorption using biosorbent prepared from persimmon tannin. Hydrometallurgy 133:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.12.003
Hagelüken C (2006) Recycling of electronic scrap at Umicore precious metals refining. Acta Metall Slovaca 12:111–120
Hagelüken C, Corti CW (2010) Recycling of gold from electronics: cost-effective use through ‘Design for Recycling. Gold Bull 43:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03214988
Hagelüken C, Lee-Shin J, Carpentier A, Heron C (2016) The EU circular economy and its relevance to metal Recycling. Recycling 1:242–253. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1020242
Hong Y, Valix M (2014) Bioleaching of electronic waste using acidophilic sulfur oxidising bacteria. J Clean Prod 65:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.08.043
Innocenzi V, Ippolito NM, De Michelis I et al (2016) A hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of terbium from fluorescent lamps: experimental design, optimization of acid leaching process and process analysis. J Environ Manag 184:552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.026
Innocenzi V, Ippolito NM, Pietrelli L, Centofanti M, Piga L, Vegliò F (2018) Application of solvent extraction operation to recover rare earths from fluorescent lamps. J Clean Prod 172:2840–2852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clepro.2017.11.129
Jha MK, Kumari A, Panda R, Rajesh Kumar J, Yoo K, Lee JY (2016) Review on hydrometallurgical recovery of rare earth metals. Hydrometallurgy 161:77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.01.003
Jing-ying L, Xiu-li X, Wen-quan L (2012) Thiourea leaching gold and silver from the printed circuit boards of waste mobile phones. Waste Manag 32:1209–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.026
Li H, Eksteen J, Oraby E (2018) Hydrometallurgical recovery of metals from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs): current status and perspectives – a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 139:122–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.08.007
Marra A, Cesaro A, Belgiorno V (2018a) Separation efficiency of valuable and critical metals in WEEE mechanical treatments. J Clean Prod 186:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.112
Marra A, Cesaro A, Rene ER, Belgiorno V, Lens PNL (2018b) Bioleaching of metals from WEEE shredding dust. J Environ Manag 210:180–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.066
Meng L, Wang Z, Zhong Y, Guo L, Gao J, Chen K, Cheng H, Guo Z (2017) Supergravity separation for recovering metals from waste printed circuit boards. Chem Eng J 326:540–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.143
Montgomery DC (1991) Design and analysis of experiments, third edn. Wiley & Sons
Nguyen VK, Lee J-U (2015) A comparison of microbial leaching and chemical leaching of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 20:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0223-1
Nicol MJ, Paul RL, Fleming CA (1987) The chemistry of the extraction of gold. Mintek
Oh CJ, Lee SO, Yang HS, Ha TJ, Kim MJ (2003) Selective leaching of valuable metals from waste printed circuit boards. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 53:897–902. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2003.10466230
Oliveira PC, Cabral M, Taborda FC et al (2009) Leaching studies for metals recovery from printed cir cuit boards scrap. CM AG, Toronto
Pietrelli L, Bellomo B, Fontana D, Montereali MR (2002) Rare earths recovery from NiMH spent batteries. Hydrometallurgy 66:135–139
Robinson BH (2009) E-waste: an assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ 408:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.044
Talebi A, Cesaro A, Marra A, Belgiorno V, Ismail N (2018) Base metal ion extraction and stripping from WEEE leachate by liquid-liquid extraction. J Phys Sci 29(3):15–28
Tanaka M, Koyama K, Narita H, Oishi T (2012) Recycling valuable metals via hydrometallurgical routes. In: Design for Innovative Value Towards a sustainable society. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 507–512
Tanskanen P (2013) Management and recycling of electronic waste. Acta Mater 61:1001–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.11.005
Tsamis A, Coyne M (2015) Recovery of rare earths from electronic wastes: an opportunity for high-tech SMEs. Dir Gen Intern POLICIES POLICY Dep Econ Sci POLICY
Tuncuk A, Stazi V, Akcil A, Yazici EY, Deveci H (2012) Aqueous metal recovery techniques from e-scrap: hydrometallurgy in recycling. Miner Eng 25:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2011.09.019
Tunsu C, Retegan T (2016) Chapter 6 - hydrometallurgical processes for the recovery of metals from WEEE. In: WEEE Recycling. Elsevier, pp 139–175
Tunsu C, Petranikova M, Gergorić M, Ekberg C, Retegan T (2015) Reclaiming rare earth elements from end-of-life products: a review of the perspectives for urban mining using hydrometallurgical unit operations. Hydrometallurgy 156:239–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.06.007
Ueberschaar M, Geiping J, Zamzow M, Flamme S, Rotter VS (2017) Assessment of element-specific recycling efficiency in WEEE pre-processing. Resour Conserv Recycl 124:25–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.04.006
UNEP (2013) Recycling Rates of Metals – A Status Report, A Report of the Working Group on the Global Metal Flows to the International Resource Panel. Graedel TE, Allwood J, Birat J-P, Reck BK, Sibley SF, Sonnemann G, Buchert M, Hagelüken C (eds)
Wang F, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Duan C, Wang L (2015) Mineralogical analysis of dust collected from typical recycling line of waste printed circuit boards. Waste Manag 43:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.021
Wang H, Zhang S, Li B, Pan D’, Wu Y, Zuo T (2017) Recovery of waste printed circuit boards through pyrometallurgical processing: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 126:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.08.001
Yang H, Liu J, Yang J (2011) Leaching copper from shredded particles of waste printed circuit boards. J Hazard Mater 187:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.051
Yoon H-S, Kim C-J, Chung KW, Lee SJ, Joe AR, Shin YH, Lee SI, Yoo SJ, Kim JG (2014) Leaching kinetics of neodymium in sulfuric acid from E-scrap of NdFeB permanent magnet. Korean J Chem Eng 31:706–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0259-5
Yörükoğlu A, Obut A, Girgin İ (2003) Effect of thiourea on sulphuric acid leaching of bastnaesite. Hydrometallurgy 68:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(02)00199-8
Zhang Y, Liu S, Xie H, Zeng X, Li J (2012) Current status on leaching precious metals from waste printed circuit boards. Procedia Environ Sci 16:560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.077
Zhang J, Shen S, Cheng Y, Lan H, Hu X, Wang F (2014) Dual lixiviant leaching process for extraction and recovery of gold from ores at room temperature. Hydrometallurgy 144-145:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.02.001
Zhao C, Zhang X, Ding J, Zhu Y (2017) Study on recovery of valuable metals from waste mobile phone PCB particles using liquid-solid fluidization technique. Chem Eng J 311:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.091
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the plant manager and the staff of the WEEE treatment facility for the sampling support. The technical support of Melania Arenas Morente as well as the analytical assistance at the SEED laboratory of Anna Farina and Paolo Napodano were deeply appreciated.
Funding
The research study was partially funded by a FARB project of the University of Salerno.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marra, A., Cesaro, A. & Belgiorno, V. Recovery opportunities of valuable and critical elements from WEEE treatment residues by hydrometallurgical processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 19897–19905 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05406-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05406-5