Abstract
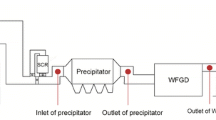
The low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator (LLT-ESP), a combination of a traditional temperature electrostatic precipitator (ESP) and a non-leakage media gas-gas exchange (MGGH), could reduce the inlet flue gas temperature below the dew point and improved the performance of the ESP. Particulate matter (PM) from the stationary sources contains filterable particulate matter (FPM) and condensable particulate matter (CPM). In this study, coal with a high ash content (coal-HA) was burned, and the emission characteristics and removal efficiencies of the particulate matter in an LLT-ESP were investigated. The standards used to test filterable and condensable PM were ISO standard 23210-2009 and U.S. EPA Method 202, respectively. The LLT-ESP was efficient in removing filterable PM, with a total filterable PM removal efficiency as high as 99.6%. The removal efficiency of filterable PM increased with increasing particulate size and decreasing imported flue gas temperature. The LLT-ESP also provided excellent removal of condensable PM with a condensable PM removal efficiency exceeding 77%. Upstream of the LLT-ESP, the concentrations of filterable PM were much higher than those of condensable PM. Downstream of the LLT-ESP, the relationship between the quantities of condensable and filterable PM reversed. To reduce the emissions of PM from coal-fired power plants, more attention should be paid to controlling condensable PM. The temperature of the flue gas upstream of the LLT-ESP played an important role in eliminating condensable PM. At lower imported flue gas temperature operation conditions, the removal efficiency of the LLT-ESP for the condensable PM and the escaping mass concentration of condensable PM increased. Among the organic fraction of the condensable PM, hydrocarbons and esters were dominant. Meanwhile, SO42− was the primary component, followed by Cl− in anions. Na+, Ca2+, and Fe3+ were the main components in metal ions. Particles with diameters ≥ 10 μm, which contained most of the Si and Al, were dominant in the fly ash collected from sections 1 and 2 of the LLT-ESP. The main particles in sections 3 and 4 were PM10, which contained the highest concentrations of Ca and Fe.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäck A 2009 Enhancing ESP Efficiency for high resistivity Fly ash by reducing the flue gas temperature[J]. Electrostatic Precipitation 406–411
Bayless DJ, Jewmaidang J, Tanneer S, Birru R (2000) Kinetics of low-temperature homogeneous SO3, formation for use in flue gas conditioning for improved electrostatic precipitator performance[J]. Proc Combust Inst 28(2):2499–2505
Bell ML, Dominici F, Ebisu K, Zeger SL, Samet JM (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in PM2.5 chemical composition in the United States for health effects studies[J]. Environ Health Perspect 115:989–995
Chandra A, Kumar S, Kumar S et al (1986) Investigations on fly ash resistivity: development of empirical relations based on experimental measurement[J]. Am J Pathol 170(1):263–271
Corio LA, Sherwell J (2000) In-stack condensable particulate matter measurements and issues[J]. Air Waste Manage Assoc 50(2):207–218
Cao G, Zhang X, Gong S et al (2008) Investigation on emission factors of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from crop residue burning[J]. J Environ Sci 20(1):50–55
Finlayson-Pitts BJ, Pitts JN (2000) Chemistry of the upper and lower atmosphere, vol. 47, no. 3. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 633–637
Janssen N, Hoek G, Simic-Lawson M et al (2011) Black carbon as an additional Indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ[J]. Health Perspect 119:1691–1699
Yoo JI, Jang KHN, Seo YC et al (2002) Emission characteristics of particulate matter and heavy metals from small incinerators and boilers[J]. Atmos Environ 36(32):5057–5066
Li JW, Qi ZF, Li M et al (2017) Physical and chemical characteristics of condensable particulate matter from an ultralow-emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Energy Fuel 31(2):1778–1785
Lin GY, Lee GR, Lin SF, Hung YH, Li SW, Wu GJ, Ye H, Huang W, Tsai CJ (2015) Ultrafine particles and PM2.5 at three urban air monitoring stations in northern Taiwan from 2011 to 2013[J]. Aerosol Air Qual Res 15:2305–2319
Lu HY, Lin SL, Mwangi JK, Wang LC, Lin HY (2016) Characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric PM2.5 at a Coastal City in southern Taiwan[J]. Aerosol Air Qual Res 16(4):1022–1034
Noda N, Makino H (2010) Influence of operating temperature on performance of electrostatic precipitator for pulverized coal combustion boiler[J]. Adv Powder Technol 21(4):495–499
Pei B (2015) Determination and emission of condensable particulate matter from coal-fired power plants[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue 05:1544–1549
Qi ZF, Li JW, Wu DL et al (2017) Particulate matter emission characteristics and removal efficiencies of a low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator[J]. Energy Fuel 31(2):1741–1746
Richards J, Holder T, Goshaw D 2005 Optimized Method 202 Sampling Train to Minimize the Biases Associated with Method 202 Measurement of Condensable Particulate Matter Emissions, Hazardous Waste Combustion Specialty Conference, St. Louis, Missouri, , Air & Waste Management Association
Shou CH, Qi ZF, Xie WY et al (2016) Experimental study on engineering application of particulate matter removal characteristics of low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE 36(16):4326–4331
Souza DZ, Vasconcellos PC, Lee H, Aurela M, Saarnio K, Teinilä K, Hillamo R (2014) Composition of PM2.5 and PM10 collected at urban sites in Brazil[J]. Aerosol Air Qual Res 14:168–176
Wang C, Liu X, Li D, Si J, Zhao B, Xu M (2015) Measurement of particulate matter and trace elements from a coal-fired power plant with electrostastic precipitators equipped the low temperature economizer[J]. Proc Combust Inst 35(3):2793–2800
Ninomiya Y, Zhang L, Sato A, Dong Z (2004) Influence of coal particle size on particulate matter emission and its chemical species produced during coal combustion[J]. Fuel Process Technol 85:1065–1088
Yang HH (2014) Filterable and condensable fine particulate emissions from stationary sources[J]. Aerosol Air Qual Res 14. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.08.0078
Yin L, Niu Z, Chen X, Chen J, Xu L, Zhang F (2012) Chemical compositions of PM2.5 aerosol during haze periods in the Mountainous City of Yong'an, China. J Environ Sci 24:1225–1233
Zagoruiko AN, Vanag SV, Balzhinimaev BS, Paukshtis EA, Simonova LG, Zykov AM, Anichkov SN, Hutson ND (2009) Catalytic flue gas conditioning in electrostatic precipitators of coal-fired power plants[J]. Chem Eng J 154(1–3):325–332
Zhao JW, Hu DQ, Shan XY et al (2015) The review of ultra-low emissions technology in coal-fired power plants[J]. Power & Energy 36(5):701–708
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhou, C., Li, J. et al. Distribution and emission characteristics of filterable and condensable particulate matter before and after a low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 12798–12806 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04570-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04570-y