Abstract
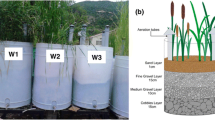
One of the possible ways to improve the operation efficiency of constructed wetlands and to prevent their clogging is the application of earthworms. They have already been successfully applied for vermicomposting and for sludge dewatering and treatment. A few studies have already examined the effect of earthworms on the treatment of wastewater by vertical flow constructed wetlands (VFCWs), but none of them have provided a yearlong research result from an open-air system or compared the effect that different seasons in a temperate climate area can have on these invertebrates. The goal of this research was to estimate the effect that earthworms and plants have on VFCW’s operation. Four mesocosms (a filter, a filter with earthworms, a VFCW and a VFCW with earthworms) were built and their influent and effluent water quality was monitored for a period of 1 year. They were fed with wastewater coming from a building of the University of Bologna (Italy). The results have shown that the presence of earthworms in this specific system did not reduce the organic matter content of the substrate, but it has positively influenced plants’ growth. However, since neither earthworms nor plants had a statistically significant effect on the effluent quality, it can be concluded that the integration of these invertebrates cannot improve wastewater treatment of vertical flow filters or constructed wetlands.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Arora S, Kazmi AA (2015) The effect of seasonal temperature on pathogen removal efficacy of vermifilter for wastewater treatment. Water Res 74:88–99
Boutilier L, Jamieson R, Gordon R, Lake C, Hart W (2009) Adsorption, sedimentation, and inactivation of E. coli within wastewater treatment wetlands. Water Res 43(17):4370–4380
Chen Z, Hu S, Hu C, Huang L, Liu H, Vymazal J (2016) Preliminary investigation on the effect of earthworm and vegetation for sludge treatment in sludge treatment reed beds system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):11957–11963
Ciria MP, Solano ML, Soriano P (2005) Role of Macrophyte Typha latifolia in a constructed wetland for wastewater treatment and assessment of its potential as a biomass fuel. Biosyst Eng 92(4):535–544
Collison RS, Grismer ME (2015) Nitrogen and COD removal from septic tank wastewater in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: plants effects. Water Environ Res 87(11):1999–2007
Díaz FJ, O’Geen AT, Dahlgren RA (2010) Efficacy of constructed wetlands for removal of bacterial contamination from agricultural return flows. Agric Water Manag 97(11):1813–1821
Edwards CA, Bater JE (1992) The use of earthworms in environmental management. Soil Biol Biochem 24(12):1683–1689
EN ISO 7899-2:2000: Water quality - Detection and enumeration of intestinal enterococci - Part 2: Membrane #ltration method (ISO 7899-2:2000). Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/wej.12088. Accessed on 4th Nov 2018
Headley T, Nivala J, Kassa K, Olsson L, Wallace S, Brix H, van Afferden M, Müller R (2013) Escherichia coli removal and internal dynamics in subsurface flow ecotechnologies: effects of design and plants. Ecol Eng 61(part B):564–574
Huang J, Wenshu C, Zhong Q, Wang S (2013) Influence of temperature on micro-environment, plant eco-physiology and nitrogen removal effect in subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 60:242–248
Kanianska R, Jad’ud’ová J, Makovníková J, Kizeková M (2016) Assessment of relationships between earthworms and soil abiotic and biotic factors as a tool in sustainable agricultural. Sustainability 8(9):906
Lavrnić S, Mancini ML (2016) Can constructed wetlands treat wastewater for reuse in agriculture? Review of guidelines and examples in South Europe. Water Sci Technol 73(11):2616–2626
Le Bayon RC, Milleret R (2009) Effects of earthworms on phosphorus dynamics—a review. Dyn Soil Dyn Plant 3(2):21–27
Li HZ, Wang S, Ye JF, Xu ZX, Jin W (2011) A practical method for the restoration of clogged rural vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment using earthworm. Water Sci Technol 63(2):283–290
Li H, Li Y, Gong Z, Li X (2013) Performance study of vertical flow constructed wetlands for phosphorus removal with water quenched slag as a substrate. Ecol Eng 53:39–45
Mancini B (2017) Application of sequence based typing (SBT) technique to typing strains of legionella spp.: development of an environmental risk map. PhD thesis. University of Bologna. Bologna, Italy
Matos GD, Arruda MAZ (2003) Vermicompost as natural adsorbent for removing metal ions from laboratory effluents. Process Biochem 39(1):81–88
Meng P, Pei H, Hu W, Shao Y, Li Z (2014) How to increase microbial degradation in constructed wetlands: influencing factors and improvement measures. Bioresour Technol 157:316–326
Molleda P, Blanco I, Ansola G, de Luis E (2008) Removal of wastewater pathogen indicators in a constructed wetland in Leon, Spain. Ecol Eng 33(3):252–257
Ngo PT, Rumpel C, Doan TT, Jouquet P (2012) The effect of earthworms on carbon storage and soil organic matter composition in tropical soil amended with compost and vermicompost. Soil Biol Biochem 50:214–220
Nivala J, Knowles P, Dotro G, García J, Wallace S (2012) Clogging in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands: measurement, modeling and management. Water Res 46(6):1625–1640
Nuengjamnong C (2010) Implementation of earthworm-assisted constructed wetlands to treat wastewater and possibility of using alternative plants in constructed wetlands. PhD thesis. Hamburg University of technology. Hamburg, Germany
Nuengjamnong C, Chiarawatchai N, Polprasert C, Otterpohl R (2011) Treating swine wastewater by integrating earthworms into constructed wetlands. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46(7):800–804
Ouattara JMP, Coulibaly L, Tiho S, Ouattara A, Goure G (2011) Panicum maximum (Jacq.) density effect upon macrofauna structure in sediments of pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 37(2):217–223
Sgroi M, Pelissari C, Roccaro P, Sezerino PH, García J, Vagliasindi FGA, Ávila C (2018) Removal of organic carbon, nitrogen, emerging contaminants and fluorescing organic matter in different constructed wetland configurations. Chem Eng J 332:619–627
Sharma PK, Takashi I, Kato K, Ietsugu H, Tomita K, Nagasawa T (2013) Seasonal efficiency of a hybrid sub-surface flow constructed wetland system in treating milking parlor wastewater at northern Hokkaido. Ecol Eng 53:257–266
Singh RP, Fu D, Jia J, Wu J (2018) Performance of earthworm-enhanced horizontal sub-surface flow filter and constructed wetland. Water 10(10):1309
Tamis J, van Schouwenburg G, Kleerebezem R, van Loosdrecht MC (2011) A full scale worm reactor for efficient sludge reduction by predation in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 45(18):5916–5924
Tanner CC, Sukias JP (1995) Accumulation of organic solids in gravel bed constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 32(3):229–239
Taylor M, Clarke WP, Greenfield PF (2003) The treatment of domestic wastewater using small-scale vermicompost filter beds. Ecol Eng 21(2–3):197–203
Tomar P, Suthar S (2011) Urban wastewater treatment using vermi-biofiltration system. Desalination 282:95–103
Torrens A, Molle P, Boutin C, Salgot M (2009) Removal of bacterial and viral indicator in vertical flow constructed wetlands and intermittent sand filters. Desalination 246(1):169–178
UNI EN ISO 9308-1:2014/A1:2017 Water quality — Enumeration of Escherichia coli and coliform bacteria — Part 1: Membrane #ltration method for waters with low bacterial background 5ora (ISO 9308-1:2014/Amd1:2016). Available online: http://store.uni.com/catalogo/index.php/uni-en-iso-9308-1-2017.html. Accessed on 7 Nov 2018
van Vliet PCJ, van der Stelt B, Rietberg PI, de Goede RGM (2007) Effects of organic matter content on earthworms and nitrogen mineralization in grassland soils. Eur J Soil Biol 43(1):S222–S229
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380(1–3):48–65
Vymazal J (2011) Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: a review. Hydrobiologia 674(1):133–156
Wu L, Li X, Song H, Wang G, Jin Q, Xu X, Gao Y (2013) Enhanced removal of organic matter and nitrogen in a vertical-flow constructed wetland with Eisenia foetida. Desalin Water Treat 51(40–42):7460–7468
Wu S, Kuschk P, Brix H, Vymazal J, Dong R (2014) Development of constructed wetlands in performance intensifications for wastewater treatment: a nitrogen and organic matter targeted review. Water Res 57:40–55
Xu D, Xu J, Wu J, Muhammad A (2006) Studies on the phosphorus sorption capacity of substrates used in constructed wetland systems. Chemosphere 63(2):344–352
Xu DF, Li YX, Zheng JW, Guan YD, Fang H (2012) Effects of earthworms and substrate on Iris pseudacorus growth. Adv Mater Res 550-553:1429–1434
Xu D, Li Y, Fan X, Guan Y, Fang H, Zhao L (2013a) Influence of earthworm Eisenia fetida on Iris pseudacorus's photosynthetic characteristics, evapotranspiration losses and purifying capacity in constructed wetland systems. Water Sci Technol 68(2):335–441
Xu D, Li Y, Howard A (2013b) Influence of earthworm Eisenia fetida on removal efficiency of N and P in vertical flow constructed wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(9):5922–5929
Xu D, Li Y, Howard A, Guan Y (2013c) Effect of earthworm Eisenia fetida and wetland plants on nitrification and denitrification potentials in vertical flow constructed wetland. Chemosphere 92(2):201–206
Zapater-Pereyra M, Ilyas H, Lavrnić S, van Bruggen JJA, Lens PNL (2015) Evaluation of the performance and space requirement by three different hybrid constructed wetlands in a stack arrangement. Ecol Eng 82:290–300
Zhao YQ, Babatunde AO, Hu YS, Kumar JLG, Zhao XH (2011) Pilot field-scale demonstration of a novel alum sludge-based constructed wetland system for enhanced wastewater treatment. Process Biochem 46:278–283
Zhou Q, Hui Z, Bañuelos G, Yan B, Liang Y, Jing Y, Li H (2017) Impacts of vegetation and temperature on the treatment of domestic sewage in constructed wetlands incorporated with ferric-carbon micro-electrolysis material. Int J Phytoremedia 19(10):915–924
Zhu H, Zhou Q-W, Yan B-X, Liang Y-X, Yu X-F, Gerchman Y, Cheng X-W (2018) Influence of vegetation type and temperature on the performance of constructed wetlands for nutrient removal. Water Sci Technol 77(3–4):829–837
Acknowledgements
The first author’s PhD scholarship was financed by the European Commission through Erasmus Mundus PhD in Marine and Coastal Management programme. The authors would like to thank Prof. Elena Fabbri from the University of Bologna for her help during the development of this project, and Dr. Marco Maglionico and Dr. Sara Simona Cipolla from CIRI (University of Bologna) for their contribution to the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavrnić, S., Cristino, S., Zapater-Pereyra, M. et al. Effect of earthworms and plants on the efficiency of vertical flow systems treating university wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 10354–10362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04508-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04508-4