Abstract
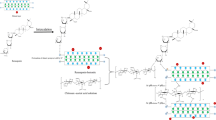
Robust and simple composite films for the removal of methyl orange (MO) and Cr(VI) have been prepared by combining chitosan, saponin, and bentonite at a specific ratio. There are several composite films (chitosan-saponin-bentonite (CSB)) prepared; among them, the composite films CSB2:3 and CSB1:1 have the highest removal efficiency toward MO and Cr(VI) where the maximum removal is 70.4% (pH 4.80) and 92.3% (pH 5.30), respectively. It was found that different types of adsorbate have different thermodynamic properties of the adsorption process; the adsorption of MO onto CSB2:3, chitosan, and acid-activated bentonite (AAB) proceeded endothermically, while the adsorption of Cr(VI) onto CSB1:1, chitosan, and AAB proceeded exothermically. The parameters of the adsorption were modeled by using isotherm and kinetic equations. The models of Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich-Peterson, Sips, and Toth were used for fitting the adsorption isotherm data at a temperature of 30, 45, and 60 °C; all of the isotherm models could represent the data well. The result indicates that CSB2:3 has the highest adsorption capacity toward MO with qm of 360.90 mg g−1 at 60 °C; meanwhile, CSB1:1 has the highest adsorption capacity toward Cr(VI) with qm 641.99 mg g−1 at 30 °C. The pseudo-second-order model could represent the adsorption kinetics data better than the pseudo-first-order equation. The adsorption mechanism was proposed, and the thermodynamic properties of the adsorption were also studied.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angkawijaya AE, Fazary AE, Hernowo E, Taha M, Ju YH (2011) Iron(III), chromium(III), and copper(II) complexes of L-norvaline and ferulic acid. J Chem Eng Data 56:532–540
Bahranowski K, Gawel A, Klimek A, Michalik-Zym A, Napruszewska BD, Nattich-Rak M, Rogowska M, Serwicka EM (2017) Influence of purification method of Na-montmorillonite on textural properties of clay mineral composites with TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl Clay Sci 140:75–80
Bassyouni DG, Hamad HA, El-Ashtoukhy E-SZ, Amin NK, El-Latif MMA (2017) Comparative performance of anodic oxidation and electrocoagulation as clean processes for electrocatalytic degradation of diazo dye acid Brown 14 in aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 335:178–187
Bhattacharyya R, Ray SK (2015) Removal of Congo red and methyl violet from water using nano clay filled composite hydrogels of poly acrylic acid and polyethylene glycol. Chem Eng J 260:269–283
Cadaval TRS, Dotto GL, Pinto LAA (2015) Equilibrium isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetic studies for the adsorption of food azo dyes onto chitosan films. Chem Eng Commun 202:1316–1323
Chiou MS, Li HY (2002) Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. J Hazard Mater 93:233–248
Crini G, Badot PM (2008) Application of chitosan, a natural amino polysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: a review of recent literature. Prog Polym Sci 33:399–447
Dotto GL, Moura JM, Cadaval TRS, Pinto LAA (2013) Application of chitosan films for the removal of food dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption. Chem Eng J 214:8–16
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Hamdaoui O (2006) Batch study of liquid-phase adsorption of methylene blue using cedar sawdust and crushed brick. J Hazard Mater 135:264–273
Hena S (2010) Removal of chromium hexavalent ion from aqueous solutions using biopolymer chitosan coated with poly 3-methyl thiophene polymer. J Hazard Mater 181:474–479
Hou H, Zhou R, Wu P, Wu L (2012) Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem Eng J 211-212:336–342
Hu XJ, Wang JS, Liu YG, Li X, Zeng GM, Bao ZL, Zeng XX, Chen AW, Long F (2011) Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 185:306–314
Huang R, Liu Q, Huo J, Yang B (2017) Adsorption of methyl orange onto protonated cross-linked chitosan. Arab J Chem 10:24–32
Jung C, Heo J, Han J, Her N, Lee SJ, Oh J, Ryu J, Yoon Y (2013) Hexavalent chromium removal by various adsorbents: powdered activated carbon, chitosan, and single/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 106:63–71
Kotaś J, Stasicka Z (2000) Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ Pollut 107:263–283
Kurniawan A, Sutiono H, Ju YH, Soetaredjo FE, Ayucitra A, Yudha A, Ismadji S (2011) Utilization of rarasaponin natural surfactant for organo-bentonite preparation: application for methylene blue removal from aqueous effluent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 142:184–193
Lalvani SB, Wiltowski T, Hübner A, Weston A, Mandich N (1998) Removal of hexavalent chromium and metal cations by a selective and novel carbon adsorbent. Carbon 36:1219–1226
Lan Y, Deng B, Kim C, Thornton EC (2007) Influence of soil minerals on chromium (VI) reduction by sulfide under anoxic conditions. Geochem Trans 8:4
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Laysandra L, Sari MWMK, Soetaredjo FE, Foe K, Putro JN, Kurniawan A, Ju YH, Ismadji S (2017) Adsorption and photocatalytic performance of bentonite-titanium dioxide composites for methylene blue and rhodamine B decoloration. Heliyon 3:e00488
Leodopoulos C, Doulia D, Gimouhopoulos K, Triantis TM (2012) Single and simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and humic acid onto bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 70:84–90
Li L, Li Y, Cao L, Yang C (2015) Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohydr Polym 125:206–213
Milonic SK (2007) A consideration of the correct calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Serb Chem Soc 72:1363–1367
Mohan D, Pittman CU (2006) Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J Hazard Mater 137:762–811
Ng JCY, Cheung WH, McKay G (2002) Equilibrium studies of the sorption of Cu(II) ions onto chitosan. J Colloid Interface Sci 255:64–74
Oh Y, Armstrong AL, Finnerty C, Zheng S, Hu M, Torrents A, Mi B (2017) Understanding the pH-responsive behavior of graphene oxide membrane in removing ions and organic micropollutants. J Membr Sci 541:235–243
Paluszkiewicz C, Stodolak E, Hasik M, Blazewicz M (2011) FT-IR study of montmorillonite-chitosan nanocomposite materials. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 79:784–788
Plazinski W, Rudzinski W, Plazinska A (2009) Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 152:2–13
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1024
Santoso SP, Laysandra L, Putro JN, Lie J, Soetaredjo FE, Ismadji S, Ayucitra A, Ju YH (2017) Preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose-montmorillonite composite via thermal radiation for liquid-phase adsorption. J Mol Liq 233:29–37
Shanmuganathan S, Loganathan P, Kazner C, Johir MAH, Vigneswaran S (2016) Submerged membrane filtration adsorption hybrid system for the removal of organic micropollutants from a water reclamation plant reverse osmosis concentrate. Desalination 401:134–141
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495
Tahir SS, Rauf N (2006) Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto bentonite clay. Chemosphere 63:1842–1848
Tong SY, Li KA (1986) The distribution of chromium(VI) species in solution as a function of pH and concentration. Talanta 33:775–777
Toth J (1971) State equations of solid-gas interface layers. Acta Chim Acad Sci Hungaricae 69:311–317
Udaybhaskar P, Iyengar L, Rao AVSP (1990) Hexavalent chromium interaction with chitosan. J Appl Polym Sci 39:739–747
Vinokurov EG, Kuznetsoz V, Bondar V (2004) Aqueous solutions of Cr(III) sulfate: modeling of equilibrium composition and physicochemical properties. Russ J Coord Chem 30:496–504
Walker GM, Hansen L, Hanna JA, Allen SJ (2003) Kinetics of a reactive dye adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Water Res 37:2081–2089
Wan X, Zhan Y, Long Z, Zeng G, He Y (2017) Core@double-shell structured magnetic halloysite nanotube nano-hybrid as efficient recyclable adsorbent for methylene blue removal. Chem Eng J 330:491–504
Wu Z, Li S, Wan J, Wang Y (2012) Cr(VI) adsorption on an improved synthesised cross-linked chitosan resin. J Mol Liq 170:25–29
Yuwei C, Jianlong W (2011) Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan nanoparticles and its application for Cu(II) removal. Chem Eng J 168:286–292
Zeng L, Xie M, Zhang Q, Kang Y, Guo X, Xiao H, Peng Y, Luo J (2015) Chitosan/organic rectorite composite for the magnetic uptake of methylene blue and methyl orange. Carbohydr Polym 123:89–98
Zhan Y, Wan X, He S, Yang Q, He Y (2017) Design of durable and efficient poly(arene ether nitrile)/bioinspired polydopamine coated graphene oxide nanofibrouscomposite membrane for anionic dye separation. Chem Eng J 330:491–504
Zhan Y, He S, Wan X, Zhang J, Liu B, Wang J, Li Z (2018) Easy-handling bamboo-like polupyrrole nanofibrous mats with high adsorption capacity for hexavalent chromium removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 529:385–395
Zhang L, Hu P, Wang J, Liu Q, Huang R (2015) Adsorption of methyl orange (MO) by Zr(IV)-immobilized cross-linked chitosan/bentonite composite. Int J Biol Macromol 81:818–827
Zhu HY, Jiang R, Xiao L, Zeng GM (2010) Preparation, characterization, adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of novel magnetic chitosan enwrapping nanosized γ-Fe2O3and multi-walled carbon nanotubes with enhanced adsorption properties for methyl orange. Bioresour Technol 101:5063–5069
Funding
Financial support from the Ministry of Research and Technology and Higher Education through Fundamental Research grant is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 243 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laysandra, L., Ondang, I.J., Ju, YH. et al. Highly adsorptive chitosan/saponin-bentonite composite film for removal of methyl orange and Cr(VI). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 5020–5037 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4035-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4035-2