Abstract
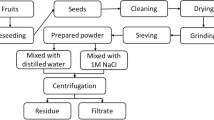
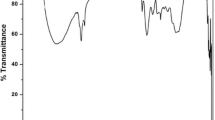
In this study, aqueous extracts of Musa paradisica (banana) peels and Dolichos lablab (Indian beans) seeds were prepared and tested as natural coagulants for turbidity removal from simulated turbid water. Effects of extraction time (15, 30, and 45 min), dosage (0.2 to 1.0 mL/L), and water pH on turbidity removals by the natural coagulants were evaluated. In both cases, the extraction time of 45 min for the preparation of aqueous extract and dosage of 0.6 mL/L gave the best results in terms of turbidity removal. Natural coagulants from M. paradisica peels powder could efficiently remove turbidity (> 83%) at all tested pH values (3.0 to 12.0) with maximum turbidity removal of 98.14% at pH 11. In the case of D. lablab seeds, low turbidity removal (71–74%) was observed at pH between 5.0 and 9.0. The maximum turbidity removal (98.84%) was obtained at pH 11. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis of the settled flocs revealed that more compact flocs formed using M. paradisica peels extract than those developed using D. lablab seeds extract. The chemical analysis and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of the extracts revealed that polymeric substances (carbohydrate and proteins) having functional groups –OH, C–N, C–C, –COOH, and N–H might be responsible for the coagulation activity. The zeta potential measurements of natural coagulants revealed that the possible coagulation mechanism would be adsorption and bridging between particles. This study demonstrated the potential use of aqueous extracts of M. paradisica peels and D. lablab seeds as low-cost natural coagulants for turbidity removal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alwi H, Idris J, Musa M, Hamid KHK (2013) A preliminary study of banana stem juice as a plant-based coagulant for treatment of spent coolant wastewater. J Chemistry 2013:7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/165057
Asrafuzzaman M, Fakhruddin ANM, Alamgir Hossain M (2011) Reduction of turbidity of water using locally available natural coagulants. ISRN Microbiology 2011:6. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/632189
Bondy SC (2016) Low levels of aluminum can lead to behavioral and morphological changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease and age-related neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicology 52:222–229
Bouaouine O, Bourven I, Khalil F, Baudu M (2018) Identification of functional groups of Opuntia ficus-indica involved in coagulation process after its active part extraction. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:11111–11119
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bratby J (2006) Coagulation and flocculation in water and wastewater treatment, 2nd edn. IWA Publishing, London
Carvalho MS, Alves BRR, Silva MF, Bergamasco R, Coral LA, Bassetti FJ (2016) CaCl2 applied to the extraction of Moringa oleifera seeds and the use for Microcystis aeruginosa removal. Chem Eng J 304:469–475
Choy SY, Prasad KMN, Wu TY, Raghunandan ME, Ramanan RN (2014) Utilization of plant-based natural coagulants as future alternatives towards sustainable water clarification. J Environ Sci 26:2178–2189
Choy SY, Prasad KMN, Wu TY, Raghunandan ME, Ramanan RN (2016) Performance of conventional starches as natural coagulants for turbidity removal. Ecol Eng 94:352–364
Deshmukh PD, Khadse GK, Shinde VM, Labhasetwar P (2017) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions using dried banana peels as an adsorbent: kinetics and equilibrium modeling. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 8:395
El-Din GA, Amer AA, Malsh G, Husseina M (2017) Study on the use of banana peels for oil spill removal. Alexandria Eng J 57:2061–2068
Kakoi B, Kaluli JW, Ndiba P, Thiong’o G (2016) Banana pith as a natural coagulant for polluted river water. Ecol Eng 95:699–705
Kamel NA, Abd El-Messieh SL, Saleh NM (2017) Chitosan/banana peel powder nanocomposites for wound dressing application: preparation and characterization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 72:543–550
Kashfi H, Mousavian S, Seyedsalehi M, Sharifi P, Hodaifa G, Seyed Salehi A, Takdastan A (2018) Possibility of utilizing natural coagulants (Trigonella foenum-graecum and Astragalus gossypinus) along with alum for the removal of turbidity. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1635-1
Kukić DV, Šćiban MB, Prodanović JM, Tepić AN, Vasić MA (2015) Extracts of fava bean (Vicia faba L.) seeds as natural coagulants. Ecol Eng 84:229–232
Mallevialle J, Brichet A, Fiessinger F (1984) How safe are organic polymers in water treatment. J Am Water Works Assoc 76:87–93
Maurya S, Daverey A (2018) Evaluation of plant-based natural coagulants for municipal wastewater treatment. 3 Biotech 8(1):77
Memon JR, Memon SQ, Bhanger MI, Memon GZ, El-Turki A, Allen GC (2008) Characterization of banana peel by scanning electron microscopy and FT-IR spectroscopy and its use for cadmium removal. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 66:260–265
Mohamed EH, Mohammad TA, Noor MJMM, Ghazali AH (2015) Influence of extraction and freeze-drying durations on the effectiveness of Moringa oleifera seeds powder as a natural coagulant. Desalin Water Treat 55(13):3628–3634
Muthuraman G, Sasikala S (2014) Removal of turbidity from drinking water using natural coagulants. J Ind Eng Chem 20(4):1727–1731
Ndabigengesere A, Subba Narasiah K, Talbot BG (1995) Active agents and mechanism of coagulation of turbid waters using Moringa oleifera. Water Res 29(2):703–710
Nharingo T, Moyo M (2016) Application of Opuntia ficus-indica in bioremediation of wastewaters. A critical review. J Environ Manag 166:55–72
Parmar KA, Prajapati S, Patel R, Dabhi Y (2011) Effective use of ferrous sulfate and alum as a coagulant in treatment of dairy industry wastewater. J Eng Appl Sci 6(9):42–45
Ramavandi R (2014) Treatment of water turbidity and bacteria by using a coagulant extracted from Plantago ovata. Water Resour Ind 6:36–50
Renault F, Sancey B, Badot P, Crini G (2009) Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation processes-an ecofriendly approach. Eur Polym J 45:1337–1348
Rondeau V, Commenges D, Jacqmin-Gadda H, Dartigues JF (2000) Relation between aluminum concentrations in drinking water and Alzheimer’s disease: an 8-year follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol 152(1):59–66
Šćiban M, KlaŠnja M, Antov M, Škrbić B (2009) Removal of water turbidity by natural coagulants obtained from chestnut and acorn. Bioresour Technol 100:6639–6643
Scott TA, Melvin EH (1953) The determination of dextran with anthrone. Anal Chem 25:1656–1661
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai S-P (2014) A comprehensive study on coagulant performance and floc characterization of natural Cassia obtusifolia seed gum in treatment of raw pulp and paper mill effluent. Ind Crop Prod 61:317–324
Swati M, Govindan VS (2005) Coagulation studies on natural seed extracts. J Indian Water Works Assoc 37(2):145–149
Ugwu SN, Umuokoro AF, Echiegu EA, Ugwuishiwu BO, Enweremadu CC (2017) Comparative study of the use of natural and artificial coagulants for the treatment of sullage (domestic wastewater). Cogent Eng 4:1365676
Walton JR (2013) Aluminum’s involvement in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 35(1):7–43
Yukselen Y, Kaya A (2003) Zeta potential of kaolinite in the presence of alkali, alkaline earth and hydrolyzable metal ions. Water Air Soil Pollut 145:155–168
Zemmouri H, Drouiche M, Sayeh A, Lounici H, Mameri N (2012) Coagulation flocculation test of Keddara’s water dam using chitosan and sulfate aluminum. J Procedia Eng 33:254–260
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Ashis Ranjan Behera for zeta potential analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have followed the accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct. The work did not involve human participants and/or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daverey, A., Tiwari, N. & Dutta, K. Utilization of extracts of Musa paradisica (banana) peels and Dolichos lablab (Indian bean) seeds as low-cost natural coagulants for turbidity removal from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34177–34183 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3850-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3850-9