Abstract
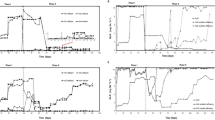
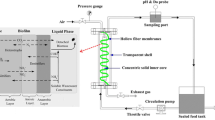
A membrane bioreactor and two hybrid moving bed bioreactor-membrane bioreactors were operated for the treatment of variable salinity wastewater, changing in cycles of 6-h wastewater base salinity and 6-h maximum salinity (4.5 and 8.5 mS cm−1 electric conductivity, which relate to 2.4 and 4.8 g L−1 NaCl, respectively), under different hydraulic retention times (6, 9.5, and 12 h) and total solids concentrations (2500 and 3500 mg L−1). The evaluation of the performance of the systems showed that COD removal performance was unaffected by salinity conditions, while BOD5 and TN removals were significantly higher in the low-salinity scenario. The microbial community structure showed differences with respect to salinity conditions for Eukarya, suggesting their higher sensitivity for salinity with respect to Prokarya, which were similar at both salinity scenarios. Nevertheless, the intra-OTU distribution of consistently represented OTUs of Eukarya and Prokarya was affected by the different salinity maximums. Multivariate redundancy analyses showed that several genera such as Amphiplicatus (0.01–5.90%), Parvibaculum (0.27–1.19%), Thiothrix (0.30–1.19%), Rhodanobacter (2.81–5.85%), Blastocatella (0.21–2.01%), and Nitrobacter (0.80–0.99%) were positively correlated with BOD5 and TN removal, and the ecological roles of these were proposed. All these genera were substantially more represented under low-salinity conditions (10–500% higher relative abundance), demonstrating that they might be of importance for the treatment of variable salinity wastewater. Evaluation of Eukarya OTUs showed that many of them lack a consistent taxonomic classification, which highlights the lack of knowledge of the diversity and ecological role of Eukaryotes in saline wastewater treatment processes. The results obtained will be of interest for future design and operation of salinity wastewater treatment systems particularly because little is known on the effect of variable salinity conditions in wastewater treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2012) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed., American Public Health Association, Washington DC.
Bassin JP, Kleerebezem R, Muyzer G, Rosado AS, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Dezotti M (2012) Effect of different salt adaptation strategies on the microbial diversity, activity, and settling of nitrifying sludge in sequencing batch reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1281–1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3428-7
Bian G, Gloor GB, Gong A, Jia C, Zhang W, Hu J, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Burton JP, Reid G, Xiao Y, Zeng Q, Yang K, Li J (2017) The gut microbiota of healthy aged Chinese is similar to that of the healthy young. mSphere 2:e00327–e00317. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00327-17
Castillo-Carvajal LC, Sanz-Martin JL, Barragan-Huerta BE (2014) Biodegradation of organic pollutants in saline wastewater by halophilic microorganisms: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9578–9588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3036-z
Cortes-Lorenzo C, Rodriguez-Diaz M, Lopez-Lopez C, Sanchez-Peinado M, Rodelas B, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2012) Effect of salinity on enzymatic activities in a submerged fixed bed biofilm reactor for municipal sewage treatment. Bioresour Technol 121:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.083
Cortés-Lorenzo C, González-Martínez A, Smidt H, González-López J, Rodelas B (2016) Influence of salinity on fungal communities in a submerged fixed bed bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 285:562–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.009
Di Trapani D, Di Bella G, Mannina G, Torregrossa M, Viviani G (2014) Comparison between moving bed-membrane bioreactor (MB-MBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems: influence of wastewater salinity variation. Bioresour Technol 162:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.126
Di Bella G, Di Prima N, Di Trapani D, Freni G, Giustra MG, Torregrossa M, Viviane G (2015) Performance of membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems for the treatment of shipboard slops: assessment of hydrocarbon biodegradation and biomass activity under salinity variation, J. Hazard. Mater. 300:765–778.
Eren AM, Borisy GG, Huse SM, Mark Welch JL (2014) PNAS plus: from the cover: oligotyping analysis of the human oral microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:E2875–E2884. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1409644111
Esmaeli A, Jokar M, Kousha M, Daneshvar E, Zilouei H (2013) Acidic dye wastewater treatment onto a marine macroalga, Nizamuddina zanardini (phylum: Ochrophyta). Chem Eng J 217:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.038
Gonzalez-Martinez A, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Lotti T, Garcia-Ruiz MJ, Osorio F, Gonzalez-Lopez J, van Loosdrecht MC (2016a) Comparison of bacterial communities of conventional and A-stage activated sludge systems. Sci Rep 6:18786. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18786
Gonzalez-Martinez A, Garcia-Ruiz MJ, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Osorio F, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2016b) Archaeal and bacterial community dynamics and bioprocess performance of a bench-scale two-stage anaerobic digester. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6013–6033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7393-z
Hao TW, Xiang P-Y, Mackey HR, Chi K, Lu H, Chui H-K, van Loosdrecht MCM, Chen G-H (2014) A review of biological sulfate conversions in wastewater treatment. Water Res 65:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.043
Kämpfer P, Schulze R, Jäckel U, Malik KA, Amann R, Spring S (2005) Hydrogenophaga defluvii sp. nov. and Hydrogenophaga atypica sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:341–344. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.03041-0
Kindaichi T, Yamaoka S, Uehara R, Ozaki N, Ohashi A, Albertsen M, Nielsen PH, Nielsen JL (2016) Phylogenetic diversity and ecophysiology of candidate phylum Saccharibacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw078
Lee S, Song EH, Lee T (2018) Eukaryotic plankton species diversity in the Western Channel of the Korea Strait using 18S rDNA sequences and its implications for water masses. Ocean Science Journal 153:119–132
Leyva-Díaz JC, Calderón K, Rodríguez FA, González-lópez J (2013) Comparative kinetic study between moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor and membrane bioreactor systems and their influence on organic matter and nutrients removal. Biochem Eng J 77:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.04.023
Leyva-Díaz JC, Martín-Pascual J, Muñío MM, González-López J, Hontoria E, Poyatos JM (2014) Comparative kinetics of hybrid and pure moving bed reactor-membrane bioreactors. Ecol Eng 70:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.05.017
Leyva-Diaz JC, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Muñio MM, Poyatos JM (2015a) Kinetic modeling and microbiological study of two-step nitrification in a membrane bioreactor and hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor–membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 259:692–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.136
Leyva-Diaz JC, Lopez-Lopez C, Martin-Pascual J, Muñio MM, Poyatos JM (2015b) Kinetic study of the combined processes of a membrane bioreactor and a hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor with advanced oxidation processes as a post-treatment stage for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 91:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.03.017
Leyva-Diaz JC, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Calderon K, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Muñio MM, Poyatos JM (2016) Microbial kinetics and enzymatic activities in hybrid moving-bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor systems. Chem Eng Technol 39:1067–1076. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201400750
Li E, Lu S (2017) Denitrification processes and microbial communities in a sequencing batch reactor treating nanofiltration (NF) concentrate from coking wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 76:11-12. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.493
McIlroy SJ, Kirkegaard RH, Mcilroy B, Nierychlo M, Kristensen JM, Karst SM (2017) MiDAS 2.0: an ecosystem-specific taxonomy and online database for the organisms of wastewater treatment systems expanded for anaerobic digester groups. Database (Oxford):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bax016
Niu W, Guo J, Lian J, Hao H, Li H, Song Y, Li H, Yin P (2018) Effect of fluctuating hydraulic retention time (HRT) on denitrification in the UASB reactors. Biochem Eng J 132:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.12.017
Okazaki Y, Fujinaga S, Tanaka A, Kohzu A, Oyagi H (2017) Ubiquity and quantitative significance of bacterioplankton lineages inhabiting the oxygenated hypolimnion of deep freshwater lakes. Nat Publ Gr 11:2279–2293. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.89
Ouyang E, Liu Y, Ouyang J, Wang X (2017) Effects of different wastewater characteristics and treatment techniques on the bacterial community structure in three pharmaceutical wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Technol. 1:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1393010
Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Leyva-Diaz JC, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Poyatos JM (2017) Linkage of microbial kinetics and bacterial community structure of MBR and hybrid MBBR-MBR systems to treat salinity-amended urban wastewater. Biotechnol Prog 33:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2513
Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Leyva-Diaz JC, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Poyatos JM (2018a) Membrane bioreactor and hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor for the treatment of variable salinity wastewater: influence of biomass concentration and hydraulic retention time. Chem Eng J 336:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.118
Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Leyva-Diaz JC, Poyatos JM, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2018b) Influent salinity conditions affect the bacterial communities of biofouling in hybrid MBBR-MBR systems. J Water Proc Engineer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.07.001
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2584
Schloss PD (2016) Application of a database-independent approach to assess the quality of. mSystems 1:2–5. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00027-16.Copyright
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Schoenle A, Nitsche F, Werner J, Arndt H (2017) Deep-sea ciliates: recorded diversity and experimental studies on pressure tolerance. Deep Sea Res I 128:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2017.08.015
Tao R, Kinnunen V, Praveenkumar R, Lakaniemi A (2017).Comparison of Scenedesmus acuminatus and Chlorella vulgaris cultivation in liquid digestates from anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper industry and municipal wastewater treatment sludge. 2845–2856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1175-6
Teske A, Salman V (2014) The family Leucotrichaceae. The Prokaryotes. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Unno T (2015) Bioinformatic suggestions on MiSeq-based microbial community analysis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:765–770
Welles L, Lopez-Vazquez CM, Hooijmans CM, van Loosdrecht MCM, Brdjanovic D (2015) Impact of salinity on the aerobic metabolism of phosphate-accumulating organisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3659–3672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6287-1
Westcott SL, Schloss PD (2015) De novo clustering methods outperform reference-based methods for assigning 16S rRNA gene sequences to operational taxonomic units. PeerJ 3:e1487. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1487
Wu Y-J, Whang L-M, Fukushima T, Chang S-H (2013) Responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaeal and betaproteobacterial populations to wastewater salinity in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant. J Biosci Bioeng 115:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.11.005
Yabuki A, Ishida K (2018) An orphan protist Quadricilia rotundata finally finds its phylogenetic home in Cercozoa. J Eukaryot Microbiol 65:729–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12502
Zhang B, Xu X, Zhu L (2017) Structure and function of the microbial consortia of activated sludge in typical municipal wastewater treatment plants in winter. Sci Rep 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17743-x
Zhen-Li Z, Xin-Qi Z, Nan W, Wen-Wu Z, Xu-Fen Z, Yi C, Min W (2018) Amphiplicatus metriothermophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermotolerant alphaproteobacterium isolated from a hot spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2805–2811. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.062471-0
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the support given by the Institute of Water Research and the Department of Civil Engineering in the University of Granada. Also, they would like to acknowledge the economic support given by the Ministry of Economy and Competitivity of the Government of Spain, which funded this project by the funding CTM2013-48154-P and grant BES-2014-067852.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 7442 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Sanchez, A., Leyva-Diaz, J.C., Muñoz-Palazon, B. et al. Influence of salinity cycles in bioreactor performance and microbial community structure of membrane-based tidal-like variable salinity wastewater treatment systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 514–527 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3608-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3608-4