Abstract
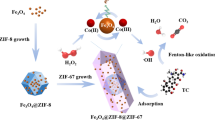
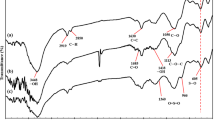
In this work, a novel magnetic carbon nanotube@zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (MCNT@ZIF-67) composite was prepared facilely by a one-pot method using Fe3O4@SiO2 as the magnetic element, CNTs as the carbon matrix, and 2-methylimidazole (2-MIM) and cobaltous nitrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O) as the organic and inorganic elements, respectively. The obtained MCNT@ZIF-67 composite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). Static adsorption experiments demonstrated that the maximum adsorption capacity of MCNTs@ZIF-67 for tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is 83.23 mg g−1, and the sorption isotherm was fitted well by the Freundlich adsorption model. Dynamic adsorption experiments illustrated that the adsorption of TBBPA on MCNTs@ZIF-67 can reach equilibrium in 20 min, and the adsorption kinetics of TBBPA were fitted well by a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption of TBBPA on MCNTs@ZIF-67 showed favorable selectivity. The pH and the NaCl and NH4Cl common salts did not affect the TBBPA adsorption. Then, the proposed magnetic composite was applied as the adsorbent for the rapid removal of TBBPA in water samples, and the removal ratio of MCNTs@ZIF-67 for TBBPA in different spiked water samples with different volumes was above 95% with RSD < 5%. Furthermore, as a new removal sorbent, the removal reproducibility of MCNTs@ZIF-67 for TBBPA was favorable and stable, with only a 6.0% decrease after 6 cycles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catherine HN, Ou MH, Manu B, Shih YH (2018) Adsorption mechanism of emerging and conventional phenolic compounds on graphene oxide nanoflakes in water. Sci Total Environ 635:629–638
Dai Y, Zhang K, Li J, Jiang Y, Chen Y, Tanaka S (2017) Adsorption of copper and zinc onto carbon material in an aqueous solution oxidized by ammonium peroxydisulphate. Sep Purif Technol 186:255–263
Dam ten G, Pardo O, Traag W, Van der Lee M, Peters R (2012) Simultaneous extraction and determination of HBCD isomers and TBBPA by ASE and LC-MSMS in fish. J Chromatogr B 898:101–110
De RM, Majewski PJ, Scales N, Luca V (2013) Hydrolytic stability of mesoporous zirconium titanate frameworks containing coordinating organic functionalities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4120–4128
Du XD, Wang CC, Liu JG, Zhao XD, Zhong J, Li YX, Li J, Wang P (2017) Extensive and selective adsorption of ZIF-67 towards organic dyes: performance and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 506:437–441
Fasfous II, Radwan ES, Dawoud JN (2010) Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics of the sorption of tetrabromobisphenol A on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Appl Surf Sci 256:7246–7252
Han T, Xiao Y, Tong M, Huang H, Liu D, Wang L, Zhong C (2015) Synthesis of CNT@MIL-68(Al) composites with improved adsorption capacity for phenol in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 275:134–141
Hasan Z, Jhung SH (2015) Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J Hazard Mater 283:329–339
Ji L, Zhou L, Bai X, Shao Y, Zhao G, Qu Y, Wang C, Li Y (2012) Facile synthesis of multiwall carbon nanotubes/iron oxides for removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and Pb(II). J Mater Chem 22:15853–15862
Jugan ML, Levi Y, Blondeau JP (2010) Endocrine disruptors and thyroid hormone physiology. Biochem Pharmacol 79:939–947
Katsumata H, Kawabe S, Kaneco S, Suzuki T, Ohta K (2004) Degradation of bisphenol A in water by the photo-Fenton reaction. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 162:297–305
Kim UJ, Oh JE (2014) Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane flame retardants in infant–mother paired serum samples, and their relationships with thyroid hormones and environmental factors. Environ Pollut 184:193–200 [10]
Lankova D, Lacina O, Pulkrabova J, Hajslova J (2013) The determination of perfluoroalkyl substances, brominated flame retardants and their metabolites in human breast milk and infant formula. Talanta 117:318–325
Li Y, Huo X, Xu X (2007) Toxic effects of brominated flame retardants on human and mammals. J Environ Health 24:119–121
Li L, Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang W (2009) Hemimicelle capped functionalized carbon nanotubes-based nanosized solid-phase extraction of arsenic from environmental water samples. Anal Chim Acta 631:182–188
Li G, Xiong J, Wong PK, An T (2016a) Enhancing tetrabromobisphenol A biodegradation in river sediment microcosms and understanding the corresponding microbial community. Environ Pollut 208:796–802
Li X, Zhang Y, Jing L, He X (2016b) Novel N-doped CNTs stabilized Cu2O nanoparticles as adsorbent for enhancing removal of malachite green and tetrabromobisphenol A. Chem Eng J 292:326–339
Liang L, Ju L, Hu J, Zhang W, Wang X (2016) Transport of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS)-dispersed carbon nanotubes and enhanced mobility of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in saturated porous media. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 497:205–213
Lin KYA, Chang HA (2015a) Ultra-high adsorption capacity of zeolitic imidazole framework-67 (ZIF-67) for removal of malachite green from water. Chemosphere 139:624–631
Lin KYA, Chang HA (2015b) Zeolitic imidazole framework-67 (ZIF-67) as a heterogeneous catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate for degradation of rhodamine B in water. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 53:40–45
Lin K, Ding J, Huang X (2012) Debromination of tetrabromobisphenol A by nanoscale zerovalent iron: kinetics, influencing factors, and pathways. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:8378–8385
Liu GB, Dai L, Gao X, Li MK, Thiemann T (2006) Reductive degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in aqueous medium. Green Chem 8:781–783
Liu K, Li J, Yan S, Zhang W, Li Y, Han D (2016) A review of status of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in China. Chemosphere 148:8–20
Liu L, Liu A, Zhang Q, Shi J, He B, Yun Z, Jiang G (2017) Determination of tetrabromobisphenol-A/S and their main derivatives in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1497:81–86
Luebke R, Belmabkhout Y, Weseliński ŁJ, Cairns AJ, Alkordi M, Norton G, Wojtas Ł, Adil K, Eddaoudi M (2015) Versatile rare earth hexanuclear clusters for the design and synthesis of highly-connected ftw-MOFs. Chem Sci 6:4095–4102
Malarvannan G, Isobe T, Covaci A, Prudente M, Tanabe S (2013) Accumulation of brominated flame retardants and polychlorinated biphenyls in human breast milk and scalp hair from the Philippines: levels, distribution and profiles. Sci Total Environ 442:366–379
McAvoy DC, Pittinger CA, Willis AM (2016) Biotransformation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in anaerobic digester sludge, soils, and freshwater sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 131:143–150
Nijem N, Canepa P, Kaipa U, Tan K, Roodenko K, Tekarli S, Halbert J, Oswald IW, Arvapally RK, Yang C (2013) Water cluster confinement and methane adsorption in the hydrophobic cavities of a fluorinated metal-organic framework. J Am Chem Soc 135:12615–12626
Qu R, Feng M, Wang X, Huang Q, Lu J, Wang L, Wang Z (2015) Rapid removal of tetrabromobisphenol A by ozonation in water: oxidation products, reaction pathways and toxicity assessment. PLoS One 10:e0139580
Qu G, Liu A, Hu L, Liu S, Shi J, Jiang G (2016) Recent advances in the analysis of TBBPA/TBBPS, TBBPA/TBBPS derivatives and their transformation products. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 83:14–24
Sun Z, Yu Y, Mao L, Feng Z, Yu H (2008) Sorption behavior of tetrabromobisphenol A in two soils with different characteristics. J Hazard Mater 160:456–461
Vander der ven LT, Van de Kuil T, Verhoef A, Verwer CM, Lilienthal H, Leonards PE, Schauer UM, Canton RF, Litens S, De Jong FH et al (2008) Endocrine effects of tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBPA) in Wistar rats as tested in a one-generation reproduction study and a subacute toxicity study. Toxicology 245:76–89
Wang X, Liu J, Liu Q, Du X, Jiang G (2013) Rapid determination of tetrabromobisphenol A and its main derivatives in aqueous samples by ultrasound-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 116:906–911
Yang B, Ying GG, Chen ZF, Zhao JL, Peng FQ, Chen XW (2014a) Ferrate (VI) oxidation of tetrabromobisphenol A in comparison with bisphenol A. Water Res 62:211–219
Yang J, Li JY, Qiao JQ, Cui SH, Lian HZ, Chen HY (2014b) Magnetic solid phase extraction of brominated flame retardants and pentachlorophenol from environmental waters with carbon doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 321:126–135
Yang Q, Ren SS, Zhao Q, Lu R, Cheng H, Chen Z, Zheng H (2018) Selective separation of methyl orange from water using magnetic ZIF-67 composites. Chem Eng J 333:49–57
Yin Y, Chen Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Liu H, Xie M (2012) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers on silica particles for selective solid-phase extraction of tetrabromobisphenol A from water samples. J Chromatogr A 1220:7–13
Zhang Y, Tang Y, Li S, Yu S (2013) Sorption and removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from solution by graphene oxide. Chem Eng J 222:94–100
Zhang Y, Jing LY, He XH, Li YF, Ma X (2015) Sorption enhancement of TBBPA from water by fly ash-supported nanostructured g-MnO2. J Ind Eng Chem 21:610–619
Zhang WW, Chen JF, Hu YY, Fang Z, Chen JH, Chen YC (2018) Adsorption characteristics of tetrabromobisphenol A onto sodium bisulfate reduced graphene oxide aerogels. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 538:781–788
Zhou L, Ji L, Ma PC, Shao Y, He Z, Gao W, Li Y (2014a) Development of carbon nanotubes/CoFe2O4 magnetic hybrid material for removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and Pb(II). J Hazard Mater 265:104–114
Zhou L, He Z, Ji L, Shao Y, Li Y (2014b) Fe3O4/MWCNT as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst: degradation pathways of tetrabromobisphenol A. RSC Adv 4:24900–24908
Zhou X, Huang W, Shi J, Zhao Z, Xia Q, Li Y, Wang H, Li Z (2014c) A novel MOF/graphene oxide composite GrO@MIL-101 with high adsorption capacity for acetone. J Mater Chem A 2:4722–4730
Zhou YS, He Z, Tao Y, Xiao Y, Zhou TT, Jing T, Zhou YK, Mei SR (2016) Preparation of a functional silica membrane coated on Fe3O4 nanoparticle for rapid and selective removal of perfluorinated compounds from surface water sample. Chem Eng J 303:156–166
Zou G, Xiong K, Jiang C, Li H, Li T, Du J, Qian Y (2005) Fe3O4 nanocrystals with novel fractal. J Phys Chem B 109:18356–18360
Acknowledgements
We appreciated the Analytical and Testing Center of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for analyzing the TEM, FT-IR, VSM, and XRD spectra.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21577043) and the National Basic Research Grant (973) of China (Grant No. 2015CB352100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2914 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, T., Tao, Y., Xu, Y. et al. Facile preparation of magnetic carbon nanotubes@ZIF-67 for rapid removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from water sample. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 35602–35613 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3239-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3239-9