Abstract
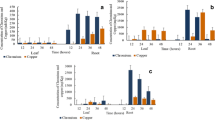
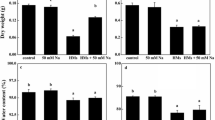
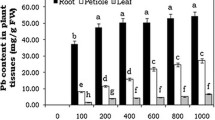
Eichhornia crassipes is a macrophyte widely used in phytoremediation, demonstrating a high ability to remove metals from water. The aim of this work was to evaluate its enzymatic detoxification strategies and metal accumulation when it is exposed to different Zn concentrations (0, 2, 4, 6, and 9 ppm) for periods of 24, 48, and 72 h. Zn concentration in roots was significantly higher than in aerial parts. Independently of the treatment, in the first 48 h, concentrations of photosynthetic pigments were not affected. However, a significant increase (between 19 and 34%) in Chl-b concentrations for all treatments was observed at 72 h. Carotenoid concentration was not affected during the first 48 h, while at 72 h, there was a significant increase regarding the control (between 11 and 24%) for all treatments. Malondialdehyde concentration in aerial parts and roots was not affected during the experiment. Nonetheless, a significant increase in the enzymatic activity of the antioxidant system was observed. Results suggest that Zn could have potential antioxidant properties, which may result in the activation of different antioxidant enzymes involved in the protection against metal stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2003) Zinc alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum L.: a free floating freshwater macrophyte. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:391–397
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2004) Zinc protects chloroplasts and associated photochemical functions in cadmium exposed Ceratophyllum demersum L.: a freshwater macrophyte. Plant Sci 166:1321–1327
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2005) Cadmium-zinc interactions in a hydroponic system using Ceratophyllum demersum L.: adaptive ecophysiology, biochemistry and molecular toxicology. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:3–20
Aravind P, Prasad MNV, Malec P, Waloszek A, Strzalka K (2009) Zinc protects Ceratophyllum demersum L. (free-floating hydrophyte) against reactive oxygen species induced by cadmium. J Trace Elem Med Biol 23:50–60
Arenas-Lago D, Carvalho LC, Santos ES, Abreu MM (2016) The physiological mechanisms underlying the ability of Cistus monspeliensis L. from São Domingos mine to withstand high Zn concentrations in soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 129:219–227
Artetxe U, García-Plazaola JI, Hernández A, Becerril JM (2002) Low light grown duckweed plants are more protected against the toxicity induced by Zn and cd. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:859–863
Baker AJM, Brooks RR (1989) Terrestrial higher plants which hyper accumulate metallic elements: a review of their distribution. Ecology and Phytochemistry Biorecovery 1:81–126
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytol 173:677–702
Cambrollé J, Mancilla-Leytón JM, Muñoz-Vallés S, Luque T, Figueroa ME (2012) Zinc tolerance and accumulation in the salt-marsh shrub Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere 86:867–874
Cakmak I (2000) Possible role of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 146:185–205
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1988) Zinc-dependent changes in ESR signals, NADPH oxidase and plasma membrane permeability in cotton roots. Physiol Plant 73:182–186
Cherif J, Mediouni C, Ben Ammar W, Jemal F (2011) Interactions of zinc and cadmium toxicity in their effects on growth and in antioxidative systems in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum). J Environ Sci 23:837–844
Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (2001) The redox status of plant cells (AsA and GSH) is sensitive to zinc imposed oxidative stress in root and primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:657–664
Deng H, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2004) Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ Pollut 132:29–40
González CI, Maine MA, Cazenave J, Sanchez GC, Benavides MP (2015a) Physiological and biochemical responses of Eichhornia crassipes exposed to Cr(III). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3739–3747
González CI, Maine MA, Cazenave J, Hadad HR, Benavides MP (2015b) Ni accumulation and its effects on physiological and biochemical parameters of Eichhornia crassipes. Environ Exp Bot 117:20–27
Hadad HR, Maine MA, Pinciroli M (2009) Nickel and phosphorous sorption efficiencies, tissue accumulation kinetics and morphological effects on Eichhornia crassipes. Ecotoxicology 18:504–513
Hadad HR, Maine MA, Mufarrege MM, Del Sastre MV, Di Luca GA (2011) Bioaccumulation kinetics and toxic effects of Cr, Ni and Zn on Eichhornia crassipes. J Hazard Mat 190:1016–1022
Hasan SH, Talat M, Rai S (2007) Sorption of cadmium and zinc from aqueous solutions by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Bioresour Technol 98:918–928
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation Archiv Biochem Biophysics 125:189–198
Hewitt EJ (1983) A perspective of mineral nutrition: essential and functional metals in plants. In: Robb DA, Pierpoint WS (eds) Metals and micronutrients: uptake and utilization by plants. Academic Press, London, pp 277–323
Hodges DM, De Long JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Hou W, Chen X, Song G, Wang Q, Chang C (2007) Effects of copper and cadmium on heavy metal polluted waterbody restoration by duckweed (Lemna minor). Plant Physiol Biochem 45:62–69
Hu Z, Wenjiao Z (2015) Effects of zinc stress on growth and antioxidant enzyme responses of Kandelia obovate seedlings. Toxicol Environ Chem 97:1190–1201
Li Y, Zhang Y, Shi D, Liu X, Qin J, Ge Q, Xu L, Pan X, Li W, Zhu Y, Xu J (2013) Spatial-temporal analysis of zinc homeostasis reveals the response mechanisms to acute zinc deficiency in Sorghum bicolor. New Phytol 200:1102–1115
Madhava Rao KV, Sresty TVS (2000) Antioxidative parameters in the seedlings of pigeon-pea (Cajanus cajan (L) Millspaugh) in response to Zn and Ni stresses. Plant Sci 157:113–128
Maine MA, Suñé N, Hadad RH, Sánchez GC, Bonetto C (2009) Influence of vegetation on the removal of heavy metals and nutrients in a constructed wetland. J Environ Manag 90:355–363
Miretzky P, Saralegui A, Cirelli AF (2004) Aquatic macrophytes potential for the simultaneous removal of heavy metals (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Chemosphere 57:997–1005
Mishra VK, Tripathi BD (2009) Accumulation of chromium and zinc from aqueous solutions using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). J Hazard Mater 164:1059–1063
Módenes AN, Espinoza-Quiñones FR, Lavarda FL, Colombo A, Borba CE, Leichtweis WA, Mora ND (2013) Removal of heavy metals cd(II), cu(II) and Zn(II) biosorption process by using the macrophyte Eichhornia crassipes. Rev Esc Minas 66:355–362
Peng D, Shafi M, Wang Y, Li S, Yan W, Chen J, Ye Z, Liu D (2015) Effect of Zn stresses on physiology, growth, Zn accumulation and chlorophyll of Phyllostachys pubescens. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:14983–14992
Prasad KVSK, Paradha Saradhi P, Sharmila P (1999) Concerted action of antioxidant enzymes and curtailed growth under zinc toxicity in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot 42:1–10
Radić S, Babić M, Skobić D, Roje V, Pevalek-Kozlina B (2010) Ecotoxicological effects of aluminum and zinc on growth and antioxidants in Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:336–342
Shier WT (1994) Metals as toxins in plants. J Toxicol - Toxin Rev 13:205–216
Srivastava S, Shrivastava M (2016) Zinc supplementation imparts tolerance to arsenite stress in Hydrilla verticillata (Lf) Royle. Int J Phytorem doi:101080/1522651420161225288
Szalontai B, Horváth LI, Debreczeny M, Droppa M, Horváth G (1999) Molecular rearrangements of thylakoids after heavy metal poisoning, as seen by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. Photosynth Res 6:241–252
Tewari RK, Kumar P, Sharma PN (2008) Morphology and physiology of zinc-stressed mulberry plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171:286–294
Tkalec M, Štefanić PP, Cvjetko P, Šikić S, Pavlica M, Balen B (2014) The effects of cadmium-zinc interactions on biochemical responses in tobacco seedlings and adult plants. PLoS One 9:1–13
Tripathi BN, Gaur JP (2004) Relationship between copper- and zinc-induced oxidative stress and proline accumulation in Scenedesmus spp. Planta 219:397–404
Tripathi BN, Mehta SK, Amar A, Gaur JP (2006) Oxidative stress in Scenedesmus sp during short- and long-term exposure to Cu2+ and Zn2+. Chemosphere 62:538–544
Turner RG, Marshall C (1972) The accumulation of zinc by subcellular fractions of roots of Agrostis tenuis Sibth in relation to zinc tolerance. New Phytol 71:671–676
USEPA (1994) Method 2002: sample preparation procedure for spectrochemical determination of total recoverable elements rev 28 United States Environmental Protection Agency. USA, Washington DC
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1986) Inhibition of photosynthesis in Phaseolus vulgaris by treatment with toxic concentration of Zn: effects on electron transport and photophosphorylation. Physiol Plant 66:717–721
Wainwright SJ, Woolhouse HW (1977) Some physiological aspects of copper and zinc tolerance in Agrostis tenuis Sibth: cell elongation and membrane damage. J Exp Bot 28:1029–1036
Wang C, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Qian J, Hou J, Zhang WJ, Lu J (2009) Excess Zn alters the nutrient uptake and induces the antioxidative responses in submerged plant Hydrilla verticillata (lf) Royle. Chemosphere 76:938–945
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 14:307–313
Xu Q, Chu W, Qiu H, Fu Y, Cai S, Sha S (2013) Responses of Hydrilla verticillata (lf) Royle to zinc: in situ localization, subcellular distribution and physiological and ultrastructural modifications. Plant Physiol Biochem 69:43–48
Yapoga S, Ossey YO, Kouamé V (2013) Phytoremediation of zinc, cadmium, copper and chrome from industrial wastewater by Eichhornia crassipes. Int J Conserv Sci 4:81–86
Yuan QH, Shi GX, Zhao J, Zhang H, Xu QS (2009) Physiological and proteomic analyses of Alternanthera philoxeroides under zinc stress. Russian J Plant Physiol 56:495–502
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this research was provided by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Universidad Nacional del Litoral (UNL)-Project CAI + D and Agencia de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, C.I., Maine, M.A., Hadad, H.R. et al. Effects on Eichhornia crassipes under Zn stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 26957–26964 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2741-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2741-4