Abstract
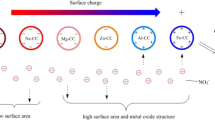
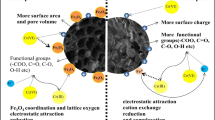
In this study, modified biochar was adopted as an adsorbent for the nitrate removal in aqueous solutions. Raw material was impregnated in sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 1 mol/L) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 2 mol/L) separately and then prepared at 600 °C. After treated with acid, the BET specific surface area was much higher than that of unmodified and alkali-modified biochars. The low adsorption capacity and specific surface area of alkali-modified biochar may be due to the precipitate on the surface according to the results of XRD. In addition, the C–OH and C–H functional groups played a major part during adsorption progress. The batch experiments demonstrated that the acid-modified biochar exhibited a more excellent absorbability (12.75 mg/g) under the circumstance of neutral solution and room temperature. The maximum adsorption capacity of MSA-CC was 34.20 mg/g, which was about 2.4 times higher than that of the unmodified. Low pH value can provide positive charge conditions to enhance the adsorption capacity. Overall, the biochar with excellent pore structure and chargeable functional group can be a potential application for nitrate removal which was low cost and effective. After treated with acid, biochar could adsorb negative charge species like nitrate due to electrostatic interaction.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin AA, Eissa MA (2017) Biochar effects on nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies of zucchini plants grown in a calcareous sandy. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 17:912–921
Baadhe RR, Potumarthi R, Mekala NK (2014) Influence of dilute acid and alkali pretreatment on reducing sugar production from corncobs by crude enzymatic method: a comparative study. Bioresour Technol 162:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.117
Bogusz A, Nowak K, Stefaniuk M, Dobrowolski R, Oleszczuk P (2017) Synthesis of biochar from residues after biogas production with respect to cadmium and nickel removal from wastewater. J Environ Manag 201:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.019
Çengeloğlu Y, Kır E, Ersöz M (2006) Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using red mud. Sep Purif Technol 51:374–378
Chatterjee S, Woo SH (2009) The removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions by chitosan hydrogel beads. J Hazard Mater 164:1012–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.001
Chen L, Wang XH, Yang HP, Lu Q, Li D, Yang Q, Chen HP (2015) Study on pyrolysis behaviors of non-woody lignins with TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. J Anal Appl Pyrol 113:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2015.03.018
Creamer AE, Gao B, Wang SS (2016) Carbon dioxide capture using various metal oxyhydroxide-biochar composites. Chem Eng J 283:826–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.037
Gao F, Xue YW, Deng PY, Cheng XR, Yang K (2015) Removal of aqueous ammonium by biochars derived from agricultural residuals at different pyrolysis temperatures. Chem Spec Bioavailab 27:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/09542299.2015.1087162
Gomez-Solís C, Ballesteros JC, Torres-Martínez LM, Juárez-Ramírez I, Torres LAD, Zarazua-Morin ME, Lee SW (2015) Rapid synthesis of ZnO nano-corncobs from Nital solution and its application in the photodegradation of methyl orange. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 298:49–54
Hafshejani LD, Hooshmand A, Naseri AA, Mohammadi AS, Abbasi F, Bhatnagar A (2016) Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by modified sugarcane bagasse biochar. Ecol Eng 95:101–111
Ho YS, Porter JF, Mckay G (2002) Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 141:1–33
Inyang M, Gao B, Pullammanappallil P, Ding W, Zimmerman AR (2010) Biochar from anaerobically digested sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour Technol 101:8868–8872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.088
Keränen A, Leiviskä T, Hormi O, Tanskanen J (2015) Removal of nitrate by modified pine sawdust: effects of temperature and co-existing anions. J Environ Manag 147:46–54
Li RH, Wang JJ, Zhou B, Awasthi MK, Ali A, Zhang Z, Gaston LA, Lahori AH, Mahar A (2016) Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci Total Environ 559:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.151
Liang YT, Pei M, Wang DD, Cao SN, Xiao X, Sun B (2017) Improvement of soil ecosystem multifunctionality by dissipating manure-induced antibiotics and resistance genes. Environ Sci Technol 51:4988–4998. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00693
Liu Z, Xue Y, Gao F, Cheng X, Yang K (2016) Removal of ammonium from aqueous solutions using alkali-modified biochars. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 28:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/09542299.2016.1142833
Long L, Xue YW, Zeng YF, Yang K, Lin CJ (2017) Synthesis, characterization and mechanism analysis of modified crayfish shell biochar possessed ZnO nanoparticles to remove trichloroacetic acid. J Clean Prod 166:1244–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.122
Mishra PC, Patel RK (2009) Use of agricultural waste for the removal of nitrate-nitrogen from aqueous medium. J Environ Manag 90:519–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.12.003
Mohan D, Sarswat A, Ok YS, Pittman CU (2014) Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—a critical review. Bioresour Technol 160:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.120
Sahin O, Taskin MB, Kaya EC, Atakol O, Emir E, Inal A, Gunes A (2017) Effect of acid modification of biochar on nutrient availability and maize growth in a calcareous soil. Soil Use Manag 33:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12360
Sika MP, Hardie AG (2014) Effect of pine wood biochar on ammonium nitrate leaching and availability in a South African sandy soil. Eur J Soil Sci 65:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12082
Sun SN, Li MF, Yuan TQ, Xu F, Sun RC (2012) Effect of ionic liquid pretreatment on the structure of hemicelluloses from corncob. J Agric Food Chem 60:11120–11127. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3021464
Ventura GD, Bellatreccia F, Cámara F, Oberti R (2014) Crystal-chemistry and short-range order of fluoro-edenite and fluoro-pargasite: a combined x-ray diffraction and ftir spectroscopic approach. Mineral Mag 78:293–310
Wang C, Lyu GJ, Yang GH, Chen JC, Jiang WK (2014) Characterization and hydrothermal conversion of lignin produced from corncob acid hydrolysis residue. Bioresources 9:4596–4607
Wang HY, Gao B, Wang SS, Fang J, Xue YW, Yang K (2015) Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour Technol 197:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.132
Xu Y, Liu Y, Liu S, Tan X, Zeng G, Zeng W, Ding Y, Cao W, Zheng B (2016) Enhanced adsorption of methylene blue by citric acid modification of biochar derived from water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:23606–23618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7572-6
Yang HP, Yan R, Chen HP, Lee DH, Zheng CG (2007) Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013
Yang Z, Zhang L, Xu P, Zhang X, Niu X, Zhou S (2015) The adsorption of nitrate from aqueous solution onto calcined Mg/Fe hydrotalcite. Desalin Water Treat 54:3400–3411
Yang Q, Yao F, Zhong Y, Wang D, Chen F, Sun J, Hua S, Li S, Li X, Zeng G (2016) Catalytic and electrocatalytic reduction of perchlorate in water—a review. Chem Eng J 306:1081–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.041
Yang J, Li H, Zhang D, Wu M, Pan B (2017) Limited role of biochars in nitrogen fixation through nitrate adsorption. Sci Total Environ 592:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.182
Yao Y, Gao B, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao XD, Pullammanappallil P, Yang LY (2011a) Biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings: characterization and phosphate removal potential. Bioresour Technol 102:6273–6278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.006
Yao Y, Gao B, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao XD, Pullammanappallil P, Yang LY (2011b) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings. J Hazard Mater 190:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.083
Yao Y, Gao B, Chen H, Jiang L, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao X, Yang L, Xue Y, Li H (2012a) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on biochar and its impact on reclaimed water irrigation. J Hazard Mater 209:408–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.046
Yao Y, Gao B, Zhang M, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR (2012b) Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium, and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 89:1467–1471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.06.002
Yuan JH, Xu RK, Zhang H (2011) The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresour Technol 102:3488–3497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.11.018
Zhang JS, Wang QQ (2016) Sustainable mechanisms of biochar derived from brewers’ spent grain and sewage sludge for ammonia-nitrogen capture. J Clean Prod 112:3927–3934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.096
Zhang P, Ren C, Sun HW, Min LJ (2018) Sorption, desorption and degradation of neonicotinoids in four agricultural soils and their effects on soil microorganisms. Sci Total Environ 615:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.097
Zhao L, Zheng W, Masek O, Chen X, Gu BW, Sharma BK, Cao XD (2017) Roles of phosphoric acid in biochar formation: synchronously improving carbon retention and sorption capacity. J Environ Qual 46:393–401. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2016.09.0344
Zhao HH, Xue YW, Long L, Hu XL (2018) Adsorption of nitrate onto biochar derived from agricultural residuals. Water Sci Technol 77:548–554. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.568
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their invaluable insight and helpful suggestions.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National “Twelfth Five-Year” Plan for Science & Technology Pillar Program [grant number 2014BAL04B04], [grant number 2015BAL01B02], the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2042016kf0173), and the Wuhan Water Engineering & Technology Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Highlights
• Acid and alkali were adopted to modify raw biochar;
• The maximum adsorption capacity of nitrate was 32.40 mg/g;
• The adsorption mechanism was studied by using various characterizations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Xue, Y., Long, L. et al. Characteristics and batch experiments of acid- and alkali-modified corncob biomass for nitrate removal from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 19932–19940 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2198-5