Abstract
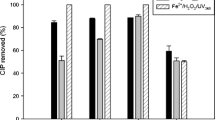
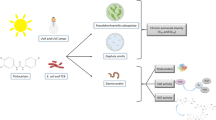
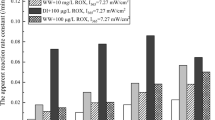
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have been highly efficient in degrading contaminants of emerging concern (CEC). This study investigated the efficiency of photolysis, peroxidation, photoperoxidation, and ozonation at different pH values to degrade doxycycline (DC) in three aqueous matrices: fountain, tap, and ultrapure water. More than 99.6% of DC degradation resulted from the UV/H2O2 and ozonation processes. Also, to evaluate the toxicity of the original solution and throughout the degradation time, antimicrobial activity tests were conducted using Gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) bacteria, and acute toxicity test using the bioluminescent marine bacterium (Vibrio fischeri). Antimicrobial activity reduced as the drug degradation increased in UV/H2O2 and ozonation processes, wherein the first process only 6 min was required to reduce 100% of both bacteria activity. In ozonation, 27.7 mg L−1 of ozone was responsible for reducing 100% of the antimicrobial activity. When applied the photoperoxidation process, an increase in the toxicity occurred as the high levels of degradation were achieved; it means that toxic intermediates were formed. The ozonated solutions did not present toxicity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agwuh KN, Macgowan A (2006) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkl224
Andreozzi R, Campanella L, Fraysse B, Garric J, Gonnella A, Giudice RL, Marotta R, Pinto G, Pollio A (2004) Effects of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) on the toxicity of a mixture of pharmaceuticals. Water Sci Technol 50:23–28
Andreozzi R, Canterino M, Lo GR et al (2006) Lincomycin solar photodegradation, algal toxicity and removal from wastewaters by means of ozonation. Water Res 40:630–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.023
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, twenty-second ed. American Public Health Organization, Washington D. C
Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas-ABNT (2012). NBR 15411:3 Ecotoxicologia aquática: - Determinação do efeito inibitório de amostras aquosas sobre a emissão de bioluminescência de Vibrio fischeri (ensaio de bactéria luminescente) Parte 3: Método utilizando bactérias liofilizadas
Caianelo M, Rodrigues-Silva C, Maniero MG, Guimarães JR (2017) Antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria during gatifloxacin degradation by hydroxyl radicals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6288–6298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6972-y
Chen Y, Li H, Wang Z, Tao T, Wei D, Hu C (2012) Photolysis of chlortetracycline in aqueous solution: kinetics, toxicity and products. J Environ Sci 24:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60775-4
Dalmázio I, Almeida MO, Augusti R, Alves TMA (2007) Monitoring the degradation of tetracycline by ozone in aqueous medium via atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 18:679–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasms.2006.12.001
Dantas RF, Contreras S, Sans C, Esplugas S (2008) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by means of ozonation. J Hazard Mater 150:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.034
de Oliveira AMD, Maniero MG, Rodrigues-Silva C, Guimarães JR (2017) Antimicrobial activity and acute toxicity of ozonated lomefloxacin solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6252–6260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8319-0
Deng W, Li N, Zheng H, Lin H (2016) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.002
Dodd MC, Kohler HPE, Von GU (2009) Oxidation of antibacterial compounds by ozone and hydroxyl radical: elimination of biological activity during aqueous ozonation processes. Environ Sci Technol 43:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8025424
Esplugas S, Gimenez J, Contreras S et al (2002) Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for phenol degradation. Water Res 36:1034–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00301-3
Esplugas S, Bila DM, Krause LGT, Dezotti M (2007) Ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies to remove endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in water effluents. J Hazard Mater 149:631–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.073
Ferreira GF, Maniero MG, Guimarães JR (2015) Degradation of sucralose by peroxidation assisted with ultraviolet radiation and photo-Fenton. Int J Eng Technol 7:438–444. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJET.2015.V7.833
Gajda A, Bladek T, Gbylik-sikorska M, Posyniak A (2017) The influence of cooking procedures on doxycycline concentration in contaminated eggs. Food Chem 221:1666–1670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.121
Ghaly MY, Härtel G, Mayer R, Haseneder R (2001) Photochemical oxidation of p -chlorophenol by UV/H2O2 and photo-Fenton process. A comparative study. Waste Manag 21:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(00)00070-2
Gómez-Pacheco CV, Sánchez-Polo M, Rivera-Utrilla J, López-Peñalver J (2011) Tetracycline removal from waters by integrated technologies based on ozonation and biodegradation. Chem Eng J 178:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.10.023
Gothwal R, Shashidhar T (2015) Antibiotic pollution in the environment: a review. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 43:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300989
Harrison JF, Blazek P (2000) Ozone for point-of use, point-of entry, and small water system water treatment applications—a reference manual. The Water Quality Association, USA
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fern AR, Barcel D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Jiao S, Zheng S, Yin D et al (2008a) Aqueous oxytetracycline degradation and the toxicity change of degradation compounds in photoirradiation process. J Environ Sci 20:806–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62130-0
Jiao S, Zheng S, Yin D, Wang L, Chen L (2008b) Aqueous photolysis of tetracycline and toxicity of photolytic products to luminescent bacteria. Chemosphere 73:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.042
Khan MH, Bae H, Jung J-Y (2010) Tetracycline degradation by ozonation in the aqueous phase: proposed degradation intermediates and pathway. J Hazard Mater 181:659–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.063
Kim I, Yamashita N, Tanaka H (2009a) Photodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products during UV and UV/H2O2 treatments. Chemosphere 77:518–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.041
Kim I, Yamashita N, Tanaka H (2009b) Performance of UV and UV/H2O2 processes for the removal of pharmaceuticals detected in secondary effluent of a sewage treatment plant in Japan. J Hazard Mater 166:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.020
Li K, Yediler A, Yang M, Schulte-Hostede S, Wong MH (2008) Ozonation of oxytetracycline and toxicological assessment of its oxidation by-products. Chemosphere 72:473–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.02.008
López-Peñalver JJ, Sánchez-Polo M, Gómez-Pacheco CV, Rivera-Utrilla J (2010) Photodegradation of tetracyclines in aqueous solution by using UV and UV/H2O2 oxidation processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1325–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2435
Nogueira RF, Oliveira MC, Paterlini WC (2005) Simple and fast spectrophotometric determination of H2O2 in photo-Fenton reactions using metavanadate. Talanta 66:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.10.001
Oliveira AMD, Maniero MG, Guimaraes JR (2015) Lomefloxacin degradation: antimicrobial activity, toxicity and byproducts. J Adv Oxid Technol 18:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2015-0205
Palamy S, Ruengsitagoon W (2017) A novel flow injection spectrophotometric method using plant extracts as green reagent for the determination of doxycycline. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 171:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.08.011
Peres MS, Maniero MG, Guimarães JR (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin and evaluation of the residual antimicrobial activity. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14:556–562. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP00256C
Rodrigues-Silva C, Maniero MG, Rath S, Guimarães JR (2013) Degradation of flumequine by photocatalysis and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Chem Eng J 224:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.002
Rodrigues-Silva C, Maniero MG, Peres MS, Guimarães JR (2014) Ocorrência e degradação de quinolonas por processos oxidativos avançados. Quim Nova 37:868–885. https://doi.org/10.5935/0100-4042.20140139
Rusu A, Hancu G, Uivarosi V (2015) Fluoroquinolone pollution of food , water and soil , and bacterial resistance. Environ Chem Lett 13:21–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-014-0481-3
Saggioro EM, Oliveira AS, Buss DF, et al (2015) Photo-decolorization and ecotoxicological effects of solar compound parabolic collector pilot plant and artificial light photocatalysis of indigo carmine dye. Dye Pigment 113:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2014.09.029
Urbano VR, Guedes M, Pèrez-Moya M, Guimarães JR (2017a) Influence of pH and ozone dose on sulfaquinoxaline ozonation. J Environ Manag 195:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.019
Urbano VR, Peres MS, Maniero MG, Guimarães JR (2017b) Abatement and toxicity reduction of antimicrobials by UV/H2O2 process. J Environ Manag 193:439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.02.028
Valcárcel Y, González Alonso S, Rodríguez-Gil JL, Gil A, Catalá M (2011) Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 84:1336–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2011.05.014
Wammer KH, Slattery MT, Stemig AM, Ditty JL (2011) Tetracycline photolysis in natural waters: loss of antibacterial activity. Chemosphere 85:1505–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.051
Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang J, Lu C, Huang Q, Wu J, Liu F (2011) Degradation of tetracycline in aqueous media by ozonation in an internal loop-lift reactor. J Hazard Mater 192:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.086
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Kolpin DW, Costanzo SD (2009) The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: from wastewater to drinking water. Sci Total Environ 407:2711–2723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.059
Wu J, Jiang Y, Zha L, Ye Z, Zhou Z, Ye J, Zhou H (2010) Tetracycline degradation by ozonation, and evaluation of biodegradability and toxicity of ozonation byproducts. Can J Civ Eng 37:1485–1491. https://doi.org/10.1139/L10-100
Yuan F, Hu C, Hu X, Wei D, Chen Y, Qu J (2011) Photodegradation and toxicity changes of antibiotics in UV and UV/H2O2 process. J Hazard Mater 185:1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.040
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge CNPq and FAPESP for scholarships granted to M. Spina-Cruz and M.G. Maniero (2013/07817-2), respectively, and the financial support provided by FAPESP (2013/04656-8 and 2013/09543-7) and CNPq (479131/2013-9 and 459078/2014-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spina-Cruz, M., Maniero, M.G. & Guimarães, J.R. Advanced oxidation processes on doxycycline degradation: monitoring of antimicrobial activity and toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 27604–27619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2149-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2149-1