Abstract
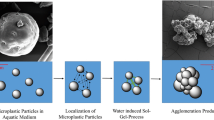
Based on a new concept for the sustainable removal of microplastics from freshwater systems, a case study for a pH-induced agglomeration and subsequent removal of polyethylene and polypropylene particles from water is presented. The two-step-based process includes firstly a localization and secondly an aggregation of microplastic particles (250–350 μM) in a physicochemical process. The research describes a strong increase in the particle size independent of pH of the aquatic milieu induced by the addition of trichlorosilane-substituted Si derivatives. The resulting Si-based microplastic aggregates (particle size after aggregation is 2–3 cm) could be easily removed by use of, e.g., sand traps. Due to the effect that microplastic particles form agglomeration products under every kind of process conditions (e.g., various pH, various polymer concentrations), the study shows a high potential for the sustainable removal of particles from wastewater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abegglen C, Siegrist H (2012) Mikroverunreinigungen aus kommunalem Abwasser. www.bafu.admin.ch/uw-1214-d. Accessed 2 Aug 2017
Al-Oweini R, El-Rassy H (2009) Synthesis and characterization by FTIR spectroscopy of silica aerogels prepared using several Si(OR)4 and R′′Si(OR′)3 precursors. J Mol Struct 919(1–3):140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.08.025
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62(8):1596–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030
Avio CG, Gorbi S, Regoli F (2016) Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: from emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Mar Environ Res 128:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.05.012
Bakir A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2012) Competitive sorption of persistent organic pollutants onto microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 64(12):2782–2789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.09.010
Bakir A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2014) Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 185:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.007
Barnes DKA, Galgani F, Thompson RC, Barlaz M (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 364(1526):1985–1998. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0205
Bergna HE (1994) The colloid chemistry of silica - an overview, Chapter 1. Adv Chem 234:1–47.https://doi.org/10.1021/ba-1994-0234.ch001
Brinker CJ (1988) Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: effects on structure. J Non-Cryst Solids 100(1–3):31–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(88)90005-1
Brook MA (1999) Organosilicon chemistry. Synthetic applications in organic, organometallic, materials, and polymer chemistry. Wiley, New York
Browne MA, Crump P, Niven SJ, Teuten E, Tonkin A, Galloway T, Thompson R (2011) Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 45(21):9175–9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201811s
Browne MA, Niven SJ, Galloway TS, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2013) Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr Biol 23(23):2388–2392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.012
Bundesministeriums der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz (2017) Verordnung über Anforderungen an das Einleiten von Abwasser in Gewässer (Abwasserverordnung - AbwV):2. https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/abwv/AbwV.pdf. Accessed 17 April 2018
Carr SA, Liu J, Tesoro AG (2016) Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 91:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.002
Choi JM, Jeong D, Cho E, Jun B-H, Park S, Yu J-H, Tahir MN, Jung S (2016) Chemically functionalized silica gel with alkynyl terminated monolayers as an efficient new material for removal of mercury ions from water. J Ind Eng Chem 35:376–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.01.020
Chuang SH, Chang TC, Ouyang CF, Leu JM (2007) Colloidal silica removal in coagulation processes for wastewater reuse in a high-tech industrial park. Water Sci Technol 55(1–2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.054
Chubarenko I, Bagaev A, Zobkov M, Esiukova E (2016) On some physical and dynamical properties of microplastic particles in marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 108(1–2):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.048
Eerkes-Medrano D, Thompson RC, Aldridge DC (2015) Microplastics in freshwater systems: a review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res 75:63–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.012
Eggen RIL, Hollender J, Joss A, Schärer M, Stamm C (2014) Reducing the discharge of micropollutants in the aquatic environment: the benefits of upgrading wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 48(14):7683–7689. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500907n
Eriksen M, Lebreton LCM, Carson HS, Thiel M, Moore CJ, Borerro JC, Galgani F, Ryan PG, Reisser J (2014) Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS One 9(12):e111913. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111913
Fruijtier-Pölloth C (2012) The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica-a nanostructured material. Toxicology 294(2–3):61–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.02.001
GRACE (2015) Sicherheitsdatenblatt 1907/2006/EG, Artikel 31: SP537-12158, Worms
Hartline NL, Bruce NJ, Karba SN, Ruff EO, Sonar SU, Holden PA (2016) Microfiber masses recovered from conventional machine washing of new or aged garments. Environ Scie Technol 50(21):11532–11538. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03045
Heinonen M, Talvitie J (2014) Preliminary study on synthetic microfibers and particles at a municipal waste water treatment plant,Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission, Helsinki, http://www.helcom.fi/Lists/Publications/Microplastics%20at%20a%20municipal%20waste%20water%20treatment%20plant.pdf. Accessed 17 April 2018
Herbort AF, Schuhen K (2016) GDCh-Monographie Bd. 50: 2nd international conference on the chemistry of contruction materials, 1. Auflage. Gesellschaft Dt. Chemiker, Frankfurt am Main
Herbort AF, Schuhen K (2017a) A concept for the removal of microplastics from the marine environment with innovative host-guest relationships. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(12):11061–11065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7216-x
Herbort AF, Schuhen K (2017b) Wasser 3.0 - Von der Idee zum Konzept in die Realität - Neues Verfahren zur Spurenstoffentfernung. https://youtu.be/xelfQxbWCzo. Accessed 11 Aug 2017
Herbort AF, Schuhen K (2017c) Problem erkannt - Mikroplastik in kommunalen Kläranlagen nachhaltig entfernen. http://www.laborpraxis.vogel.de/mikroplastik-in-kommunalen-klaeranlagen-nachhaltig-entfernen-a-617719/. Accessed 1 Aug 2017
Hurkes N, Ehmann HMA, List M, Spirk S, Bussiek M, Belaj F, Pietschnig R (2014) Silanol-based surfactants: synthetic access and properties of an innovative class of environmentally benign detergents. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 20(30):9330–9335. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201402857
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Marine pollution. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science (New York, NY) 347(6223):768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Karapanagioti HK, Klontza I (2008) Testing phenanthrene distribution properties of virgin plastic pellets and plastic eroded pellets found on Lesvos island beaches (Greece). Mar Environ Res 65(4):283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2007.11.005
Kershaw P (2015) Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: a global assessment. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/marine/good-environmental-status/descriptor-10/pdf/GESAMP_microplastics%20full%20study.pdf. Accessed 14 Nov 2017
Kirstein IV, Kirmizi S, Wichels A, Garin-Fernandez A, Erler R, Loder M, Gerdts G (2016) Dangerous hitchhikers? Evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles. Mar Environ Res 120:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.07.004
Lares M, Ncibi MC, Sillanpää M, Sillanpää M (2018) Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res 133:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.049
Lechner A, Ramler D (2015) The discharge of certain amounts of industrial microplastic from a production plant into the River Danube is permitted by the Austrian legislation. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex : 1987) 200:159–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.02.019
Leslie H, van Velzen M, Vethaak A (2013) Microplastic survey of the Dutch environment. Novel data set of microplastics in North Sea sediments, treated wastewater effluents and marine biota. Final report R-13/11
Liu Y, Li J, Yang Y, Li B (2015) Facile immobilization of polyaspartate onto silica gels via poly(dopamine) for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 351:831–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.007
LyondellBasell (2018a) Density HDPE. https://www.lyondellbasell.com/en/products-technology/polymers/resin-type/hdpe/. Accessed 18 Feb 2018
LyondellBasell (2018b) Density LDPE. https://www.lyondellbasell.com/en/products-technology/polymers/resin-type/ldpe/. Accessed 18 Feb 2018
Magnusson K, Nóren F (2014) Screening of microplastic particles in and downstream a wastewater treatment plant. IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute, Stockholm
Mintenig SM, Int-Veen I, Loder MGJ, Primpke S, Gerdts G (2016) Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res 108:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.015
Mitsubishi Engineering-Plastics Corporation (2017) Rate of water and moisture absorption. http://www.m-ep.co.jp/en/pdf/product/iupi_nova/physicality_06.pdf. Accessed 25 Jul 2017
Murphy F, Ewins C, Carbonnier F, Quinn B (2016) Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5800–5808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05416
Napper IE, Bakir A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC (2015) Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar Pollut Bull 99(1–2):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.029
Neumeyer F, Auner N (2016) One-step synthesis of siloxanes from the Direct Process Disilane Residue. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 22(48):17165–17168. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201603842
Palaprat G, Ganachaud F (2003) Synthesis of polydimethylsiloxane microemulsions by self-catalyzed hydrolysis/condensation of dichlorodimethylsilane. C R Chim 6(11–12):1385–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2003.09.002
Pascall MA, Zabik ME, Zabik MJ, Hernandez RJ (2005) Uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from an aqueous medium by polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene films. J Agric Food Chem 53(1):164–169. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048978t
PlasticsEurope (2015) Plastics - the facts 2015 - an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. http://www.corepla.it/documenti/5f2fa32a-7081-416f-8bac-2efff3ff2fbd/Plastics+TheFacts+2015.pdf. Accessed 17 April 2018
PlasticsEurope (2016) Plastics—the facts 2016—an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. http://www.plasticseurope.org/documents/document/20161014113313-plastics_the_facts_2016_final_version.pdf. Accessed 2 Mar 2017
PlasticsEurope (2017) Plastics—the facts 2017—an analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. http://www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/5715/1717/4180/Plastics_the_facts_2017_FINAL_for_website_one_page.pdf. Accessed 18 Feb 2018
Pope E, Mackenzie JD (1986) Sol-gel processing of silica. J Non-Cryst Solids 87(1–2):185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(86)80078-3
Primpke S, Imhof H, Piehl S, Lorenz C, Löder M, Laforsch C, Gerdts G (2017) Mikroplastik in der Umwelt. Chem Unserer Zeit 51(6):402–412. https://doi.org/10.1002/ciuz.201700821
Ratola N, Ramos S, Homem V, Silva JA, Jiménez-Guerrero P, Amigo JM, Santos L, Alves A (2016) Using air, soil and vegetation to assess the environmental behaviour of siloxanes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(4):3273–3284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5574-4
Schwarzenbach RP, Escher BI, Fenner K, Hofstetter TB, Johnson CA, von Gunten U, Wehrli B (2006) The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science (New York, NY) 313(5790):1072–1077. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127291
Soleimani Dorcheh A, Abbasi MH (2008) Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Technol 199(1–3):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.060
Sundt P, Schulze P-E, Syversen F (2014) Sources of microplastics-pollution to the marine environment. http://www.miljodirektoratet.no/Documents/publikasjoner/M321/M321.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2016
Teuten EL, Saquing JM, Knappe DRU, Barlaz MA, Jonsson S, Björn A, Rowland SJ, Thompson RC, Galloway TS, Yamashita R, Ochi D, Watanuki Y, Moore C, Viet PH, Tana TS, Prudente M, Boonyatumanond R, Zakaria MP, Akkhavong K, Ogata Y, Hirai H, Iwasa S, Mizukawa K, Hagino Y, Imamura A, Saha M, Takada H (2009) Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364(1526):2027–2045. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0284
von Moos N, Burkhardt-Holm P, Kohler A (2012) Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ Sci Technol 46(20):11327–11335. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302332w
Wawrzkiewicz M, Wiśniewska M, Wołowicz A, Gun’ko VM, Zarko VI (2017) Mixed silica-alumina oxide as sorbent for dyes and metal ions removal from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 250:128–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.05.016
Welden NAC, Cowie PR (2016) Long-term microplastic retention causes reduced body condition in the langoustine, Nephrops norvegicus. Environ Pollut\ (Barking, Essex : 1987) 218:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.020
Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (2013) The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environ Pollut 178:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.031
Zarfl C, Matthies M (2010) Are marine plastic particles transport vectors for organic pollutants to the Arctic? Mar Pollut Bull 60(10):1810–1814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.05.026
Ziajahromi S, Neale PA, Leusch FDL (2016) Wastewater treatment plant effluent as a source of microplastics: review of the fate, chemical interactions and potential risks to aquatic organisms. Water Sci Technol 74(10):2253–2269. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.414
Funding
The research projects of Wasser 3.0 (www.wasserdreinull.de) are conducted by means of the financial support by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy through the provision of ZIM (Central Innovation Program for SME) project funds. The enterprise abcr GmbH (www.abcr.de) from Karlsruhe (GERMANY) is directly involved in the project as an industrial partner for the material science scale-up. IR spectra are provided by SAS Hagmann (www.sas-hagmann.de) from Horb am Neckar (GERMANY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbort, A.F., Sturm, M.T. & Schuhen, K. A new approach for the agglomeration and subsequent removal of polyethylene, polypropylene, and mixtures of both from freshwater systems – a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 15226–15234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1981-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1981-7